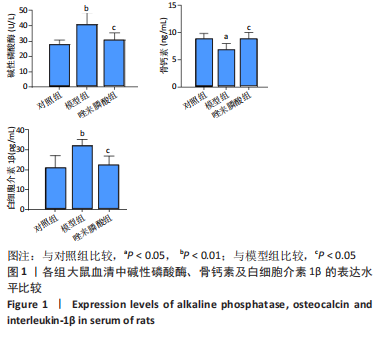
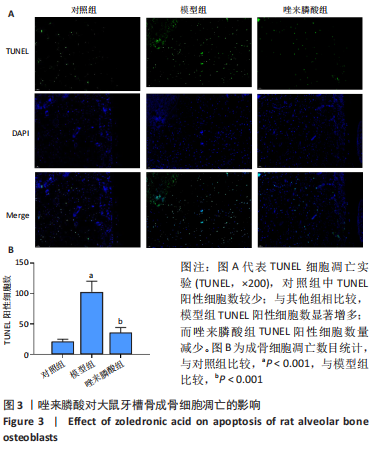
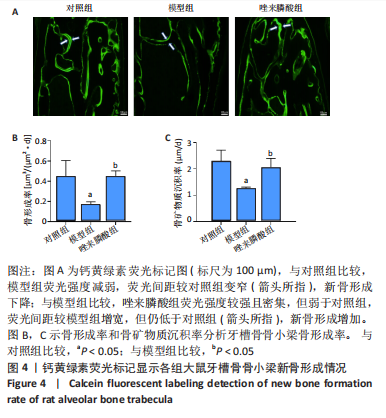
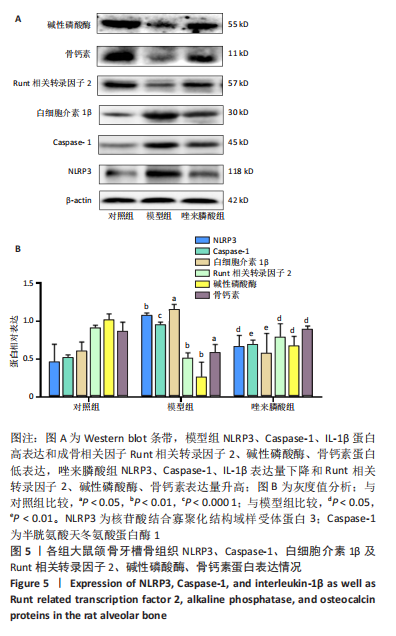
[1] CHEN X, MORIYAMA Y, TAKEMURA Y, et al. Influence of osteoporosis and mechanical loading on bone around osseointegrated dental implants: A rodent study. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;123: 104771.
[2] ALIPPE Y, MBALAVIELE G. Omnipresence of inflammasome activities in inflammatory bone diseases. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(5):607-618.
[3] HENDRICKS R, VICATOS G. Creation of bone and soft tissue in postmaxillectomy patients using curvilinear transport distraction osteogenesis. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2019;9(2):319-325.
[4] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21.
[5] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623.
[6] PARIHAR AS, MADHURI S, DEVANNA R, et al. Assessment of failure rate of dental implants in medically compromised patients. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020;9(2):883-885.
[7] DIACHKOVA E, ABRAMOVA EV, BLAGUSHINA NA, et al. Surgical treatment with dental implants in a patient with secondary loss of teeth and osteoporosis caused by an imbalance of vitamin D. BMJ Case Rep. 2020;13(11):e235585.
[8] GIRO G, CHAMBRONE L, GOLDSTEIN A, et al.Impact of osteoporosis
in dental implants: A systematic review. word J Orthop,2015,6(2):
31-35.
[9] SCALA R, MAQOUD F, ANTONACCI M, et al. Bisphosphonates targeting ion channels and musculoskeletal effects. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 837534.
[10] DERENNE S, AMIOT M, BARILLÉ S, et al. Zoledronate is a potent inhibitor of myeloma cell growth and secretion of IL-6 and MMP-1 by the tumoral environment. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(12):2048-2056.
[11] PLOTKIN LI, MANOLAGAS SC, BELLIDO T. Dissociation of the pro-apoptotic effects of bisphosphonates on osteoclasts from their anti-apoptotic effects on osteoblasts/osteocytes with novel analogs. Bone. 2006;39(3):443-452.
[12] FREDIANI B, SPREAFICO A, CAPPERUCCI C, et al. Long-term effects of neridronate on human osteoblastic cell cultures. Bone. 2004;35(4): 859-869.
[13] RUGGIERO SL, DODSON TB, FANTASIA J, et al. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw--2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(10):1938-1956.
[14] SRIVICHIT B, THONUSIN C, CHATTIPAKORN N, et al. Impacts of bisphosphonates on the bone and its surrounding tissues: mechanistic insights into medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Arch Toxicol. 2022;96(5):1227-1255.
[15] VERGARA-HERNANDEZ FB, NIELSEN BD, COLBATH AC. Is the Use of bisphosphonates putting horses at risk? An Osteoclast Perspective. Animals (Basel). 2022;12(13):1722.
[16] HUANG X, HUANG S, GUO F, et al. Dose-dependent inhibitory effects of zoledronic acid on osteoblast viability and function in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(1):613-622.
[17] 李颉颃, 苏志飞, 白璇, 等. 唑来膦酸对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化的作用研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2019,37(3):242-247.
[18] LI JH, SU ZF, BAI X, et al. Effect of zoladronate on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;37(3):242-247.
[19] BASSO FG, PANSANI TN, CARDOSO LM, et al. Influence of bisphosphonates on the behavior of osteoblasts seeded onto titanium discs. Braz Dent J. 2020;31(3):304-309.
[20] 霍花, 刘官娟, 宋娜, 等. 唑来膦酸干预去势大鼠牙槽骨骨代谢及核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3炎症小体表达的变化 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(17):2660-2666.
[21] 程余婷, 伍超, 黄晓林, 等. 低剂量唑来膦酸对去势拔牙大鼠破骨及成骨细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2686-2693.
[22] CHENG YT, LIAO J, ZHOU Q, et al. Zoledronic acid modulates osteoclast apoptosis through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021;246(15):1727-1739.
[23] HUANG XL, HUANG LY, CHENG YT, et al. Zoledronic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation and function through the regulation of NF-κB and JNK signalling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 2019;44(2):582-592.
[24] HUANG XL, LIU C, SHI XM, et al. Zoledronic acid inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorptive function by suppressing RANKL‑mediated NF‑κB and JNK and their downstream signalling pathways. Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(2):59.
[25] BASSO FG, SILVEIRA TURRIONI AP, HEBLING J, et al. Zoledronic acid inhibits human osteoblast activities. Gerontology. 2013;59(6):534-541.
[26] JIANG N, AN J, YANG K, et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome: A new target for prevention and control of osteoporosis? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:752546.
[27] CLINE-SMITH A, AXELBAUM A, SHASHKOVA E, et al. Ovariectomy activates chronic low-grade inflammation mediated by memory T cells, which promotes osteoporosis in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(6): 1174-1187.
[28] XIN W, WANG X, ZHANG W, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibits bone marrow stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts by downregulating microRNA-34a expression. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019;49(3):324-329.
[29] LATZ E, DUEWELL P. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in inflammaging. Semin Immunol. 2018;40:61-73.
[30] YOUSEFZADEH N, KASHFI K, JEDDI S, et al. Ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis: a practical guide. Excli J. 2020;19:89-107.
[31] JAYUSMAN PA, MOHAMED IN, ALIAS E, et al. The Effects of quassinoid-rich eurycoma longifolia extract on bone turnover and histomorphometry indices in the androgen-deficient osteoporosis rat model. Nutrients. 2018;10(7):799.
[32] ARIOKA M, ZHANG X, LI Z, et al. Osteoporotic changes in the periodontium impair alveolar bone healing. J Dent Res. 2019;98(4): 450-458.
[33] LIU Y, LI Z, ARIOKA M, et al. WNT3A accelerates delayed alveolar bone repair in ovariectomized mice. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(9):1873-1885.
[34] CHEN CH, WANG L, SERDAR TULU U, et al. An osteopenic/osteoporotic phenotype delays alveolar bone repair. Bone. 2018;112:212-219.
[35] Só BB, SILVEIRA FM, LLANTADA GS, et al. Effects of osteoporosis on alveolar bone repair after tooth extraction: A systematic review of preclinical studies. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;125:105054.
[36] LOTZ EM, COHEN DJ, SCHWARTZ Z, et al. Titanium implant surface properties enhance osseointegration in ovariectomy induced osteoporotic rats without pharmacologic intervention. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020;31(4):374-387.
[37] LIU W, ZHOU L, ZHOU C, et al. GDF11 decreases bone mass by stimulating osteoclastogenesis and inhibiting osteoblast differentiation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12794.
[38] SHAPIRO JR, BOSKEY AL, DOTY SB, et al. Zoledronic acid improves bone histomorphometry in a murine model of Rett syndrome. Bone. 2017; 99:1-7.
[39] OCHIAI H, OKADA S, SAITO A, et al. Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) expression by prolonged transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) administration suppresses osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(27):22654-22661.
[40] ALSALIH A, DAM A, LINDBERG P, et al. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws initiated by zoledronic acid and potential pathophysiology. Dent J (Basel). 2021; 9(8):85.
[41] MCGOWAN K, MCGOWAN T, IVANOVSKI S. Risk factors for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: A systematic review. Oral Dis. 2018; 24(4):527-536.
[42] YING G, BO L, YANJUN J, et al. Effect of a local, one time, low-dose injection of zoledronic acid on titanium implant osseointegration in ovariectomized rats. Arch Med Sci. 2016;12(5):941-949.
[43] GREY A, BOLLAND MJ, HORNE A, et al. Bone mineral density and bone turnover 10 years after a single 5 mg dose or two 5-yearly lower doses of zoledronate in osteopenic older women: an open-label extension of a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2022;37(1):3-11.
[44] OMIDVAR MH, SOLTANI-ZANGBAR MS, ZAMANI M, et al. The effect of osteoporotic and non-osteoporotic individuals’ T cell-derived exosomes on osteoblast cells’ bone remodeling related genes expression and alkaline phosphatase activity. BMC Res Notes. 2022;15(1):272.
[45] SHAIKHOMAR OA, ABDELGHNAY AH, QUTOB HMH. Diagnosis of low bone mass density: serological versus radiological methods. Int J Gen Med. 2022;15:5937-5945.
[46] 张萌萌, 张秀珍, 邓伟民, 等. 骨代谢生化指标临床应用专家共识(2020) [J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(6):781-796.
[47] QI S. Synergistic effects of genistein and zinc on bone metabolism and the femoral metaphyseal histomorphology in the ovariectomized rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018;183(2):288-295.
[48] MIZOKAMI A, KAWAKUBO-YASUKOCHI T, HIRATA M. Osteocalcin and its endocrine functions. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;132:1-8.
[49] YU C, LI L, XIE F, et al. LncRNA TUG1 sponges miR-204-5p to promote osteoblast differentiation through upregulating Runx2 in aortic valve calcification. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114(1): 68-179.
[50] YANG JX, XIE P, LI YS, et al. Osteoclast-derived miR-23a-5p-containing exosomes inhibit osteogenic differentiation by regulating Runx2. Cell Signal. 2020;70:109504.
[51] XU X, CHEN Y, TAN B, et al. Circular RNA circ_0011269 sponges miR-122 to regulate RUNX2 expression and promotes osteoporosis progression. J Cell Biochem. 2020; doi: 10.1002/jcb.29709.
[52] NAITO J, KAJI H, SOWA H, et al. Menin suppresses osteoblast differentiation by antagonizing the AP-1 factor, JunD. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(6):4785-4791.
[53] XU L, SHEN L, YU X, et al. Effects of irisin on osteoblast apoptosis and osteoporosis in postmenopausal osteoporosis rats through upregulating Nrf2 and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(2):1084-1090.
[54] SCHRODER K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010;140(6):821-832.
[55] MURAKAMI T, NAKAMINAMI Y, TAKAHATA Y, et al. Activation and function of NLRP3 inflammasome in bone and joint-related diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5365.
[56] CHENG C, CHEN L, CHEN K. Osteoporosis due to hormone imbalance: an overview of the effects of estrogen deficiency and glucocorticoid overuse on bone turnover. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1376.
[57] PINGALI U, NUTALAPATI C. Shilajit extract reduces oxidative stress, inflammation, and bone loss to dose-dependently preserve bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteopenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytomedicine. 2022;105:154334.
[58] XU L, ZHANG L, WANG Z, et al. Melatonin suppresses estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis and promotes osteoblastogenesis by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;103(4): 400-410.
[59] TAO H, LI W, ZHANG W, et al. Urolithin a suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and postmenopausal osteoporosis by, suppresses inflammation and downstream NF-κB activated pyroptosis pathways. Pharmacol Res. 2021;174:105967.
[60] AN Y, ZHANG H, WANG C, et al. Activation of ROS/MAPKs/NF-κB/NLRP3 and inhibition of efferocytosis in osteoclast-mediated diabetic osteoporosis. Faseb J. 2019;33(11):12515-12527.
[61] CHEN L, CHENG S, SUN K, et al. Changes in macrophage and inflammatory cytokine expressions during fracture healing in an ovariectomized mice model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):494. |