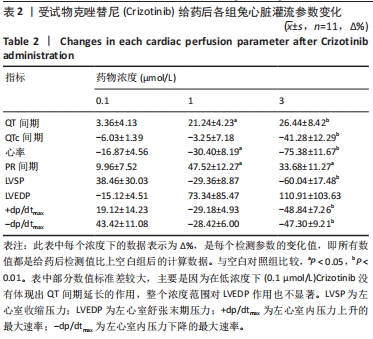
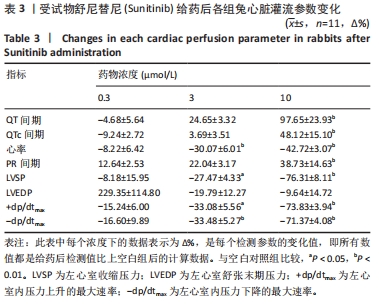
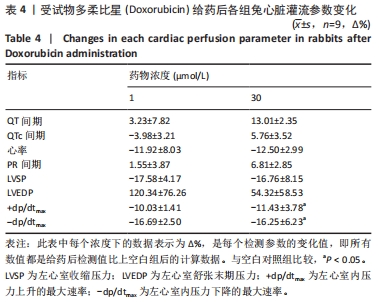
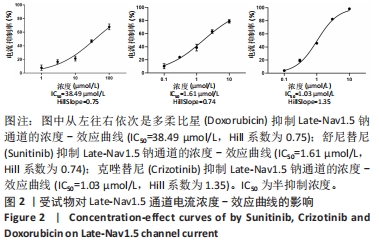
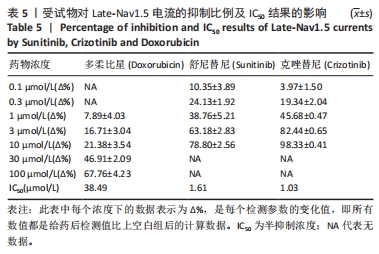
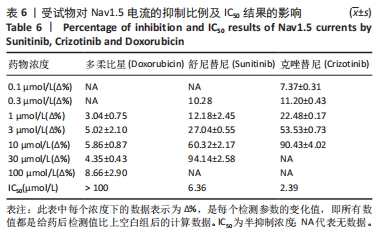
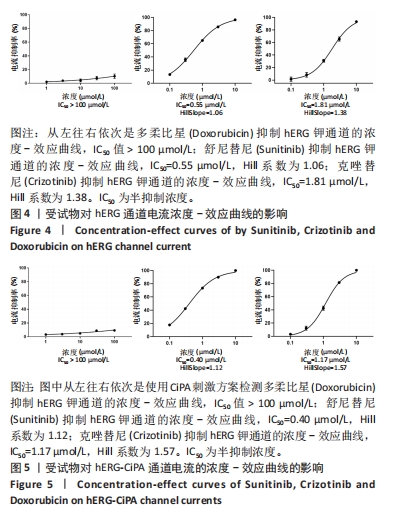
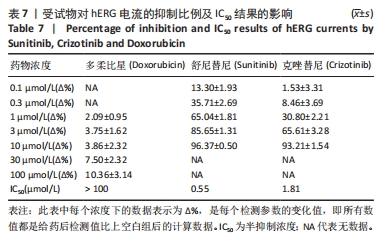
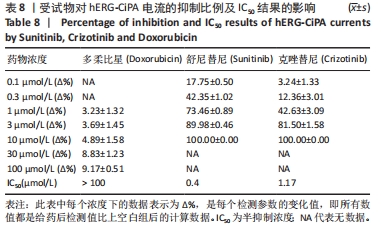
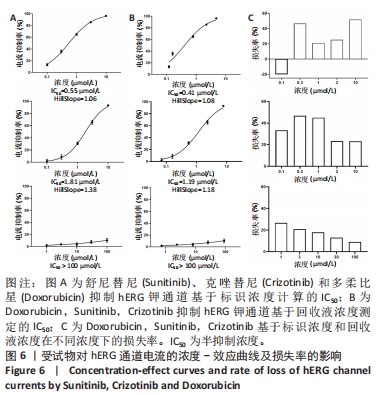
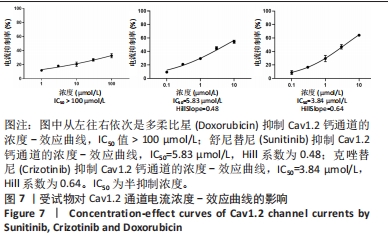
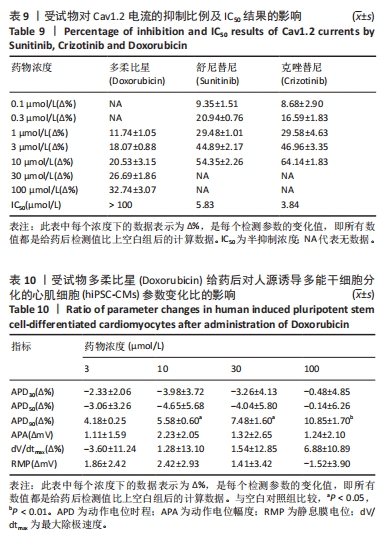
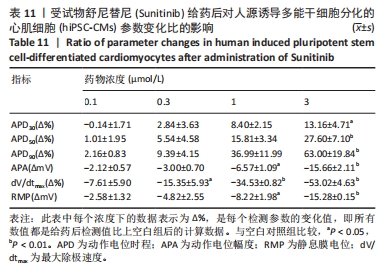
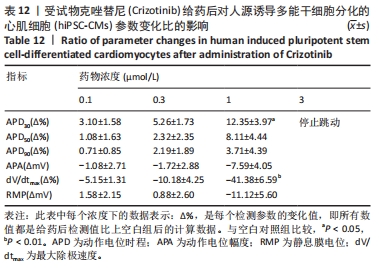
[1] 司丹妮,李彩娥,陈馨嵘,等.酪氨酸激酶抑制剂诱导的心脏毒性发病情况、评估和监测研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2022,62(33):97-102.
[2] SELTZER JH, GINTANT G, AMIRI-KORDESTANI L, et al. Assessing cardiac safety in oncology drug development. Am Heart J. 2019;214:125.
[3] SHYAM SUNDER S, SHARMA UC, POKHAREL S. Adverse effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy: pathophysiology, mechanisms and clinical management. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):262
[4] WANG H, WANG Y, LI J, et al. Three tyrosine kinase inhibitors cause cardiotoxicity by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in cardiomyocytes. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):147
[5] KADDOURA R, DABDOOB WA, AHMED K, et al. A practical guide to managing cardiopulmonary toxicities of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1163137.
[6] YAMAMICHI Y, KUSUOKA H, MORISHITA K, et al. Metabolism of iodine-123-BMIPP in perfused rat hearts. J Nucl Med. 1995;36(6):1043-1050.
[7] RUMSEY WL, PATEL B, LINDER KE. Effect of graded hypoxia on retention of technetium-99m-nitroheterocycle in perfused rat heart. J Nucl Med. 1995;36(4): 632-636.
[8] KUBURAS R, GHARANEI M, HAUSSMANN I, et al. Metformin protects against sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity: investigating the role of AMPK. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022;79(6):799-807.
[9] OBEJERO-PAZ CA, BRUENING-WRIGHT A, KRAMER J, et al. Quantitative profiling of the effects of vanoxerine on human cardiac ion channels and its application to cardiac risk. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17623.
[10] JONSSON MK, DUKER G, TROPP C, et al. Quantified proarrhythmic potential of selected human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):189-200.
[11] GILLIE DJ, NOVICK SJ, DONOVAN BT, et al. Development of a high-throughput electrophysiological assay for the human ether-à-go-go related potassium channel hERG. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2013;67(1):33-44.
[12] COHEN JD, BABIARZ JE, ABRAMS RM, et al. Use of human stem cell derived cardiomyocytes to examine sunitinib mediated cardiotoxicity and electrophysiological alterations. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011;257(1):74-83.
[13] WHITMIRE ML, BRYAN P, HENRY TR, et al. Nonclinical dose formulation analysis method validation and sample analysis. AAPS J. 2010;12:628-634.
[14] ROCHE O, TRUBE G, ZUEGGE J, et al. A virtual screening method for prediction of the hERG potassium channel liability of compound libraries. Chembiochem. 2002;3(5):455-459.
[15] GINTANT GA, LIMBERIS JT, MCDERMOTT JS, et al. The canine Purkinje fiber: an in vitro model system for acquired long QT syndrome and drug-induced arrhythmogenesis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001;37(5):607-618.
[16] TAKASUNA K, KATSUYOSHI C, MANABE S. Pre-clinical QT risk assessment in pharmaceutical companies-issues of current QT risk assessment. Biomol Ther. 2009;17(1):1-11.
[17] SHARMA A, BURRIDGE PW, MCKEITHAN WL, et al. High-throughput screening of tyrosine kinase inhibitor cardiotoxicity with human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(377):eaaf2584.
[18] NAZEYROLLAS P, PREVOST A, BACCARD N, et al. Effects of amifostine on perfused isolated rat heart and on acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43:227-232.
[19] TOKARSKA-SCHLATTNER M, ZAUGG M, DA SILVA R, et al. Acute toxicity of doxorubicin on isolated perfused heart:response of kinases regulating energy supply. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289:H37-H47.
[20] WANG YX, KORTH M. Effects of doxorubicin on excitation-concentration coupling in guinea pig ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 1995;76:645-653.
[21] STEINBERG JS, COHEN AJ, WASSERMAN AG, et al. Acute arrhythmogenicity of doxorubicin administration. Cancer. 1987;60:1213-1218.
[22] DUCROQ J, MOHA OU MAATI H, GUILBOT S, et al. Dexrazoxane protects the heart from acute doxorubicin-induced QT prolongation: a key role for IKs. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159:93-101.
[23] FAIVRE S, DELBALDO C, VERA K, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel oral multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(1):25-35.
[24] KHOSRAVAN R, TOH M, LAFARGUE J, et al. Sunitinib pharmokinetic (PK) and safety data in subejcts with renal impairment and hemodialysis. 2008.
[25] CHU TF, RUPNICK MA, KERKELA R, et al. Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Lancet. 2007;370:2011-2019.
[26] DI LORENZO G, AUTORINO R, BRUNI G, et al. Cardiovascular toxicity following sunitinib therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a multicenter analysis. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:1535-1542.
[27] COHEN JD, BABIARZ JE, ABRAMS RM, et al. Use of human stem cell derived cardiomyocytes to examine sunitinib mediated cardiotoxicity and electrophysiological alterations. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011;257(1):74-83.
[28] OBRIEN Z, F MOGHADDAM M. A systematic analysis of physicochemical and ADME properties of all small molecule kinase inhibitors approved by US FDA from January 2001 to October 2015. Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(29):3159-3184.
[29] KURATA Y, MIYAUCHI N, SUNO M, et al. Correlation of plasma crizotinib trough concentration with adverse events in patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2015;1(1):1-5.
[30] LESTER RM. Update on ICH E14/S7B cardiac safety regulations: the expanded role of preclinical assays and the “double-negative” scenario. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021;10(9):964-973.
[31] CURIGLIANO G, SPITALERI G, DE BRAUD F, et al. QTc prolongation assessment in anticancer drug development: clinical and methodological issues. Ecancermedicalscience. 2009;3:130.
[32] PANG L, SAGER P, YANG X, et al. Workshop report: FDA workshop on improving cardiotoxicity assessment with human-relevant platforms. Circ Res. 2019;125(9):855-867.
[33] SHARMA A, BURRIDGE PW, MCKEITHAN WL, et al. High-throughput screening of tyrosine kinase inhibitor cardiotoxicity with human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(377):eaaf2584.
[34] SELTZER JH, GINTANT G, AMIRI-KORDESTANI L, et al. Assessing cardiac safety in oncology drug development. Am Heart J. 2019;214:125-133.
[35] XIAO L, SALEM JE, CLAUSS S, et al. Ibrutinib-mediated atrial fibrillation attributable to inhibition of C-Terminal Src kinase. Circulation. 2020;142(25):2443-2455.
|