Development of an augmented Damerau–Levenshtein method for correcting spelling errors in Kazakh texts
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289187Keywords:
NLP, algorithm, text data, probability, spelling error, edit distance, similarityAbstract
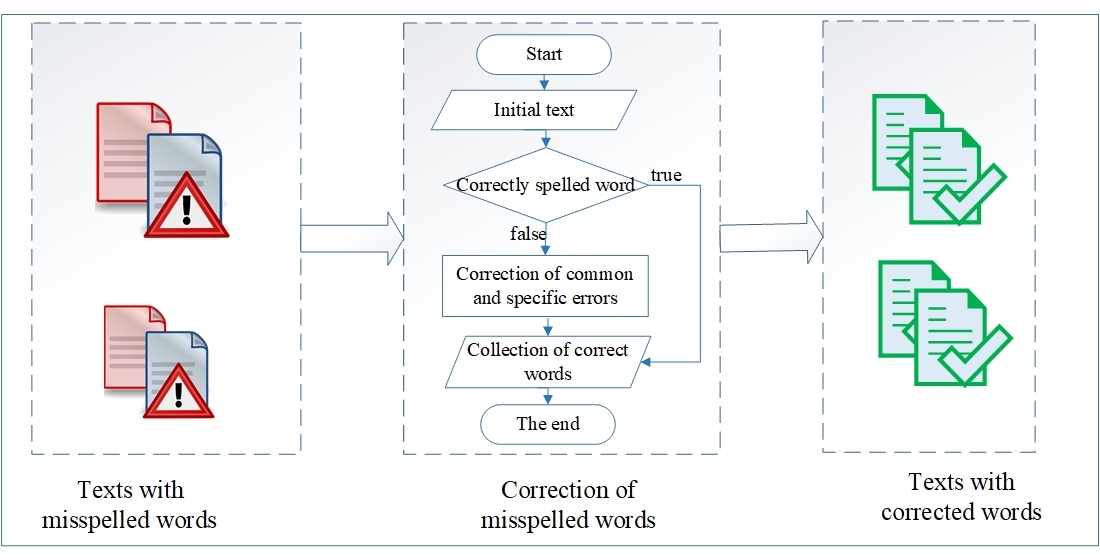
The presented paper is devoted to the development of a method for identifying and correcting spelling errors in Kazakh texts. In this paper, the study object is methods for more accurate correction of spelling errors in Kazakh texts. The aim of the study is to develop an augmented version of the Damerau-Levenshtein method for correcting spelling errors in Kazakh language texts. Automatic detection and correction of spelling errors have become a default feature in modern text editors for working with text data, in text messaging applications such as chatbots, messengers, etc. However, although this task is well solved in geographically widespread languages, it has not been fully solved in languages with a small audience, such as the Kazakh language. The methods developed so far cannot correct all spelling errors found in Kazakh texts. Therefore, the development of a method with specific algorithms for spelling error correction in Kazakh texts is considered. As a result of the research work, algorithms for correcting errors found in Kazakh language texts were developed, and the developed algorithms were included in the Damerau-Levenshtein method. The experimental testing results of the augmented Damerau- Levenshtein method showed 97.2 % accuracy in correcting specific errors found only in Kazakh words and 92.8 % accuracy in correcting common errors from letter symbols. The standard Damerau-Levenshtein method testing results showed 76.4 % accuracy in correcting specific errors found only in Kazakh words. The results of the tests in correcting common errors from letter symbols with the standard Damerau-Levenshtein were approximately the same with the augmented Damerau-Levenshtein method, the accuracy is 92.2 %. The extent and conditions of practical application of the results are implemented by including them in text editors, messengers, e-mails and similar applications that work with text data.
References
- Damerau, F. J. (1964). A technique for computer detection and correction of spelling errors. Communications of the ACM, 7 (3), 171–176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/363958.363994
- Kwon, S., Lee, G. G. (2023). Self-feeding training method for semi-supervised grammatical error correction. Computer Speech & Language, 77, 101435. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2022.101435
- Sheng, L., Xu, Z., Li, X., Jiang, Z. (2023). EDMSpell: Incorporating the error discriminator mechanism into chinese spelling correction for the overcorrection problem. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 35 (6), 101573. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.101573
- Nagata, R., Takamura, H., Neubig, G. (2017). Adaptive Spelling Error Correction Models for Learner English. Procedia Computer Science, 112, 474–483. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.08.065
- Zukarnain, N., Abbas, B. S., Wayan, S., Trisetyarso, A., Kang, C. H. (2019). Spelling Checker Algorithm Methods for Many Languages. 2019 International Conference on Information Management and Technology (ICIMTech). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icimtech.2019.8843801
- Kartbayev, A., Mamyrbayev, O., Khairova, N., Ybytayeva, G., Abilkaiyr, N., Mussayeva, D. (2021). Correction of Kazakh synthetic text using finite state automata. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 99 (22), 5559–5570. Available at: http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol99No22/29Vol99No22.pdf
- Sorokin, A., Shavrina, T. (2016). Automatic spelling correction for Russian social media texts. Conference: Dialogue, International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Moscow, 688–701. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303813582_Automatic_spelling_correction_for_Russian_social_media_texts
- Song, X., Min, Y. J., Da-Xiong, L., Feng, W. Z., Shu, C. (2019). Research on Text Error Detection and Repair Method Based on Online Learning Community. Procedia Computer Science, 154, 13–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.06.004
- Abdellah, Y., Lhoussain, A. S., Hicham, G., Mohamed, N. (2020). Spelling correction for the Arabic language space deletion errors-. Procedia Computer Science, 177, 568–574. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.10.080
- Kumar, R., Bala, M., Sourabh, K. (2018). A study of spell checking techniques for Indian Languages. JK Research Journal in Mathematics and Computer Sciences, 1 (1), 105–113. Available at: http://jkhighereducation.nic.in/jkrjmcs/issue1/15.pdf
- Chaabi, Y., Ataa Allah, F. (2022). Amazigh spell checker using Damerau-Levenshtein algorithm and N-gram. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 34 (8), 6116–6124. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.07.015
- Goslin, K., Hofmann, M. (2022). English Language Spelling Correction as an Information Retrieval Task Using Wikipedia Search Statistics. Proceedings of the Thirteenth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference. Marseille, 458–464. Available at: https://aclanthology.org/2022.lrec-1.48/
- Gowri, S., Sathish Kumar, P. J., Geetha Rani, K., Surendran, R., Jabez, J. (2022). Usage of a binary integrated spell check algorithm for an upgraded search engine optimization. Measurement: Sensors, 24, 100451. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measen.2022.100451
- Gupta, P. (2020). A Context-Sensitive Real-Time Spell Checker with Language Adaptability. 2020 IEEE 14th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icsc.2020.00023
- Makazhanov, A., Makhambetov, O., Sabyrgaliyev, I., Yessenbayev, Z. (2014). Spelling Correction for Kazakh. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 533–541. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54903-8_44
- Yanfi, Y., Gaol, F. L., Soewito, B., Warnars, H. L. H. S. (2022). Spell Checker for the Indonesian Language: Extensive Review. International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering, 12 (5), 1–7. doi: https://doi.org/10.46338/ijetae0522_01
- Friendly, F. (2019). Jaro–Winkler Distance Improvement For Approximate String Search Using Indexing Data For Multiuser Application. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1361 (1), 012080. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1361/1/012080
- Kantrowitz, M., Baluja, S. (2003). Pat. No. US6618697B1. Method for Rule-Based Correction of Spelling and Grammar Errors. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US6618697B1/en
- Sarkar, D. (2016). Text Analytics with Python. Apress Berkeley, 385. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-2388-8
- Ceska, Z., Hanak, I., Tesar, R. (2007). Teraman: A Tool for N-gram Extraction from Large Datasets. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iccp.2007.4352162
- Levenshtein, V. I. (1966). Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions, and reversals. Soviet Physics-Doklady, 10 (8), 707–710. Available at: https://nymity.ch/sybilhunting/pdf/Levenshtein1966a.pdf
- Rauf, S. A., Saeed, R., Khan, N. S., Habib, K., Gabrail, P., Aftab, F. (2017). Automated Grammatical Error Correction: a Comprehensive Review. NUST Journal of Engineering Sciences, 10 (2), 72–85. Available at: https://journals.nust.edu.pk/index.php/njes/article/view/219
- Jurafsky, D., Martin, J. H. (2023). Spelling Correction and the Noisy Channel. Speech and Language Processing. Available at: https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/B.pdf
- On the transfer of Kazakh writing from Latinized to a new alphabet based on Russian (1981). Collection of laws of the Kazakh USR and decrees of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Kazakh USR, 1, 1938–1981.
- The development of Kazakh Soviet linguistics (1980). Publishing house "Science" of the Kazakh USR, 128–242.
- Kazsur 903-90. Computer facilities. Keyboards. The location of the letters of the Kazakh alphabet (2023). Available at: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?Doc_id=1045019&pos=1;-16#pos=1;-16
- Norvig, P. (2016). How to Write a Spelling Corrector. Available at: https://norvig.com/spell-correct.html
- Zhubanov, A. K., Zhanabekova, A. A., Karbozova, B. D., Kozhakhmetov, A. K. (2016). Frequency dictionary of the Kazakh language. Almaty, 792.
- Desta, S. G., Lehal, G. S. (2023). Automatic spelling error detection and correction for Tigrigna information retrieval: a hybrid approach. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 12 (1), 387–394. doi: https://doi.org/10.11591/eei.v12i1.4209
- Yeleussinov, A., Amirgaliyev, Y., Cherikbayeva, L. (2023). Improving OCR Accuracy for Kazakh Handwriting Recognition Using GAN Models. Applied Sciences, 13 (9), 5677. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095677
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Nurzhan Mukazhanov, Zhibek Alibiyeva, Aigerim Yerimbetova, Aizhan Kassymova, Nursulu Alibiyeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









