中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5173-5177.doi: 10.12307/2023.825
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
改良椎板切除法构建脊髓损伤模型大鼠
杜凯然1,邓 强2,郭铁峰2,张彦军2,彭冉东2,李军杰2,王雨榕1,张凯东1,罗林钊1
- 1甘肃中医药大学,甘肃省兰州市 730030;2甘肃省中医院,甘肃省兰州市 730050
Improved laminectomy for constructing a rat model of spinal cord injury
Du Kairan1, Deng Qiang2, Guo Tiefeng2, Zhang Yanjun2, Peng Randong2, Li Junjie2, Wang Yurong1, Zhang Kaidong1, Luo Linzhao1
- 1Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; 2Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
牙科磨钻打磨法:定位准确后,选择牙科打磨机安装圆饼形钻头,调整合适转速后以180°水平面打磨棘突,将凸起棘突打磨平整后,再以30°-45°刮磨,初始打磨骨头呈白色,经打磨后慢慢变薄,逐渐转变为红白相间,伴随刺激神经,后下肢无自主性抬起,此时立即停止打磨。
显微器械摘除法:选用精确的显微剪刀沿着T10椎间隙向上剪开被打磨过的骨面,待椎体脊髓正中上方的骨头剔除干净后,两侧的残余不规则的骨头及关节突则选用弯头显微持针器轻轻夹除。
背景:目前脊髓损伤已成为世界性难题,实验动物造模是探索疾病的第一步,但现缺乏较为有效的实验动物模型。
目的:建立一种可复制、可调控、创伤小、死亡率低、出血量少、适用范围广、术中时间短的脊髓损伤大鼠模型。
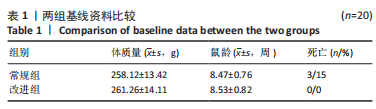
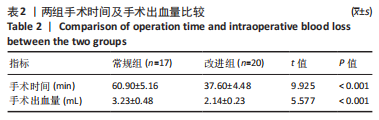
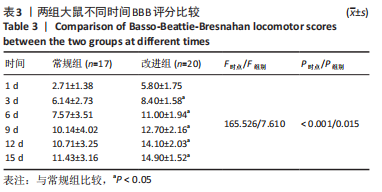
方法:将选用的体质量相似的40只SD大鼠随机分为常规组和改进组,每组20只,常规组采用Allen法构建脊髓损伤模型,改良组在原有模型的基础上,运用牙科磨钻代替器械咬除,比较两组大鼠手术时间、术中出血量、死亡率及击打后1,3,6,9,12,15 d的BBB运动功能学评分。
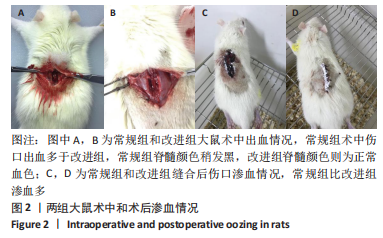
结果与结论:改良继发性脊髓损伤模型建立方法比常规建模方法出血量少、死亡率低、造模时间短、BBB评分结果更集中,由此可证明改良后的击打方法更适用于继发性脊髓损伤模型的建立。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3042-5192 (邓强)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: