Corynebacterium accolens inhibits Staphylococcus aureus induced mucosal barrier disruption
- 1Department of Surgery-Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Basil Hetzel Institute for Translational Health Research, Central Adelaide Local Health Network, Woodville South, SA, Australia
- 2Adelaide Medical School, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
- 3Department of Rhinology, The ENT Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 4Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China
A corrigendum on
Corynebacterium accolens inhibits Staphylococcus aureus induced mucosal barrier disruption
by Huang, S., Hon, K., Bennett, C., Hu, H., Menberu, M., Wormald, P.-J., Zhao, Y., Vreugde, S., and Liu, S. (2022). Front. Microbiol. 13:984741. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.984741
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 4 as published. One of the images (sc+90% C1) was misplaced. The corrected Figure 4 and its caption appear below.
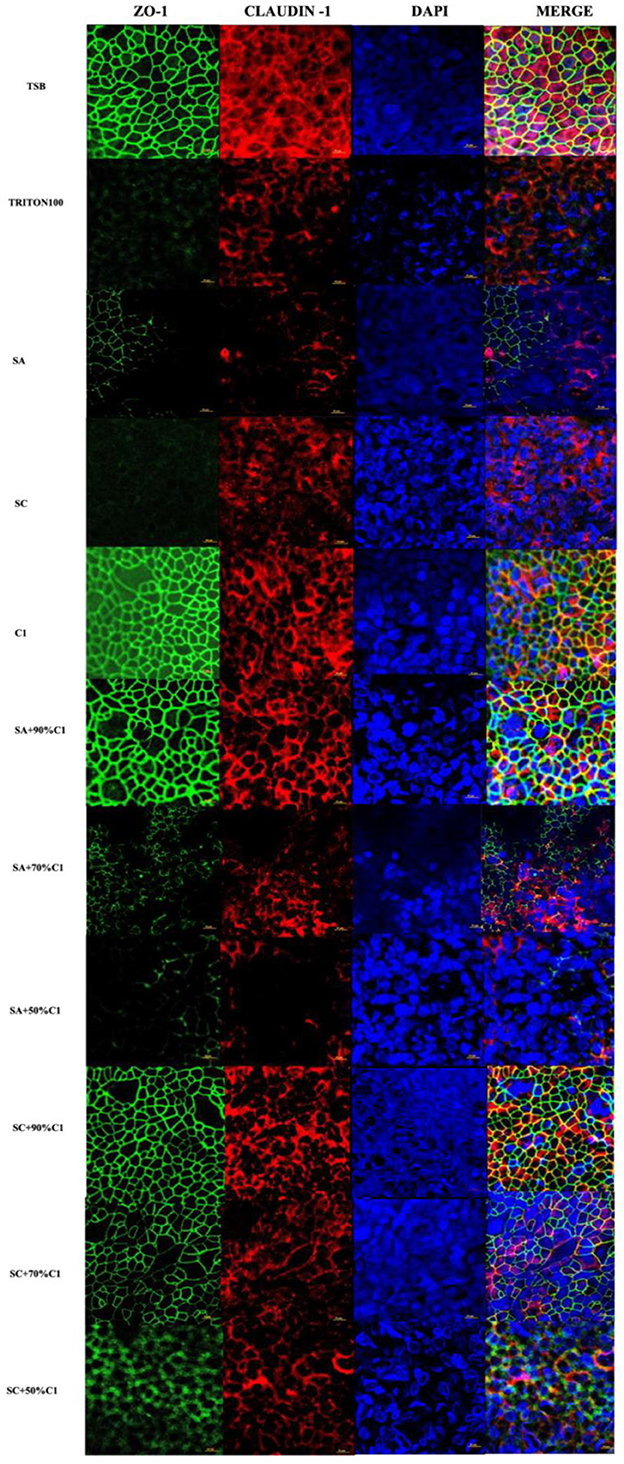
Figure 4. Corynebacterium accolens cell-free culture supernatants reduce S. aureus cell-free culture supernatants-induced detrimental effects on HNEC-ALI cultures tight junctions. Immunofluorescence staining of tight junction proteins of HNEC-ALI cultures treated with cell-free culture supernatants from SA and SC co-cultured with C. accolens in different ratios. HNEC-ALI cultured cells were stained with antibodies against Z0-1(green), claudin-1 (red) and DAPI to resolve nuclei (blue). TSB treatment was used as the negative control. Triton-100 was used as the positive control. Images were examined with confocal laser-scanning microscope (Scale bar = 10μm). C1, C. accolens clinical isolate 1; SA, S. aureus ATCC51650; SC, S. aureus clinical strain.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Corynebacterium accolens, Staphylococcus aureus, planktonic, biofilm, TER, cell-free culture supernatants
Citation: Huang S, Hon K, Bennett C, Hu H, Menberu M, Wormald P-J, Zhao Y, Vreugde S and Liu S (2023) Corrigendum: Corynebacterium accolens inhibits Staphylococcus aureus induced mucosal barrier disruption. Front. Microbiol. 14:1279422. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1279422
Received: 18 August 2023; Accepted: 21 August 2023;
Published: 01 September 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Huang, Hon, Bennett, Hu, Menberu, Wormald, Zhao, Vreugde and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sha Liu, sha.liu@adelaide.edu.au
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shuman Huang
Shuman Huang Karen Hon
Karen Hon Catherine Bennett
Catherine Bennett Hua Hu1,2,4
Hua Hu1,2,4 Martha Menberu
Martha Menberu Peter-John Wormald
Peter-John Wormald Yulin Zhao
Yulin Zhao Sarah Vreugde
Sarah Vreugde Sha Liu
Sha Liu