| [1]Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016;315(8):788-800.[2]Sweeney RM, McAuley DF. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet. 2016;388(10058):2416-2430.[3]凌亚豪,魏金锋,王爱平,等.急性肺损伤和急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制的研究进展[J].癌变·畸变·突变,2017,29(2): 151-154.[4]Chang YS, Oh W, Choi SJ, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hyperoxia- induced lung injury in neonatal rats. Cell Transplant. 2009; 18(8):869-886.[5]Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13-27.[6]Aslam M, Baveja R, Liang OD, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate lung injury in a murine model of neonatal chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180(11):1122-1130.[7]Lavoie JR, Rosu-Myles M. Uncovering the secretes of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2212-2221.[8]Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N Jr, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63-70.[9]Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.[10]Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. 1998;4(5): 594-600.[11]Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383.[12]Clayton A, Turkes A, Navabi H, et al. Induction of heat shock proteins in B-cell exosomes. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 16): 3631-3638.[13]Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.[14]van Niel G, Raposo G, Candalh C, et al. Intestinal epithelial cells secrete exosome-like vesicles. Gastroenterology. 2001; 121(2):337-349.[15]Yáñez-Mó M, Siljander PR, Andreu Z, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27066.[16]Huotari J, Helenius A. Endosome maturation. EMBO J. 2011;30(17):3481-3500.[17]Kim HS, Choi DY, Yun SJ, et al. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(2):839-849.[18]Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13-27.[19]Choi DS, Kim DK, Kim YK, et al. Proteomics, transcriptomics and lipidomics of exosomes and ectosomes. Proteomics. 2013;13(10-11):1554-1571.[20]Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22.[21]Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27031.[22]Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312.[23]Lee C, Mitsialis SA, Aslam M, et al. Exosomes mediate the cytoprotective action of mesenchymal stromal cells on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2012; 126(22):2601-2611.[24]Chen J, Chen LA. LATE-BREAKING ABSTRACT: Human mesenchymal stem cell exosomes attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and the MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Eur Respir J. 2015; 46:OA4471.[25]Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2012;7(3): e33115.[26]Chen W, Lin YJ, Zhou XY, et al. Rosiglitazone protects rat liver against acute liver injury associated with the NF-κB signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;94(1): 28-34.[27]Katsuda T, Tsuchiya R, Kosaka N, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1197.[28]Herold S, Gabrielli NM, Vadász I. Novel concepts of acute lung injury and alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013;305(10):L665-681.[29]Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(21):2063.[30]Lee JW, Krasnodembskaya A, McKenna DH, et al. Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cells in ex vivo human lungs injured with live bacteria. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187(7):751-760.[31]Tan CY, Lai RC, Wong W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote hepatic regeneration in drug-induced liver injury models. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014; 5(3):76.[32]Zhang S, Chu WC, Lai RC, et al. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016; 24(12):2135-2140.[33]Qin Y, Wang L, Gao Z, et al. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21961.[34]Zhang Y, Chopp M, Zhang ZG, et al. Systemic administration of cell-free exosomes generated by human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured under 2D and 3D conditions improves functional recovery in rats after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Int. 2017;111:69-81.[35]Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):116-125.[36]Ionescu L, Byrne RN, van Haaften T, et al. Stem cell conditioned medium improves acute lung injury in mice: in vivo evidence for stem cell paracrine action. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;303(11):L967-977.[37]杨尧,朱耀斌,李志强,等.间充质干细胞外泌体对大鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2017,31(7): 628-631.[38]Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6): 654-659.[39]Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509-524.[40]Kubo H. Extracellular Vesicles in Lung Disease. Chest. 2018;153(1):210-216.[41]Park J, Jeong S, Park K, et al. Expression profile of microRNAs following bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):5495-5502.[42]Velu CS, Baktula AM, Grimes HL. Gfi1 regulates miR-21 and miR-196b to control myelopoiesis. Blood. 2009;113(19): 4720-4728.[43]Chang SW, Yue J, Wang BC, et al. miR-503 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by targeting E2F3. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10): 12853-12860.[44]Zeng Z, Gong H, Li Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-146a contributes to the suppression of inflammatory responses in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Exp Lung Res. 2013;39(7): 275-282.[45]Ghosh S, Hayden MS. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(11):837-848.[46]Song Y, Dou H, Li X, et al. Exosomal miR-146a Contributes to the Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Interleukin-1β-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Sepsis. Stem Cells. 2017; 35(5):1208-1221.[47]Tan KS, Choi H, Jiang X, et al. Micro-RNAs in regenerating lungs: an integrative systems biology analysis of murine influenza pneumonia. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:587.[48]Basu J, Ludlow JW. Exosomes for repair, regeneration and rejuvenation. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(4):489-506. [49]Spees JL, Olson SD, Whitney MJ, et al. Mitochondrial transfer between cells can rescue aerobic respiration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(5):1283-1288. [50]Schumacker PT, Gillespie MN, Nakahira K, et al. Mitochondria in lung biology and pathology: more than just a powerhouse. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014; 306(11):L962-L974.[51]Yamada M, Emmanuele V, Sanchez-Quintero MJ, et al. Genetic Drift Can Compromise Mitochondrial Replacement by Nuclear Transfer in Human Oocytes. Cell Stem Cell. 2016; 18(6):749-754.[52]Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Modulate Macrophages in Clinically Relevant Lung Injury Models by Extracellular Vesicle Mitochondrial Transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(10):1275-1286.[53]Islam MN, Das SR, Emin MT, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung injury. Nat Med. 2012;18(5): 759-765. [54]Torralba D, Baixauli F, Sánchez-Madrid F. Mitochondria Know No Boundaries: Mechanisms and Functions of Intercellular Mitochondrial Transfer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:107.[55]Guescini M, Guidolin D, Vallorani L, et al. C2C12 myoblasts release micro-vesicles containing mtDNA and proteins involved in signal transduction. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(12): 1977-1984.[56]Guescini M, Genedani S, Stocchi V, et al. Astrocytes and Glioblastoma cells release exosomes carrying mtDNA. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2010;117(1):1-4.[57]Hough KP, Trevor JL, Strenkowski JG, et al. Exosomal transfer of mitochondria from airway myeloid-derived regulatory cells to T cells. Redox Biol. 2018;18:54-64.[58]Riazifar M, Pone EJ, Lötvall J, et al. Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles: Extended Messages of Regeneration. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017;57:125-154. |
.jpg)
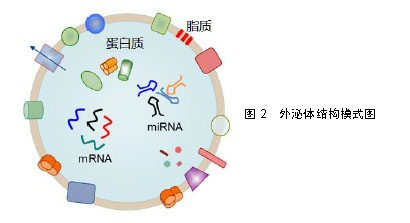
.jpg)
.jpg)