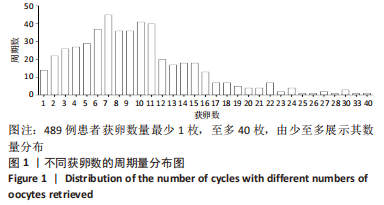
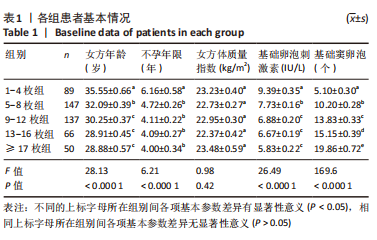
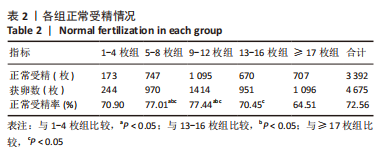
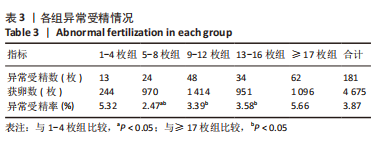
[1] BRIGGS R, KOVACS G, MACLACHLAN V, et al. Can you ever collect too many oocytes? Hum Reprod. 2015;30(1):81-87.
[2] ZHUANG LL, HAO CF, ZHANG N, et al. Effects of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Autoantibodies on Pregnancy Outcome After in Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer. The Journal of Reproductive Medicine. 2017;62(4):391-396.
[3] 梁晓燕,李轶,杜静,等.反复控制性卵巢刺激对卵巢功能状态的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2008,29(2):186-189.
[4] BLONDIN P, COENEN K, GUILBAULT LA, et al. Superovulation can reduce the developmental competence of bovine embryos. Theriogenology. 1996;46(7):1191-1203.
[5] SUNKARA SK, RITTENBERG V, RAINE-FENNING N, et al. Association between the number of eggs and live birth in IVF treatment: an analysis of 400 135 treatment cycles. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(7):1768-1774.
[6] 孙青,王秀霞,张松英,等.胚胎实验室关键指标质控专家共识[J].生殖医学杂志,2018,27(9):836-851.
[7] 黄国宁,孙海翔.体外受精-胚胎移植实验室技术[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012:240-243.
[8] OLIVENNES F, HAZOUT A, LELAIDIER C, et al. Four indications for embryo transfer at the blastocyst stage. Hum Reprod. 1994;9(12): 2367-2373.
[9] GARDNER DK, LANE M, STEVENS J, et al. Blastocyst score affects implantation and pregnancy outcome: towards a single blastocyst transfer. Fertil Steril. 2000;73(6):1155-1158.
[10] ZACÀ C, BAZZOCCHI A, PENNETTA F, et al. Cumulative live birth rate in freeze-all cycles is comparable to that of a conventional embryo transfer policy at the cleavage stage but superior at the blastocyst stage. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(4):703-709.
[11] SHAPIRO BS, DANESHMAND ST, GARNER FC,et al. Embryo cryopreservation rescues cycles with premature luteinization. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(2):636-641.
[12] BLOCKEEL C, DRAKOPOULOS P, SANTOS-RIBEIRO S, et al. A fresh look at the freeze-all protocol: a SWOT analysis. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(3):491-497.
[13] KOK JD, LOOMAN CW, WEIMA SM, et al. A high number of oocytes obtained after ovarian hyperstimulation for in vitro fertilization or intracytoplasmic sperm injection is not associated with decreased pregnancy outcome. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(4):918-924.
[14] JI J, LIU Y, TONG XH, et al. The optimum number of oocytes in IVF treatment: an analysis of 2455 cycles in China. Hum Reprod. 2013; 28(10):2728-2734.
[15] CHEN YH, WANG Q, ZHANG YN, et al. Cumulative live birth and surplus embryo incidence after frozen-thaw cycles in PCOS: how many oocytes do we need? J Assist Reprod Genet. 2017;34(9):1153-1159.
[16] VAN DER GAAST MH, EIJKEMANS MJ, VAN DER NET JB, et al. Optimum number of oocytes for a successful first IVF treatment cycle. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;13(4):476-480.
[17] MAGNUSSON Å, KÄLLEN K, THURIN-KJELLBERG A, et al. The number of oocytes retrieved during IVF: a balance between efficacy and safety. Hum Reprod. 2018;33(1):58-64.
[18] LAW YJ, ZHANG N, VENETIS CA, et al. The number of oocytes associated with maximum cumulative live birth rates per aspiration depends on female age: a population study of 221 221 treatment cycles. Hum Reprod. 2019;34(9):1778-1787.
[19] CASCALES A, LLEDÓ B, ORTIZ JA, et al. Effect of ovarian stimulation on embryo aneuploidy and mosaicism rate. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2021;67(1):42-49.
[20] HUANG J, LI T, DING CH, et al. Insufficient histone-3 lysine-9 deacetylation in human oocytes matured in vitro is associated with aberrant meiosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;97(1):178-184.e3.
[21] LOBACH VN, CASALECHI M, DELA CRUZ C, et al. Caspase-3 gene expression in human luteinized granulosa cells is inversely correlated with the number of oocytes retrieved after controlled ovarian stimulation. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2019;22(1):33-38.
[22] MCCULLOH DH, ALIKANI M, NORIAN J, et al. Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) parameters associated with euploidy rates in donor oocytes. Eur J Med Genet. 2019;62(8):103707.
[23] BAART EB, MARTINI E, EIJKEMANS MJ, et al. Milder ovarian stimulation for in-vitro fertilization reduces aneuploidy in the human preimplantation embryo: a randomized controlled trial. Hum Reprod. 2007;22(4):980-988.
[24] MILLIKEN EL, LOZADA KL, JOHNSON E, et al. Ovarian hyperstimulation induces centrosome amplification and aneuploid mammary tumors independently of alterations in p53 in a transgenic mouse model of breast cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27(12):1759-1766.
[25] SALDEEN P, KÄLLEN K, SUNDSTRÖM P. The probability of successful IVF outcome after poor ovarian response. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2007;86(4):457-461.
[26] 路红琴,何玉洁.长方案IVF/ICSI周期中女性年龄和获卵数对妊娠结局的影响[J].生殖医学杂志,2019,28(9):1017-1026.
[27] VERBERG MF, EIJKEMANS MJ, MACKLON NS, et al. The clinical significance of the retrieval of a low number of oocytes following mild ovarian stimulation for IVF: a meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2009;15(1):5-12.
[28] FIGUEIRA RDE C, BRAGA DP, NICHI M, et al. Poor ovarian response in patients younger than 35 years: is it also a qualitative decline in ovarian function? Hum Fertil (Camb). 2009;12(3):160-165. |