Abstract
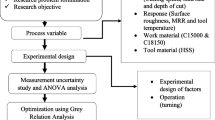
In this study, the machinability of test pieces obtained from two different white cast irons, NiHARD-4 and HCWCI, were investigated by boring method, a machining process. The impacts of cutting parameters on cutting forces were identified. Analysis of variance was used to determine the effect ratios of the cutting parameters. Moreover, Taguchi analyses were used in the experiments to examine the impacts of cutting parameters on cutting forces. Considering the results in terms of dry and wet test conditions, it has been revealed that the cutting forces such as Fc, Fr and Ff of HCWCI material are lower than NiHARD-4 material in all test conditions. In dry cutting, high cutting speed and low feed have decreased the cutting forces. In wet cutting when the cutting speed has increased, Fr and Ff have increased. In terms of the cutting parameters, it was found that the most impact parameter on Fc is feed rate, the most impact parameter on Fr is material and the most impact parameter on Ff is cutting speed in dry cutting. In wet cutting, the most effective factor on Fc is feed rate, whereas the most effective factor on Fr and Ff is the material. Consequently, it can be said that to lower the cutting forces is required to reduce the feed rate and raise the cutting speed when NiHARD-4 and HCWCI materials are machined by boring operations with CBN inserts.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suyama, D.I.; Diniz, A.E.; Pederiva, R.: Tool vibration in internal turning of hardened steel using cBN tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 88, 2485–2495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8964-y
Klocke, F.; Brinksmeier, E.; Weinert, K.: Capability profile of hard cutting and grinding processes. CIRP Ann. 54.2, 22–45 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60018-3
Bartarya, G.; Choudhury, S.K.: State of the art in hard turning. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 53, 1–14 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2011.08.019
Huddle, D.: New hard turning tools and techniques offer a cost-effective alternative to grinding. Tooling and Production Magazine 80, 96–103 (2001)
Davis, J. R. 1996 Classification and basic metallurgy of cast irons. ASM specialty handbook cast iron, 4–7.
ASTM A532 Standard specification for abrasion resistant cast iron, ASTM Standards, 2014
Jinzhu, L.; Shizhuo, Li.; Yongfa, M.: Wear resistance of Ni-hard 4 and high-chromium cast iron re-evaluated. Wear 166(1), 37–40 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(93)90276-R
Badadhe, A. M.; Bhave, S. Y.; Navale, L. G. Optimization of cutting parameters in boring operation. In: Second National Conference on Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering. 2005, 10–15.
Vieira, J.T.; Pereira, R.B.D.; Freitas, S.A., et al.: Multi-objective robust evolutionary optimization of the boring process of AISI 4130 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 112, 1745–1765 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06455-8
Fallah, M.; Moetakef-Imani, B.: Investigation on nonlinear dynamics and active control of boring bar chatter. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 43, 116 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-02808-w
Chockalingam, S.; Natarajan, U.; Kalyana Sundaram, S.: Modeling and optimization of tool wear in a passively damped boring process using response surface methodology. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 69, 1443–1448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0707-5
Chockalingam, S.; Natarajan, U.; Selvam, M., et al.: Investigation on machinability and damping properties of nickel-phosphorus coated boring bar. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 669–676 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1830-7
Singaravelu, C.; Varatharajan, P.; Ramu, G., et al.: Investigation of damping characteristics on copper-based shape memory alloy frictional damper in boring process. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 11859–11870 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05719-z
Kaliński, K.J.; Galewski, M.A.; Mazur, M.R.; Stawicka-Morawska, N.: An improved method of minimizing tool vibration during boring holes in large-size structures. Materials 14, 4491 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164491
Akdeniz, E.; Arslan, H.: A new design of boring bar using TiNi3 alloy to reduce vibration in turning operations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 237(1–2), 105–121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/09544054221104607
Precision turning with instrumented vibration-damped boring bars. Procedia CIRP 77: 666–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.08.181
Beno, J.: Theory of cutting metals. SjF TUKE, Kosice, Slovakia (1999)
Ramesh, K.; Baranitharan, P.; Sakthivel, R.: Investigation of the stability on boring tool attached with double impact dampers using Taguchi based Grey analysis and cutting tool temperature investigation through FLUKE-Thermal imager. Measurement 131, 143–155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.08.055
Lawrance, G.; Daniel, E.; Paul, P.S.; Shaji, J.; Thankachan, T.: Study on the influence of multi-layered nano metal oxide coating on cutting performance during boring of hardened steel. Mater. Today Proceed. 22, 1731–1736 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.192
McKendrick, I. R.; Tungka, J.; Arsecularatne, J. A.; Mathew, P.: Application of Oxley machining theory to boring and reaming, 2001, 375–391. https://doi.org/10.1081/MST-100108621
Lawrance, G.; Sam Paul, P.; Varadarajan, A.S.; Paul Praveen, A.; Ajay Vasanth, X.: Attenuation of vibration in boring tool using spring-controlled impact damper. Int. J Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 11(4), 903–915 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-015-0292-1
Ravi, A.M.; Murigendrappa, S.M.; Mukunda, P.G.: Experimental investigation of influence of tool temperature on cutting forces in the thermally enhanced machining of high chrome white cast iron. Procedia Mater. Sci. 5, 2099–2104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.545
Ravi, A.M.; Murigendrappa, S.M.; Mukunda, P.G.: Machinability investigations on high chrome white cast iron using multi coated hard carbide tools. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 67(4), 485–502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-013-0369-0
Ravi, A.M.; Murigendrappa, S.M.; Mukunda, P.G.: Experimental investigation on thermally enhanced machining of high-chrome white cast iron and to study its machinability characteristics using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 72(9–12), 1439–1454 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5752-4
Ravi, A.M.; Murigendrappa, S.M.; Mukunda, P.G.: Experimental and analytical based investigations on machinability of high-chrome white cast iron USING CBN Tools. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 68(1), 61–77 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-014-0431-6
Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Bushlya, V.; Gutnichenko, O.; Stahl, J.E.: Performance assessment of pCBN and bCBN tools in machining of high-chromium white cast iron. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 79, 635–644 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6863-2
Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Bushlya, V.; Stahl, J.E.: Influences of micro mechanical property and microstructure on performance of machining high chromium white cast iron with CBN tools. Procedia CIRP 31, 172–178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.03.092
Yücel, E.; Günay, M.: Modelling and optimization of the cutting conditions in hard turning of high-alloy white cast iron (Ni-Hard). Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 227(10), 2280–2290 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406212471755
Günay, M.; Yücel, E.: Application of Taguchi method for determining optimum surface roughness in turning of high-alloy white cast iron. Measurement 46(2), 913–919 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2012.10.013
Yücel, E.; Günay, M.: Yüksek alaşımlı beyaz dökme demirlerin (Ni-Hard) tornalanmasında kesme kuvvetinin modellenmesi, 3. Ulusal Talaşlı İmalat Sempozyumu, Ankara-Türkiye 489, 495 (2012)
Kalyon, A.; Günay, M.; Özyürek, D.: Application of grey relational analysis based on Taguchi method for optimizing machining parameters in hard turning of high chrome cast iron. Adv. Manuf. 6(4), 419–429 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-018-0231-z
Ranganath, S.; Guo, C.; Hegde, P.: A finite element modeling approach to predicting white layer formation in nickel superalloys. CIRP Ann. 58(1), 77–80 (2009)
Ulutan, D.; Ozel, T.: Machining induced surface integrity in titanium and nickel alloys: A review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 513, 250–280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.11.003
Sandvik Coromant - manufacturing tools and machining solutions (2023). https://www.sandvik.coromant.com/tr-tr/product-details?c=TCGW110304S01020F%20%20%207115. Accessed 10 Aug 2019
Sandvik Coromant - manufacturing tools and machining solutions (2023). https://www.sandvik.coromant.com/en-gb/product-details?c=a25t-stfcr%2011-rb1. Accessed 10 Aug 2019
https://docs.steinerelectric.com/Sandvik_5736303_Catalog.pdf
https://api.dgisupply.ca/uploads/literature/X2F5AUmwvWyJk7MBfa0hjKfAUYEQF3L7ySbXYbJi.pdf
Cetin, M.H., et al.: Evaluation of vegetable based cutting fluids with extreme pressure and cutting parameters in turning of AISI 304L by Taguchi method. J. Clean. Prod. 1917, 2049–2056 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.07.013
Abhang, L.B.; Hameedullah, M.: Determination of optimum parameters for multi-performance characteristics in turning by using grey relational analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 63, 13–24 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3857-6
Ahmed, T.; Mollick, N.; Mahmud, S.: Analysis of effects of machining parameters on cutting force components in turning AISI 201 stainless steel using cemented carbide cutting tool insert. Mater. Today Proceed. 42, 832–837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.416
Özdemir, M.; Kaya, M.; Akyildiz, H.: Analysis of surface roughness and cutting forces in hard turning of 42CrMo4 steel using Taguchi and RSM method. Mechanika (2020). https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.mech.26.3.23600
Tekaslan, Ö.; Gerger, N.; Günay, M.; Şeker, U.: AISI 304 Östenitik Paslanmaz Çeliklerin Titanyum Karbür Kaplamalı Kesici Takım İle Tornalama İşleminde Kesme Kuvvetlerinin Incelenmesi. Pamukkale Üniversitesi Mühendislik Bilimleri Dergisi 13(2), 135–144 (2011)
Kara, F.; Aslantaş, K.; Çiçek, A.: ANN and multiple regression method-based modelling of cutting forces in orthogonal machining of AISI 316L stainless steel. Neural Comput. Appl. 26(1), 237–250 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1721-y
Fnides, B.; Aouici, H.; Elbah, M.; Boutabba, S.; Boulanouar, L.: Comparison between mixed ceramic and reinforced ceramic tools in terms of cutting force components modelling and optimization when machining hardened steel AISI 4140. Mech. Ind. 16(6), 609 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1051/meca/2015036
Özlü, B.: Investigation of the effect of cutting parameters on cutting force, surface roughness and chip shape in turning of Sleipner cold work tool steel. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 36(3), 1241–1251 (2021). https://doi.org/10.17341/gazimmfd.668169
Abas, M.; Salah, B.; Khalid, Q.S.; Hussain, I.; Babar, A.R.; Nawaz, R.; Saleem, W.: Experimental investigation and statistical evaluation of optimized cutting process parameters and cutting conditions to minimize cutting forces and shape deviations in Al6026-T9. Materials 13(19), 4327 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194327
Aramcharoen, A.; Mativenga, P.T.: White layer formation and hardening effects in hard turning of H13 tool steel with CrTiAlN and CrTiAlN/MoST-coated carbide tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 36(7), 650–657 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0899-2
Azizi, M.W.; Belhadi, S.; Yallese, M.A.; Mabrouki, T.; Rigal, J.F.: Surface roughness and cutting forces modeling for optimization of machining condition in finish hard turning of AISI 52100 steel. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26(12), 4105–4114 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0885-6
Sivaraman, V.; Sankaran, S.; Vijayaraghavan, L.: The effect of cutting parameters on cutting force during turning multiphase microalloyed steel. Procedia CIRP 4, 157–160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2012.10.028
Funding
For the successful completion of this work, the authors thanks the financial assistance granted by the Gazi University Scientific Research Project Unit (Grant No. 07/2019–07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no financial conflict of interest between them. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest between them in a non-financial sense. Research grants from funding agencies: Gazi University's coordinator ship of scientific research projects has subsidized this study (Project No. 07/2019–07).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Erkoçak, Y., Kayır, Y. Analyzing the Impacts of Cutting Parameters on Cutting Forces in the Taguchi Method for Boring High-Alloy White Cast Irons with CBN Inserts. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 12569–12585 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08008-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08008-z