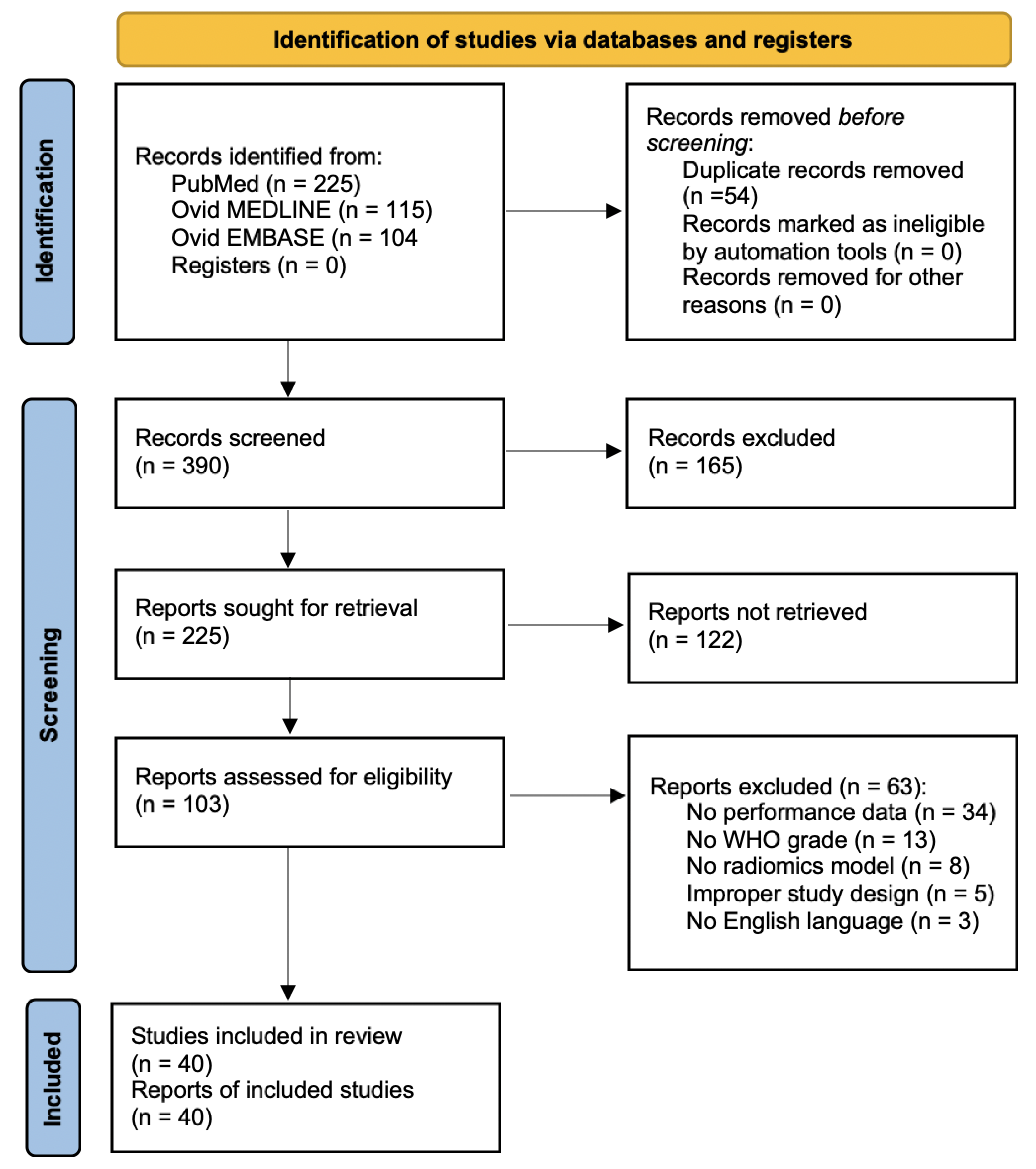
Background: Multiple radiomics models have been proposed for
grading glioma using different algorithms, features, and sequences of magnetic
resonance imaging. The research seeks to assess the present overall performance
of radiomics for grading glioma. Methods: A systematic literature review
of the databases Ovid MEDLINE PubMed, and Ovid EMBASE for publications published
on radiomics for glioma grading between 2012 and 2023 was performed. The
systematic review was carried out following the criteria of Preferred Reporting
Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis. Results: In the
meta-analysis, a total of 7654 patients from 40 articles, were assessed.
R-package mada was used for modeling the joint estimates of specificity (SPE) and
sensitivity (SEN). Pooled event rates across studies were performed with a
random-effects meta-analysis. The heterogeneity of SPE and SEN were based on the