2.1 文献分布
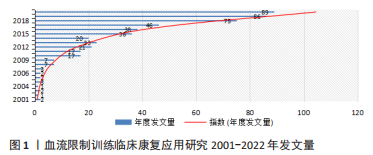
2.1.1 年度发文量分布 分析年度发文量数量变化趋势,紧密追查BFRT在临床康复应用中的动态走向。以年度为单位划分,如图1所示,其整体研究趋势呈稳定上升,以上升趋势陡度划分为4个区间。区间一:起步萌芽阶段(2001-2009年),该区间内年发文量最高7篇,最低1篇,BFRT应用在临床康复中的尝试阶段,仅有小部分先锋作者研究;区间二:缓慢发展阶段(2010-2014年),该区间总体年度发文量相对于区间一有增长趋势,除了个别年份有回落减少趋势(2014年发文量20篇);区间三:发展过渡阶段(2015-2017年),有明显增长趋势,得益于BFRT理论研究热度升高,对临床康复研究有良性影响;区间四:热点关注阶段(2018-2022),在该阶段对BFRT应用康复治疗的研究热点居高不下,BFRT与临床康复结合的研究发展持续受到国外热点关注。
2.1.2 核心作者分布 使用SATI软件从合作文献中抽取作者关键词,构建作者及所属单位矩阵,利用Ucinet构建发文量前十名作者网络,并利用NetDraw实现可视化。普莱斯定律是文献计量法的研究方法之一,是衡量各个学科领域文献作者分布规律,可确定该领域内的核心作者,计算公式如下:M=0749 Nmax公式中用 M 表示核心作者的最小发文量,用 Nmax表示该选定研究领域或主题内同一作者的最大发文量。通过表1可知BFRT应用在临床康复治疗研究中,Loenneke教授发文量高达58篇位居榜首,代入计算公式Nmax=58,M=6篇(向上取整),即表示此领域中作者发文量≥6篇即可被确定为核心作者,515篇文献中所涉及第一作者共116位,其中发文量超过6篇共有53位,合计发文351篇,占比68.16%,核心作者发文量占据总发文量68.84%,说明在该领域中已形成较为核心、规模大的研究作者群。
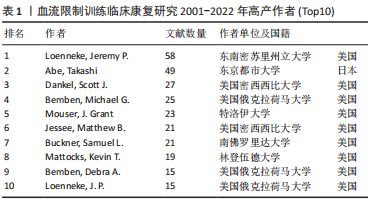
表1中前10位高产作者单位90%来自美国,其中3位作者来自俄克拉荷马大学,2位来自密西西比大学。一个研究领域的迅速发展,不仅表现在研究成果的不断涌现,同时也表现在学术共同体规模的持续壮大。对于所属同一国家、单位机构的合作研究较为紧密,而对于BFRT更好地应用在临床康复治疗中,跨地区、跨机构、跨学科的合作是打破传统研究的最佳方式。
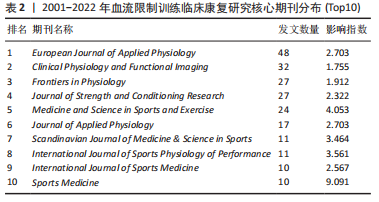
2.1.3 核心期刊分布 运用Netdraw分析软件绘制出BFRT应用临床康复研究领域载文量前10位发布期刊各自的发文量、影响指数,经统计分析,前10位期刊的发文量占全部文献比例为52.04%,表明该研究领域的学术期刊分布较为集中,已形成较为系统的核心期刊。根据布拉德福定律布拉福德定律,当某一研究领域相关文献发表的学术期刊的发文量呈现为不均匀分布时,发文数量与所发表期刊的专业密切程度相关,按其刊载发文量以递减顺序排列,可将期刊分为每区数量相等的核心区、相关区和非相关区。其核心区计算式如下:P=2Ln(eE×Y)
公式中,P为核心区数量,E 为欧拉系数,E=0.577 2,Y为最大发文量期刊的载文量。如表2所示,《欧洲应用生理学杂志》为最大发文量期刊,代入公式P=2Ln(1.781×48)9篇。因而,表2发文量前10位期刊是BFRT应用临床康复研究领域中期刊分布的核心区,共发文量217篇。
 2.1.4 高产机构分布 为考察BFRT临床康复研究的主要学术团体,通过Ucinet、Netdraw可视化分析软件将发文机构的发文量及地区分布进行汇总,见表3。样本研究文献所涉及的143个机构主要分布于欧美、亚洲地区,其中发文量排名前3位的分别是美国密西西比大学(56篇)、日本东京大学(54篇)、美国俄克拉荷马大学(51篇),表明这3个研究机构在BFRT临床康复研究中成绩斐然,在该领域中已较有高权威影响力。
2.1.4 高产机构分布 为考察BFRT临床康复研究的主要学术团体,通过Ucinet、Netdraw可视化分析软件将发文机构的发文量及地区分布进行汇总,见表3。样本研究文献所涉及的143个机构主要分布于欧美、亚洲地区,其中发文量排名前3位的分别是美国密西西比大学(56篇)、日本东京大学(54篇)、美国俄克拉荷马大学(51篇),表明这3个研究机构在BFRT临床康复研究中成绩斐然,在该领域中已较有高权威影响力。
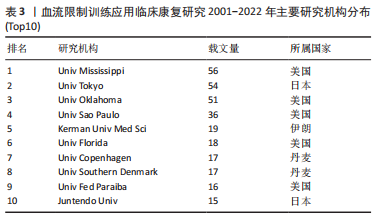
在2001-2022年参加BFRT临床康复的研究机构143个,其中美国发文量221篇,占发文总量42.91%,其次日本发文量112篇,占总发文量21.75%,第三巴西发文量77篇,占总发文量14.95.95%。由此可得,关于BFRT临床康复研究美国为研究主力,其次日本、巴西、英国等国家,已形成较为成熟的研究地区。每个研究领域热点主题的出现、发展都与国家整体的社会环境息息相关[6],近年来美国、英国等发达国家为中心代表研究BFRT各方面的应用效果,扩展研究视野,引领BFRT研究潮流。
2.2 高频关键词分布 高频关键词反映了该研究领域发展方向和变化趋势演变,具有动态特征,是一定时期内学者们重点关注的研究热点。通过SAIT软件对515篇文献的关键词进行统计分析,形成前50个关键词的相异矩阵,再通过Netdraw软件对前50个关键词的相异性矩阵进行共现网络可视化分析,通过研究对象、研究内容、干预措施、研究方法对高频关键词进行划分归类,见表4。
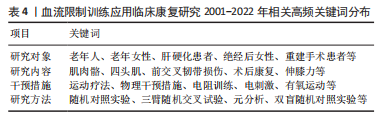
运用SPSS 20.0对2001-2022年高频关键词的相异矩阵进行因子分析,主要采用的方法有主成分分析、协方差矩阵、最大方差法。结果显示有21个公共因子(因篇幅限制,具体过程从略)。为了缩小类团,继续将相异矩阵导入到SPSS 20.0 中进行系统聚类,在聚类方法中选择Ward 法进行分析,最终确定了3个类团,BFRT与骨骼肌肉康复、人类认知和功能活动、慢性疾病康复研究3个方面。
BFRT临床康复研究紧紧围绕着老年人、膝盖、韧带损伤等患者,以低强度运动疗法或矫形器等物理干预措施对骨骼肌肉力量、基础性疾病(心血管、高血压)、术后康复病症等方面的研究,研究方法主要以试验对照(随机对照试验、安慰剂对照试验、双盲随机对照试验等),理论研究(元分析、文献计量法等)两种手段为主。
2.3 研究主题分布
2.3.1 BFRT与骨骼肌肉康复研究 该类团主题涉及的热点关键词:骨骼肌肥大、肌肉力量、力量训练、意志衰竭、进展、肌肉减少症等。
肌肉力量是保持健康、身体功能以及提高生活质量所必需的基本身体特征,BFRT提高肌肉力量、耐力、横截面积应用效果已被证实,其低负荷训练强度实现与传统抗阻训练效果无明显差异。BFRT已被提出作为运动治疗的一种康复方式,在较短时间内以轻阻力实现肌肉力量、耐力增长,达到术后恢复要求,对不同骨骼肌肉病症,BFRT不失为一种很好的恢复手段。在BFRT康复应用文章中广泛搜索,发现BFRT在骨骼肌肉康复研究领域主要针对前交叉韧带重建术后肌肉萎缩康复、衰老患者护理康健、膝骨关节炎、脊髓损伤患者(植物人)、髌骨骨痛患者、散发性包涵肌炎患者等。
前交叉韧带重建术是一种很常见的骨科手术,术后会出现股四头肌无力、膝盖积水、疼痛等病症长时间持续存在。针对研究股四头肌力量丧失与前交叉韧带损伤和重建相关的靶向治疗,肌肉纤维类型转换、细胞外基质扩张和肌卫星细胞丰度减少等负面改变阻碍了骨骼肌的可塑性[7-10]。利用免疫组织化学和组织化学评估术后3 d组、术后6-7个月2个组别记录的肌肉活检的肌纤维类型、卫星细胞增殖、细胞外基质等细胞特征,有助于临床医生更好地理解BFRT对股四头肌肌内细胞变化到肌肉形态特征以及训练整体关节力量和运动力学等多个层面积极影响的潜在机制[11],证明了BFRT对前交叉韧带重建患者康复的有效性。
ACSM运动处方指出阻力训练最佳训练模型是循序渐进负荷强度练习,优化练习强度质量。在康复领域中HUGHES等[12](2019)以标准康复训练方案的血流限制-抗阻训练(30%1RM,n=14,BFR-RT)和高负荷抗阻训练(70%1RM,n=14,HL-RT)组对比分析中,分别观察到肌肉厚度、三角肌角的肌肉变化显著增加,关节活动度、膝关节疼痛减少、平衡性能和积液减少(33% vs. 22%)的多项指标中,BFR-RT可以改善骨骼肌肥大和力量的程度类似于HL-RT,膝关节疼痛和积液减少康复效果更佳,与HL-RT相比,BFR-RT可能更适合于术后康复的渐进肢体负荷初级阶段,具有显著的临床重要性。
BFRT阻力练习减少骨骼系统压力,对于行动不便、运动障碍、受伤人群是一种很有吸引力的临床康复运动方式[13]。相对于传统抗阻训练康复计划,研究人员更注重改变BFRT袖带类型、袖口压力、运动负荷、重复次数、训练量、训练周期,寻求最大限度适应,在临床康复效益最佳化。综上所述,临床应用中BFRT是康复护理的一种辅助手段,临床医生以渐进训练计划可将BFRT作为康复早期阶段的工具[14],提高康复保护阶段的肌肉围度与力量,有效促进肌肉萎缩而导致力量的衰减。BFRT相对于高负荷抗阻训练、低负荷抗阻训练(LL-RT)是一个较为安全且有效的康复方式,但需要针对不同年龄、病症、性别、健康情况等特征制定个性化闭塞压力(临床建议个体肢体闭塞压力的百分比范围40%-80%)和训练项目。
2.3.2 BFRT与人类认知和功能活动康复研究 该类团主题涉及的高频关键词:动脉闭塞压力(AOP)、心血管系统、内皮功能、缺血、免疫系统等关键词。
BFRT在临床中有提高肌肉力量、耐力等积极作用,不良作用可忽略不计,但神经肌肉、血液动力学、代谢和知觉反应时会产生不同的急性效应是血流限制相关的潜在不良作用和安全性问题[15],也是局限血流限制作为常规康复手段应用到临床的主要原因。对于血流限制影响人类心血管、血压、认知等功能的争议较为激烈。
在BFRT里动脉闭塞压力过高诱导血管阻塞可能导致肌肉反射过度激活(例如,激活Ⅳ和Ⅲ组传入纤维),从而使交感神经过度活跃,心功能、血压、血管阻力升高,并增加心血管相关不良事件的风险[16]。但在日本进行的一项由来自232家机构的BFRT指导人员参与的大型调查未证实任何大损伤事件,在临床特征差异很大,受试者(如老年人和肥胖、糖尿病患者)中存在脑出血、脑梗死或血栓形成。脑血管和心血管疾病,报道的不良作用一般较轻,包括短暂性麻木或头晕、皮下出血和发痒。考虑到缺乏针对临床人群的长期前瞻性试验,以及文献中仍然很大程度上忽略了一些残留的不良反应的可能性,关于BFRT安全性的一般假设需要谨慎对待。
BFRT袖口压力带越宽压力越大,越容易导致动脉闭塞、内皮功能受损,医生需牢记在临床中血流限制袖带压力应该相对于个体而变化,而不是在绝对基础上应用。在不断实验研究确定出一种周期性BFR-RT训练模型[17],对于保护心血管健康、内皮功能具有实用的临床价值。该模型为4个周期的5 min闭塞/5 min放气再灌注的有氧运动(20%1RM,动脉闭塞压力220 mmHg),与抗阻训练组(65%1RM)相比之下,血浆中去甲肾上腺素水平、心率、心输出量、每博量和总外周阻力,抑制了交感神经活动的参加,保护心血管健康。制定血流限制康复计划时动脉闭塞压力值低于动脉压力百分比的60%促进心血管、血压功能,确保临床康复中的安全性。
使用血流限制阻力训练在增加肌肉力量、肥大方面有效,对干预认知的效率也可提高,下肢血流限制与步行结合是衰老患者改善身体功能、保持健康的一种替代方案,在训练计划中增加轻阻力血流限制可以增强诱导积极的认知和心血管适应的能力,轻阻力血流限制对特殊人群的临床康复更加有益。血流限制运动激活诱导类胰岛素增长因子1浓度升高改善大脑认知能力[18],运动后大脑前额叶皮质活动减少,有效改善日常生活活动(如安全行走)的运动控制功能,在临床人群应用有氧式血流限制提高氧合功能水平,引起适应过程更有利于认知表现,可作为改善认知能力一种潜在干预手段[19]。了解慢性血流限制如何积极或消极地影响血管、心脏、认知等功能,并优化认知功能恶化的个体(老年痴呆症患者、抑郁症)的康复策略,血流限制的阻力训练可能是一个有希望的运动干预策略。
2.3.3 BFRT与慢性疾病康复研究 该类团主题涉及的高频关键词:安全性、心脏康复、疼痛、骨关节炎、线粒体、代谢应力、老年人等关键词。
通过运动锻炼的方式降低对疼痛的敏感性被称为锻炼导致痛觉减弱(exerciseinduced hypoalgesia,EIH),BFRT进行的低强度运动在前膝疼痛患者中已证明会引发痛觉减弱。对于康复人群LI-BFR运动方式是HL-RT的最佳替代,明显减少了高负荷强度给慢性疼痛患者带来的更多运动疼痛。BFRT增加肌肉中的代谢应激水平可能会触发阿片样物质和内源性大麻素介导的痛觉减退机制,同时代谢应激通过代谢物积累优化局部环境,刺激心血管、肌肉、骨骼适应,对于慢性疼痛人群具有双重效果。在临床康复试验中,血流限制(≤30% 1RM)会出现EIH现象[20-21],且LI-BFR膝关节伸展运动后可立即减轻前膝关节疼痛,这种中度到重度疼痛的缓解持续了至少45 min。对于纤维疼痛、骨关节炎、负荷受损等慢性疼痛患者,BFRT可结合电阻、有氧、振动等运动方式发展为缓解疼痛、提高生活质量的一种康复管理手段。
LOENNEKE等[17](2012)提出BFRT康复循序渐进模式,包括卧床休息(BFRT静止)、血流限制步行、血流限制阻力训练、低负荷到高负荷抗阻运动4个阶段,证明BFRT的不同阶段都有肌肉力量、耐力等积极训练效应。对于长期卧床脊髓损伤患者BFRT与电刺激结合,可有效缓解肌肉萎缩、无力等症状,其中LOENNEKE教授在试验中发现卧床时间延长刺激类似自重力的压力,身体对心脏负荷降低的偏心性心脏萎缩和左心室顺应性降低作出反应,有效缓解心血管疾病[22]。这种训练模式方案血流限制负荷(20%-40%1RM)、重复次数(2-4组)、总限制时间(5-10 min),对于石膏固定患者的肌肉力量和腿围的减少,以及由慢性卸载引起的肌肉无力,该种训练模式可有效减少术后长期卧床休息导致的肌肉萎缩。
2型糖尿病是一种以葡萄糖代谢受损、骨骼肌肉衰退和肌肉减少症恶化为特征的慢性疾病,可伴有并发症和共病,如大血管(冠心病)和微血管并发症(视网膜病、肾病、微量白蛋白尿)或自主神经病变[23]。BFRT低氧张力内皮功能障碍进一步诱导毛细血管新生增加肌内活性氧的产生,降低胰岛素含量,促进线粒体发生和葡萄糖转运蛋白4的表达,可能会改善2型糖尿病患者的代谢控制。这些适应性改变可提高2型糖尿病患者的运动能力,BFRT是相对于传统治疗风险相当的一种潜在康复训练方法。同时研究表明,每周2次持续12周血流限制坐姿伸腿、屈腿、水平腿,与抗阻训练对比肌肉横截面积和力量类似增加;每周3次连续4周血流限制同样训练内容,发现血流限制可改善健康老年人的血管内皮功能和外周血液循环,被提议对冠心病患者LI-BFR是一种有价值的运动选择[24]。
BFRT在较低强度下,通过血流限制实现对生长细胞、肌纤维的影响使这种训练方法可能适用于肌少症、骨质疏松、糖尿病、风湿病等长期慢性疾病的伴随改善。临床医生可设计康复渐进模型,合理制定血流限制卧床、血流限制行走、血流限制训练、高负荷抗阻运动4个康复阶段,根据不同临床人群训练水平、健康情况、训练反应及时反馈调整,将BFRT作为缓解长期慢性疾病一种有效的物理干预策略。
2.4 BFRT研究重点与未来方向
(1)未来研究可与虚拟现实技术等高科技相结合,以探索新的康复结合方式,确保BFRT在临床应用中的有效性。然而,BFRT仅是康复治疗的一种辅助手段,为实现康复更好地改善病症,需要结合标准护理中的康复理论、营养学,针对不同康复病症,BFRT在安全可控条件下可与阻力、有氧、振动、水疗等运动方式结合。
(2)BFRT对于长期慢性疾病研究关注点较低,对于肾炎、髌骨股痛、糖尿病等慢性疾病通过BFRT辅助手段缓解病症,BFRT应用在临床人群中的长期治疗,延长随访期、登记更大和更多样的样本量以及使用随机技术来确定康复患者的适当处方适应证。未来更应注重BFRT在临床康复中的长期适应性,慢性反应对于身体机制有无其他不良影响。
(3)临床医生对于不同病症康复患者影响必须排除一切干扰因素(横纹肌溶解、迟发性肌肉酸痛和静脉血栓)[24],保证BFRT在临床应用中的安全性。排除干扰康复中的一切影响因素,理论研究更应该注重去探寻临床研究BFRT与健康效益的量效关系,包括个性化肢体袖口压力、运动负荷、运动持续时间、重复次数等不同因素,定量分析针对不同临床人群制定和完善最小有效剂量发挥最大效应的康复训练方案。







