中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (15): 2380-2384.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3813
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
Salter骨盆截骨及植入物内固定治疗儿童发育性髋关节脱位的中长期随访
刘永裕1,徐景利2,林天烨2,吴 峰1,沈楚龙1,熊冰朗2,邹启昭2,赖启忠2,张庆文3
- 1佛山市中医院,广东省佛山市 528000;2广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510080;3广州中医药大学第一附属医院关节骨科,广东省广州市 510080
Medium-and long-term follow-up of Salter pelvic osteotomy and implant fixation for children with developmental hip dislocation
Liu Yongyu1, Xu Jingli2, Lin Tianye2, Wu Feng1, Shen Chulong1, Xiong Binglang2, Zou Qizhao2, Lai Qizhong2, Zhang Qingwen3
- 1Foshan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Foshan 528000, Guangdong Province, China; 2First Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
发育性髋关节发育不良:又称发育性髋关节脱位,是儿童骨科最常见的髋关节疾病,发病率为4‰-11‰,女孩的发病率是男孩的6倍左右,双侧约占35%。发育性髋关节发育不良包括髋关节脱位、半脱位和髋臼发育不良。
Salter骨盆截骨:通过截骨后骨盆远端的旋转从而改变髋臼方向,即在髋臼结构和容积保持不变的前提下,增加股骨头前外缘的包容。使异常的髋臼方向变为正常的生理方向,相对增加了髋臼深度。
摘要
背景:儿童发育性髋关节脱位是一种临床常见的儿童骨科髋关节疾病,Salter骨盆截骨治疗此病的短期随访效果满意,目前国内尚缺少中长期的临床随访研究。
目的:探究Salter骨盆截骨治疗儿童发育性髋关节脱位的中长期随访效果及并发症。
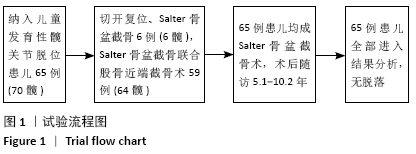
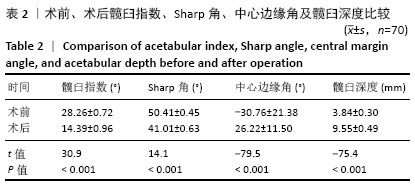
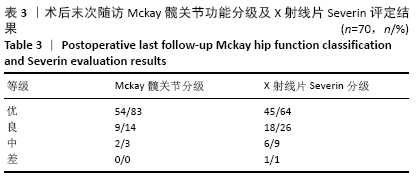
方法:回顾性分析广州中医药大学第一附属医院2010年1月至2015年3月收治的发育性髋关节脱位患儿65例(70髋),采用切开复位、Salter骨盆截骨或Salter骨盆截骨联合股骨近端截骨(锁定加压钢板固定)治疗。按Tonnis分度:Ⅰ度10髋,Ⅱ度17髋,Ⅲ度12髋,Ⅳ度31髋。观察患儿术前及术后中心边缘角、髋臼指数、Sharp角、髋臼深度,术后疗效采用Mckay功能标准及X射线片Severin标准评定。
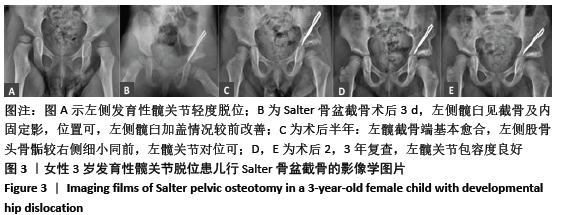
结果与结论:①65例患儿均获得随访,随访时间5.1-10.2年;②患儿术后髋臼指数及Sharp角均较术前明显减小,中心边缘角、髋臼深度均较术前明显增大,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③术后末次随访,按Mckay功能评定标准,优良率为97%;按X射线片Severin评定标准,优良率为90%;④3例患儿出现患侧股骨头坏死,1例患儿出现髋关节再脱位,1例患儿出现股骨近端畸形,1例患儿出现患侧肢体感觉异常;⑤提示Salter骨盆截骨联合股骨近端截骨治疗儿童发育性髋关节脱位中长期随访临床疗效满意,可有效改善患儿髋臼覆盖,提高髋关节功能。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0137-9799 (刘永裕)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: