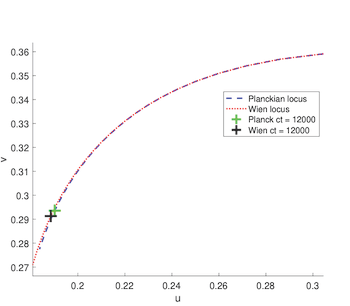
Planck’s law and Wien’s approximation of this law are both widely used to calculate the spectral radiation of a black-body based on its color temperature. The Wien approximation is a slightly simpler equation and has the advantage that the logarithm of a Wien light can be written as a linear sum of two basis vectors plus an offset (a fact that is exploited in some computer vision algorithms). In this paper, we show that the Wien formulation can, in general, be used to approximate Planckian lights assuming there is a mapping function taking Planckian to corrected Wien temperature. Significantly, we show that a correction function <i>f</i>() exists and for the range of color temperatures of interest the Wien spectrum calculated for <i>f</i>(T) has a very similar shape to the actual spectrum of a Planckian light with temperature T. We find that defining <i>f</i>() as a polynomial-type function models to a good extent the relationship between the color temperatures of Planckians and their closest Wien-Planckians lights both in terms of the angular error between their two respective spectral functions and their projections to u’v’ coordinates.
Rada Deeb, Graham Finlayson, Michael Brill, "Approximating Planckian Black-body Lights using Wien's Approximation" in Color and Imaging Conference, 2022, pp 194 - 199, https://doi.org/10.2352/CIC.2022.30.1.34
 Find this author on Google Scholar
Find this author on Google Scholar Find this author on PubMed
Find this author on PubMed