[1] MAQBOOL M, FEKADU G, JIANG X, et al. An up to date on clinical prospects and management of osteoarthritis. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021;72:103077.
[2] MAN GS, MOLOGHIANU G. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis - a complex process that involves the entire joint. J Med Life. 2014;7(1):37-41.
[3] CHEN Y, YU Y, WEN Y, et al. A high-resolution route map reveals distinct stages of chondrocyte dedifferentiation for cartilage regeneration. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):38.
[4] GAO Y, LIU S, HUANG J, et al. The ECM-cell interaction of cartilage extracellular matrix on chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:648459.
[5] XU J, YAN L, YAN B, et al. Osteoarthritis Pain Model Induced by Intra-Articular Injection of Mono-Iodoacetate in Rats. J Vis Exp. 2020;(159).doi: 10.3791/60649.
[6] YANG P, TAN J, YUAN Z, et al. Expression profile of cytokines and chemokines in osteoarthritis patients: Proinflammatory roles for CXCL8 and CXCL11 to chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;40:16-23.
[7] WATANABE K, PENFOLD ME, MATSUDA A, et al. Pathogenic role of CXCR7 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(11):3211-3220.
[8] WANG G, LI Y, MENG X, et al. The study of targeted blocking SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway with three antagonists on MMPs, type II collagen, and aggrecan levels in articular cartilage of guinea pigs. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):195.
[9] XIANG Y, LI Y, YANG L, et al. miR-142-5p as a CXCR4-Targeted MicroRNA Attenuates SDF-1-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Cartilage Degradation via Inactivating MAPK Signaling Pathway. Biochem Res Int. 2020;2020:4508108.
[10] LI C, HE Y, LI Y, et al. A novel method to establish the rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis: intra-articular injection of SDF-1 induces OA. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):329.
[11] 王国梁,李彦林,向耀宇,等.基质细胞衍生因子1诱导骨关节炎软骨细胞的miRNA表达谱分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(31):4948-4953.
[12] ZHANG X, WANG C, ZHAO J, et al. miR-146a facilitates osteoarthritis by regulating cartilage homeostasis via targeting Camk2d and Ppp3r2. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(4):e2734.
[13] YAMASAKI K, NAKASA T, MIYAKI S, et al. Expression of MicroRNA-146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(4):1035-1041.
[14] JIA D, LI Y, HAN R, et al. miR‑146a‑5p expression is upregulated by the CXCR4 antagonist TN14003 and attenuates SDF‑1‑induced cartilage degradation. Mol Med Rep. 2019; 19(5):4388-4400.
[15] WU X, BIAN B, LIN Z, et al. Identification of exosomal mRNA, lncRNA and circRNA signatures in an osteoarthritis synovial fluid-exosomal study. Exp Cell Res. 2022;410(1):112881.
[16] 李晓林,李彦林,马珂,等.SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路在骨性关节炎病理进程中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(15):2805-2808.
[17] HE X, GAO K, LU S, et al. LncRNA HOTTIP leads to osteoarthritis progression via regulating miR-663a/ Fyn-related kinase axis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):67.
[18] SKRZYPA M, SZALA D, GABLO N, et al. miRNA-146a-5p is upregulated in serum and cartilage samples of patients with osteoarthritis. Pol Przegl Chir. 2019;91(3):1-5.
[19] SI HB, ZENG Y, LIU SY, et al. Intra-articular injection of microRNA-140 (miRNA-140) alleviates osteoarthritis (OA) progression by modulating extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(10):1698-1707.
[20] REN T, WEI P, SONG Q, et al. MiR-140-3p Ameliorates the Progression of Osteoarthritis via Targeting CXCR4. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43(5):810-816.
[21] SHAO J, DING Z, PENG J, et al. MiR-146a-5p promotes IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis through the TRAF6-mediated NF-kB pathway. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(6):619-630.
[22] ZHAO G, GU W. Effects of miR-146a-5p on chondrocyte interleukin-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis involving thioredoxin interacting protein regulation. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(11):300060520969550.
[23] QIN H, WANG C, HE Y, et al. Silencing miR-146a-5p Protects against Injury-Induced Osteoarthritis in Mice. Biomolecules. 2023;13(1):123.
[24] ZHANG G, ZHANG Q, ZHU J, et al. LncRNA ARFRP1 knockdown inhibits LPS-induced the injury of chondrocytes by regulation of NF-κB pathway through modulating miR-15a-5p/TLR4 axis. Life Sci. 2020;261:118429.
[25] JATHAR S, KUMAR V, SRIVASTAVA J, et al. Technological Developments in lncRNA Biology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1008:283-323.
[26] HU J, WANG Z, SHAN Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes osteoarthritis progression via miR-17-5p/FUT2/β-catenin axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):711.
[27] KONG H, SUN ML, ZHANG XA, et al. Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:774370.
[28] ZHU Y, LI R, WEN LM. Long non-coding RNA XIST regulates chondrogenic differentiation of synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells from temporomandibular joint via miR-27b-3p/ADAMTS-5 axis. Cytokine. 2021;137:155352.
[29] ZHANG H, SONG B, PAN Z. Downregulation of microRNA-9 increases matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression levels and facilitates osteoarthritis onset. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3):3708-3714.
[30] ZHAN S, WANG K, SONG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates intervertebral disc degenerative changes via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):201.
[31] LI D, WANG X, YI T, et al. LncRNA MINCR attenuates osteoarthritis progression via sponging miR-146a-5p to promote BMPR2 expression. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(22):2417-2432.
[32] HUANG Y. The novel regulatory role of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(12):5768-5775.
[33] SUN H, PENG G, NING X, et al. Emerging roles of long noncoding RNA in chondrogenesis, osteogenesis, and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(1):16-30.
|

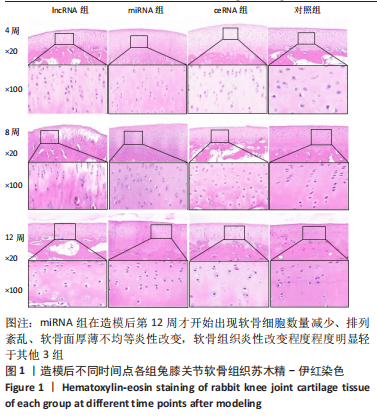
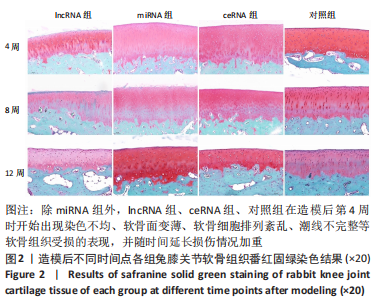
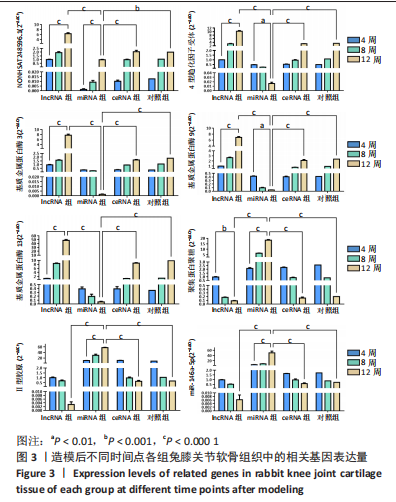
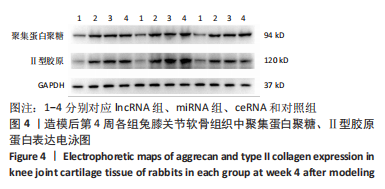
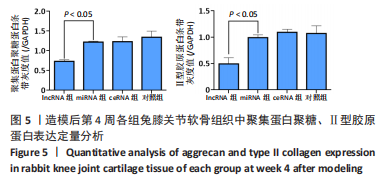

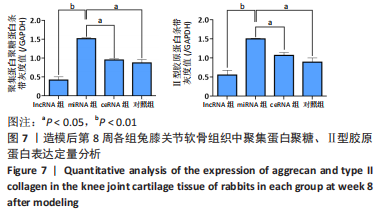
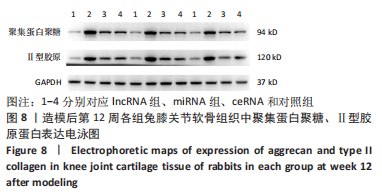
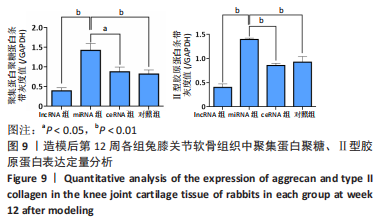


 课题组在前期体外实验中发现,NONHSAT248596.1能作为miR-146a-5p的天然海绵发挥内源性竞争作用,直接与miR-146a-5p 结合并抑制其表达和活性,调控SDF-1/CXCR4轴影响骨关节炎软骨退变的进程,有研究证明CXCR4是miR-146a-5p的直接靶点[21]。在对照组兔膝骨关节炎的软骨细胞中也观察到 miR-146a-5p的低表达和CXCR4、SDF-1的高表达,可见lncRNA可能通过结合miR-146a-5p使其对SDF-1/CXCR4轴的抑制作用减弱,在骨关节炎疾病的病理变化中发挥相关作用。
课题组在前期体外实验中发现,NONHSAT248596.1能作为miR-146a-5p的天然海绵发挥内源性竞争作用,直接与miR-146a-5p 结合并抑制其表达和活性,调控SDF-1/CXCR4轴影响骨关节炎软骨退变的进程,有研究证明CXCR4是miR-146a-5p的直接靶点[21]。在对照组兔膝骨关节炎的软骨细胞中也观察到 miR-146a-5p的低表达和CXCR4、SDF-1的高表达,可见lncRNA可能通过结合miR-146a-5p使其对SDF-1/CXCR4轴的抑制作用减弱,在骨关节炎疾病的病理变化中发挥相关作用。