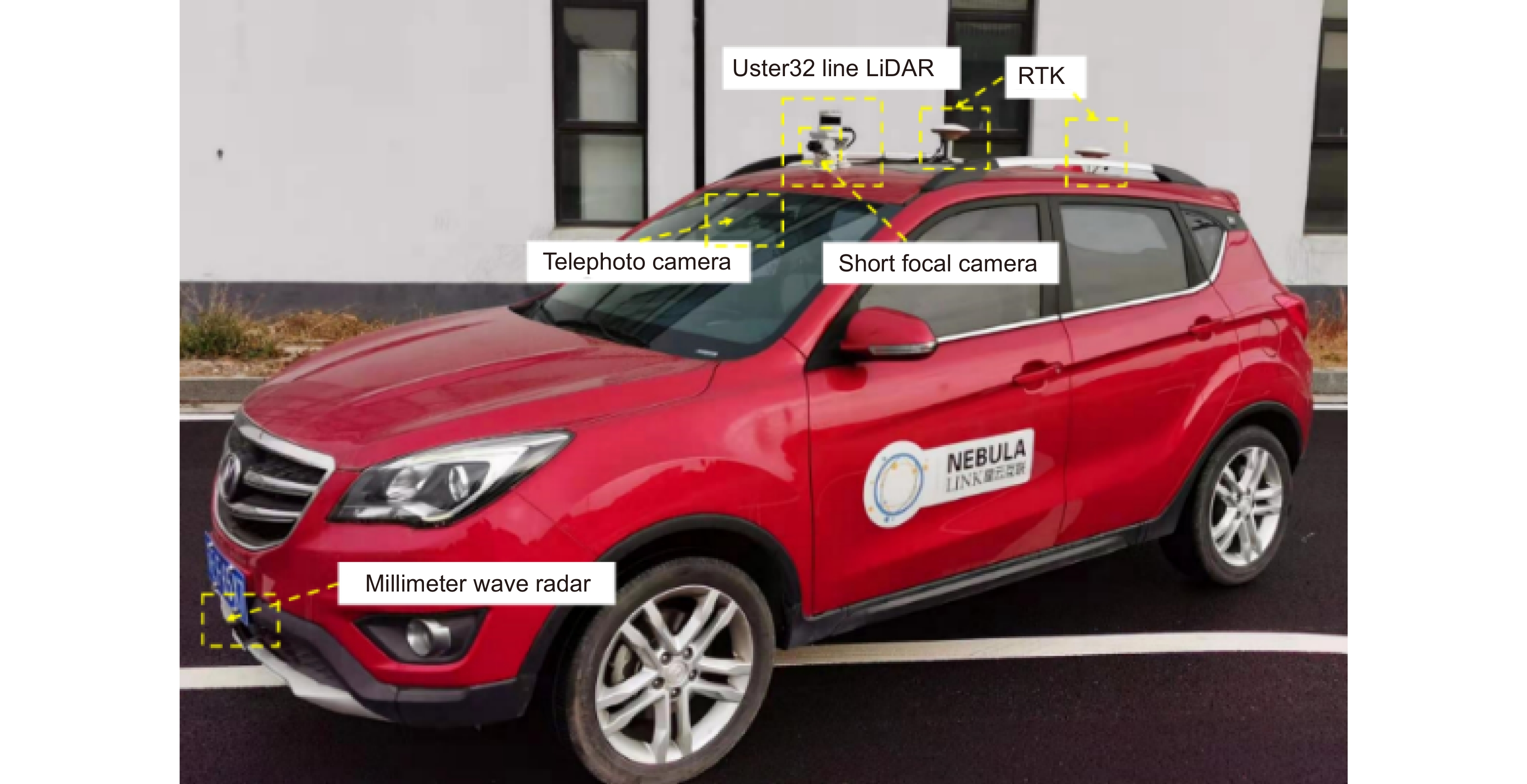
-
摘要:
针对自动驾驶目标跟踪领域中,目标遮挡引起特征点损失,从而导致丢失跟踪目标的问题,本文提出了一种融合空间掩膜预测与点云投影的多目标跟踪算法,以减少遮挡产生的不利影响。首先,通过实例分割掩膜提取模型处理时序图像数据,获得基掩膜数据。其次,将获取掩膜数据输入跟踪器,通过预测模型获取后续序列图像掩膜输出,并利用验证器进行对比分析,以获得准确的目标跟踪输出。最后,将获取的二维目标跟踪数据投影到对应的点云图像中,获得最终的三维目标跟踪点云图像。本文在多个数据集上进行仿真实验,实验结果表明本文算法的跟踪效果优于其他同类算法。此外,在实际道路上进行测试,对于车辆的检测精度达到81.63%,验证了本文算法也可以满足实际路况下目标跟踪的实时性需求。
Abstract:In the field of automatic driving target tracking, there is a problem that the target occlusion will cause the loss of feature points, resulting in the loss of tracking targets. In this paper, a multi-target tracking algorithm combining spatial mask prediction and point cloud projection is proposed to reduce the adverse effects of the occlusion. Firstly, the temporal image data is processed by an example segmentation mask extraction model, and the basic mask data is obtained. Secondly, the obtained mask data is input into the tracker, the mask output of subsequent sequence images is obtained through the prediction model, and the verifier is used for a comparative analysis to obtain an accurate target tracking output. Finally, the obtained 2D target tracking data is projected into the corresponding point cloud image to obtain the final 3D target tracking point cloud image. In this paper, simulation experiments are carried out on multiple data sets. The experimental results show that the tracking effect of this algorithm is better than other similar algorithms. In addition, this paper is also tested on the actual road, and the vehicle detection accuracy reaches 81.63%. The results verify that the algorithm can also meet the real-time requirements of target tracking under the actual road conditions.
-
Overview: In the field of computer vision, target tracking plays a key role in automatic driving. In the field of automatic driving target tracking, there is the problem of feature point loss caused by the target occlusion, which will lead to the loss of tracking target. In this paper, a multi-target tracking algorithm combining spatial mask prediction and point cloud projection is proposed to reduce the adverse effects of the occlusion.
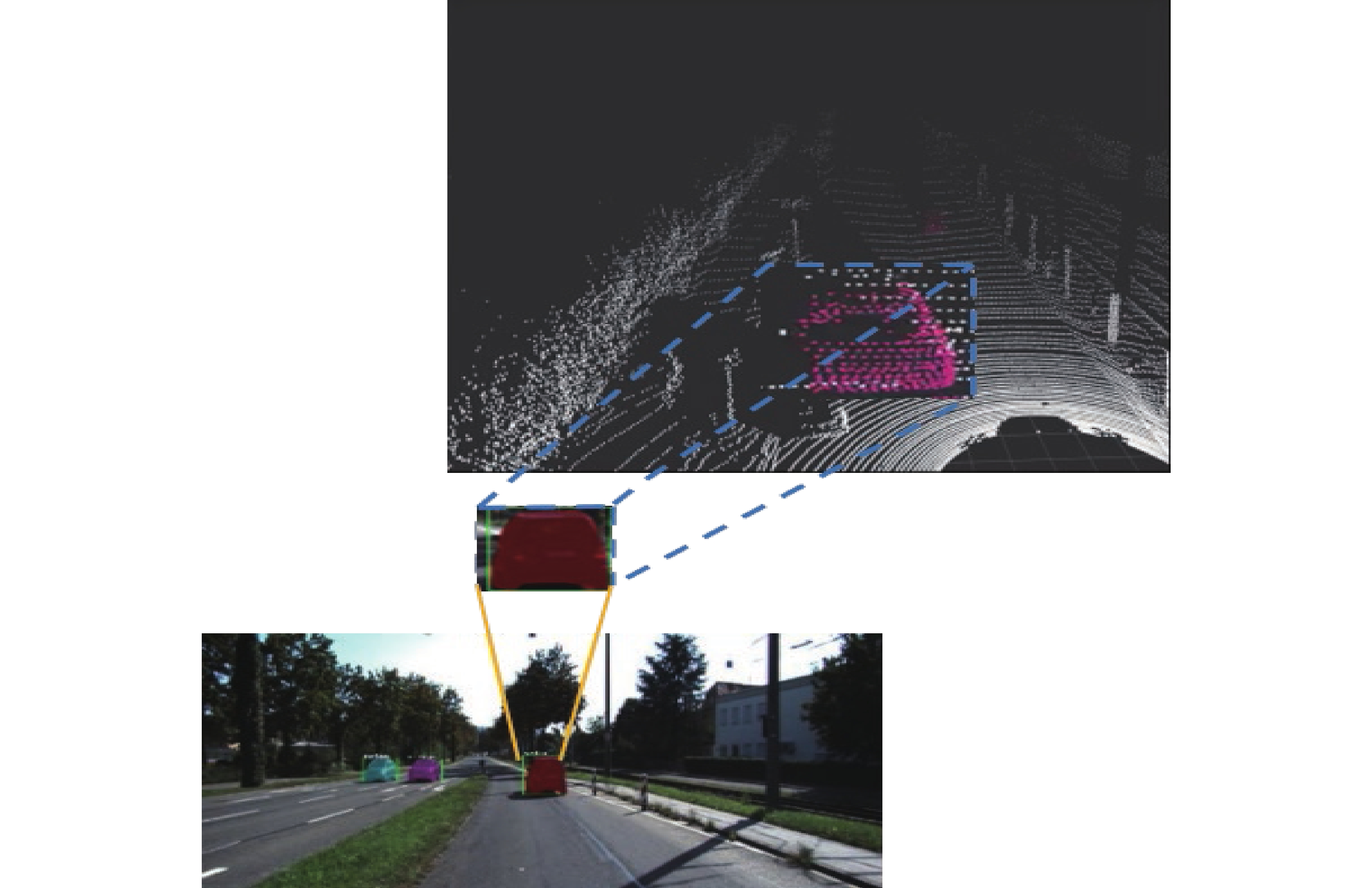
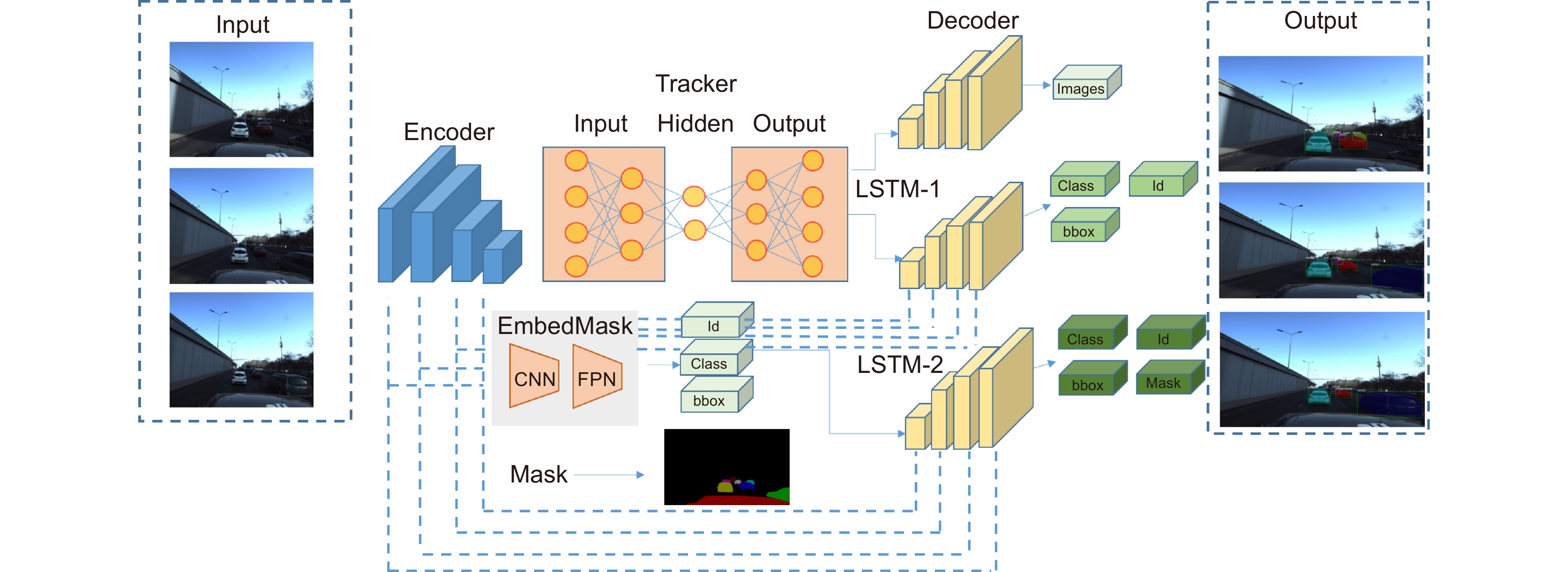
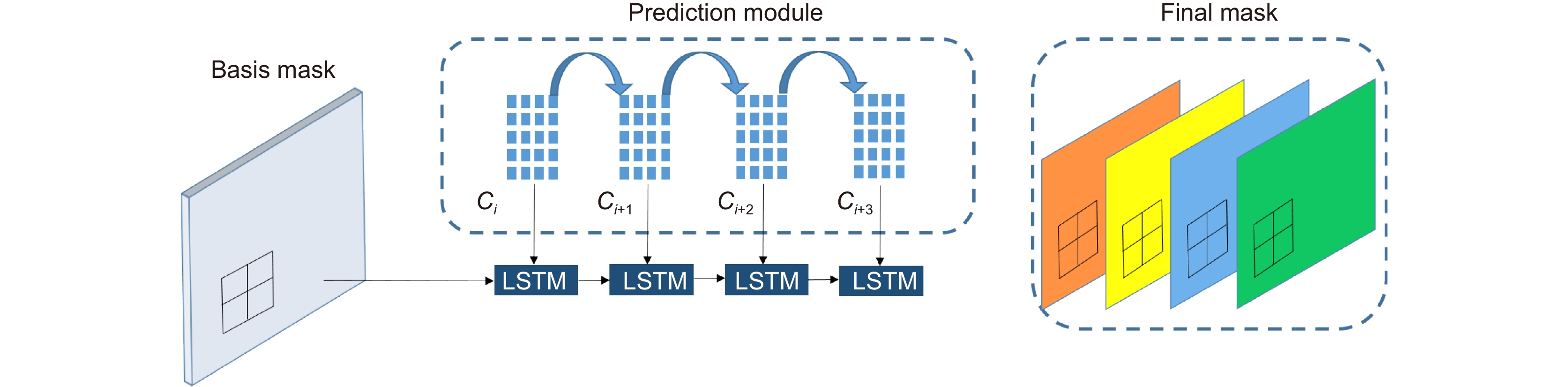
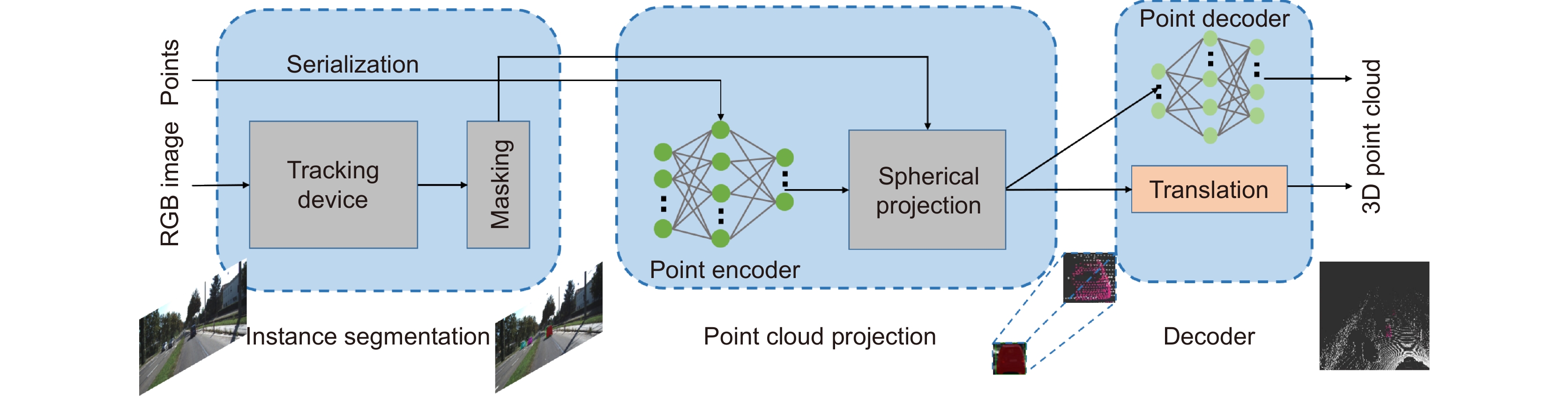
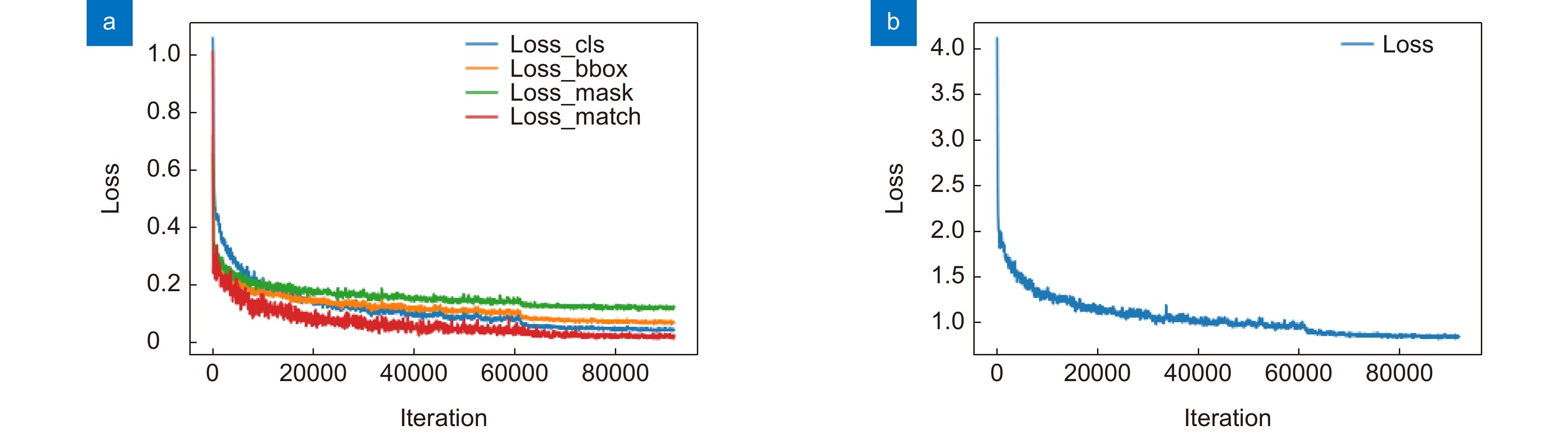
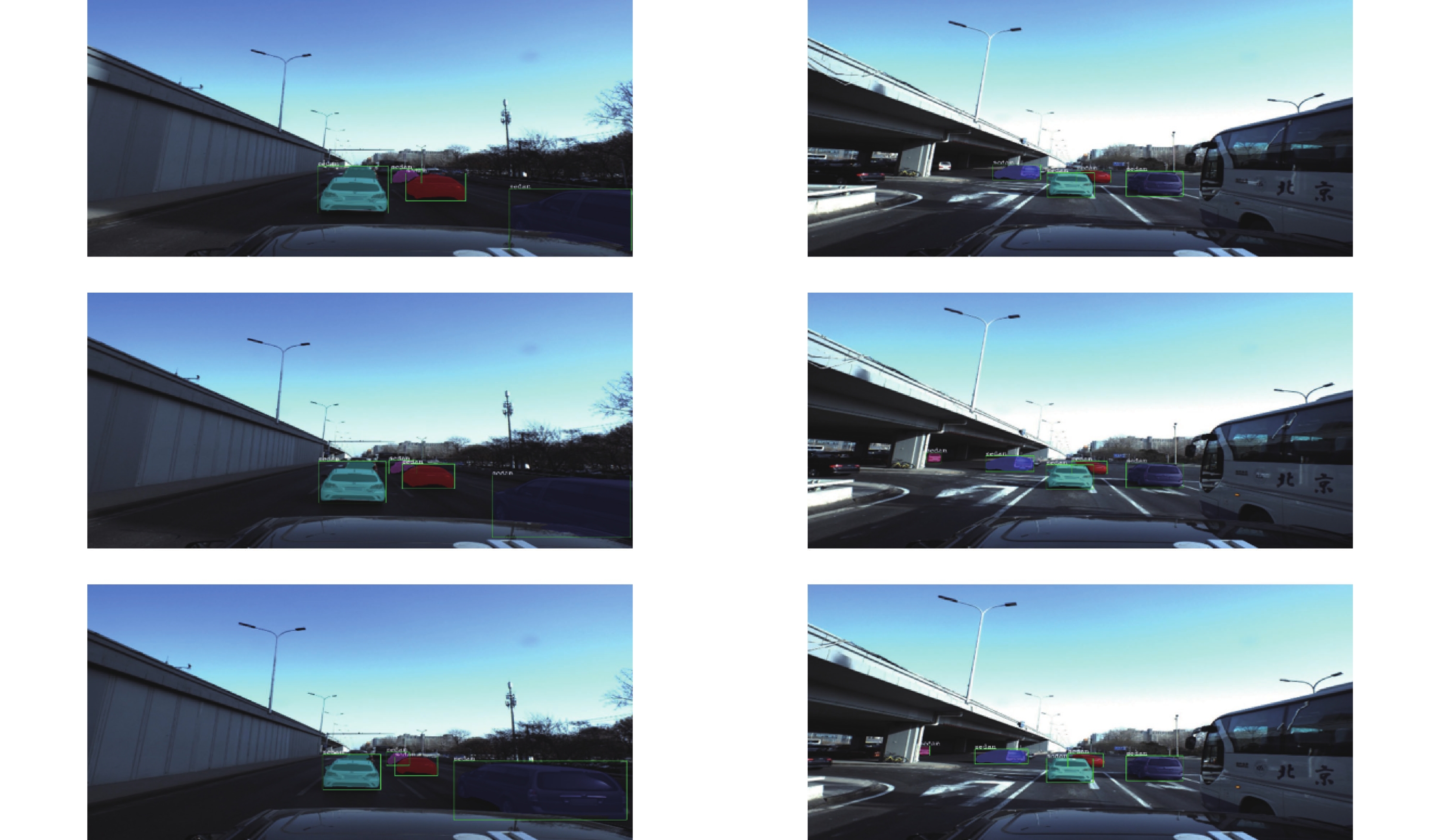
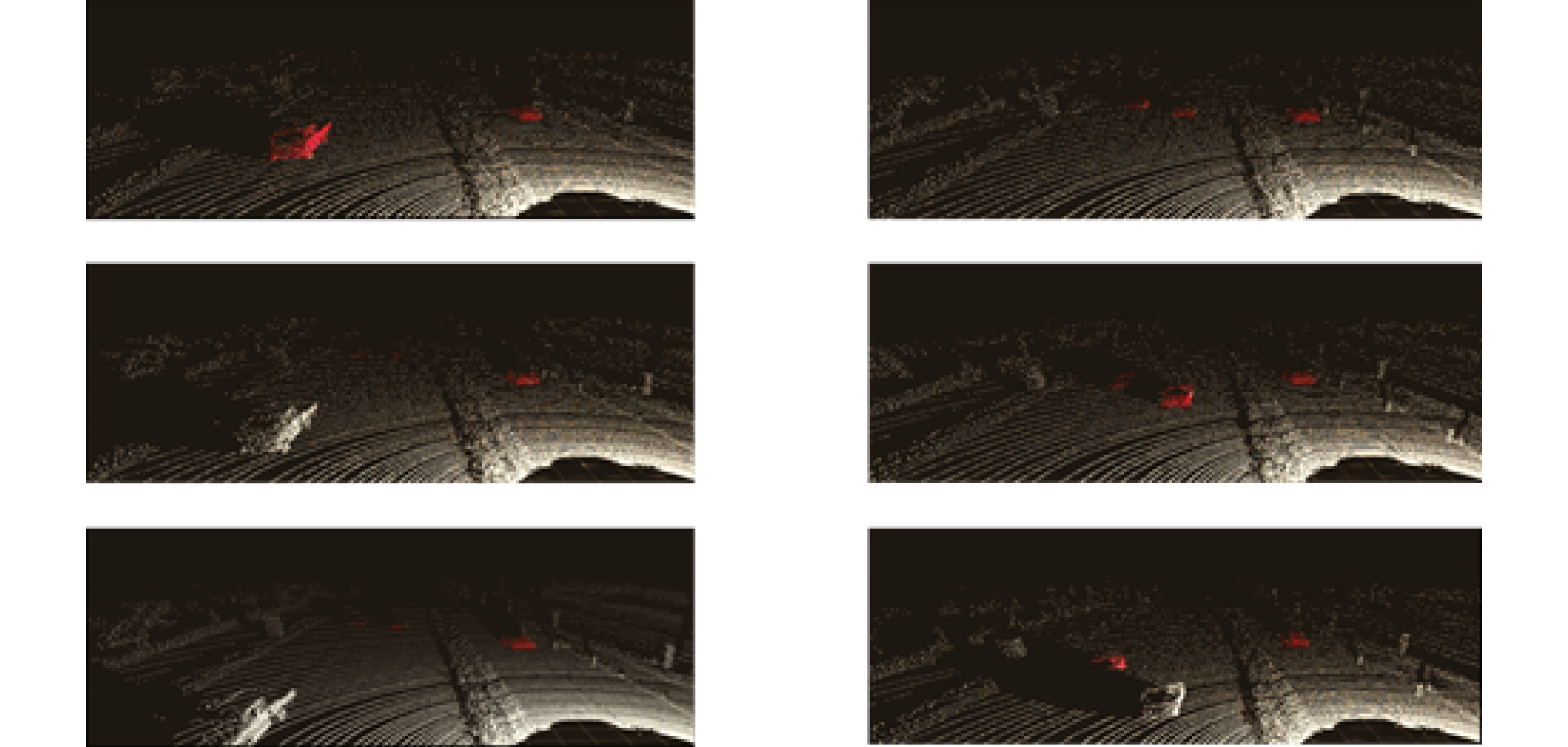
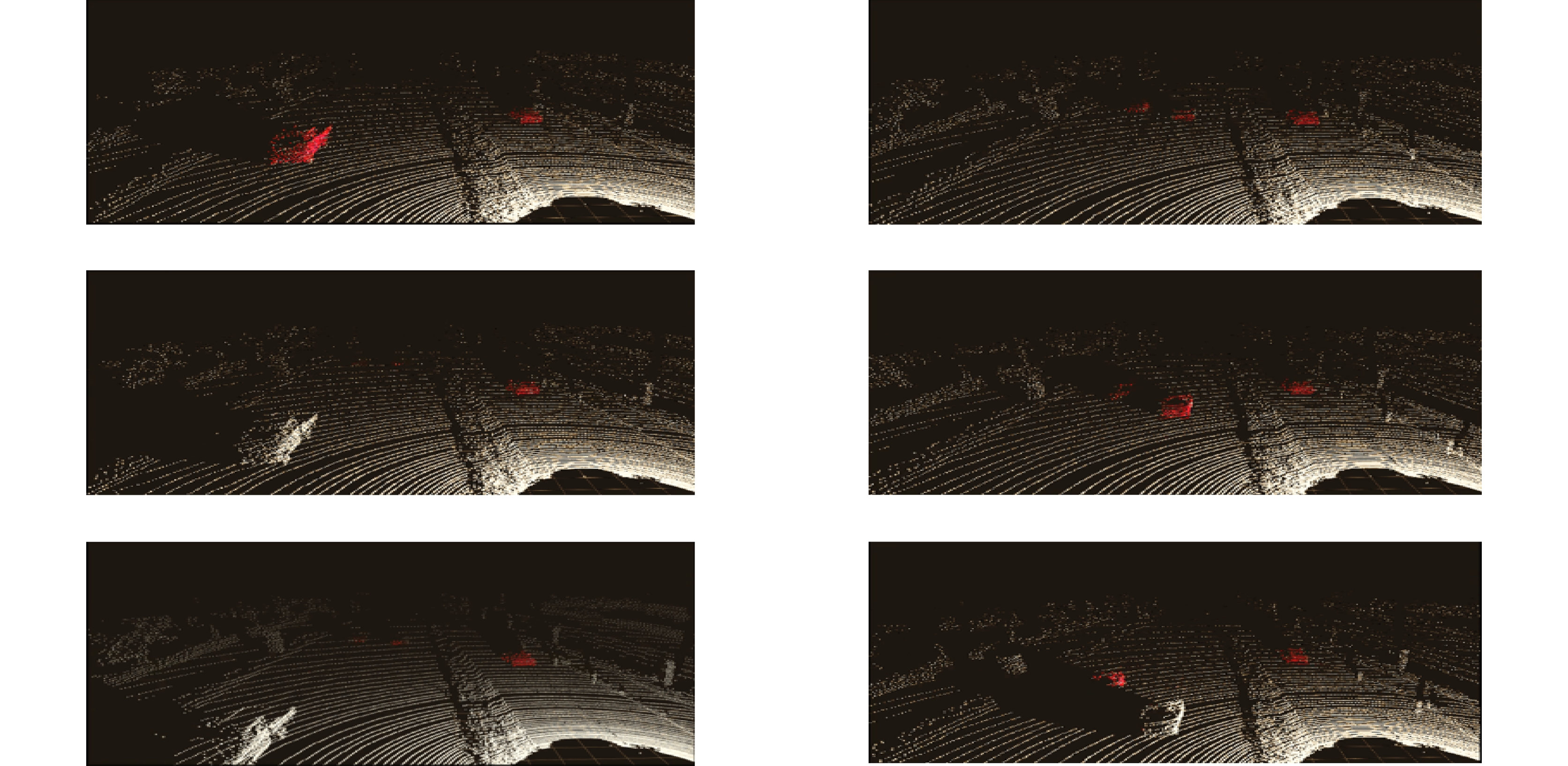
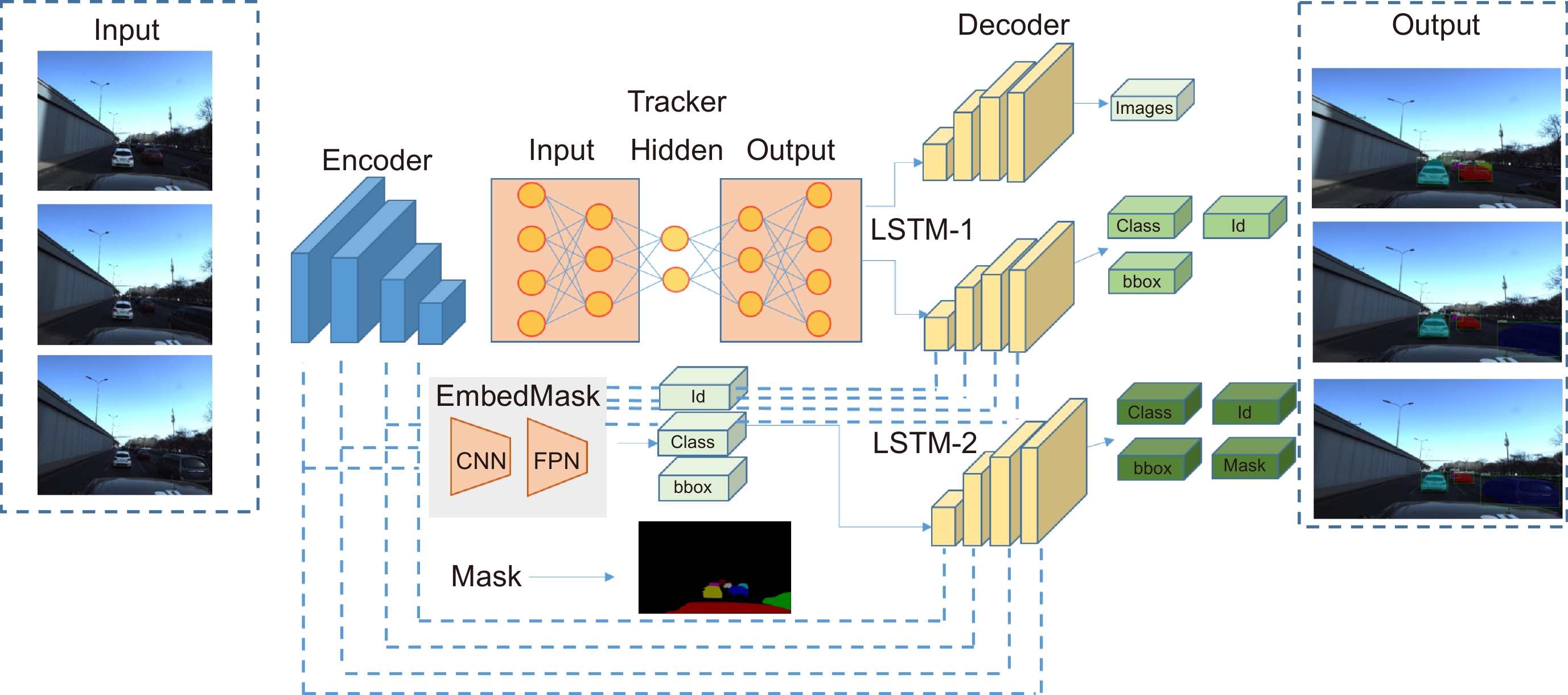
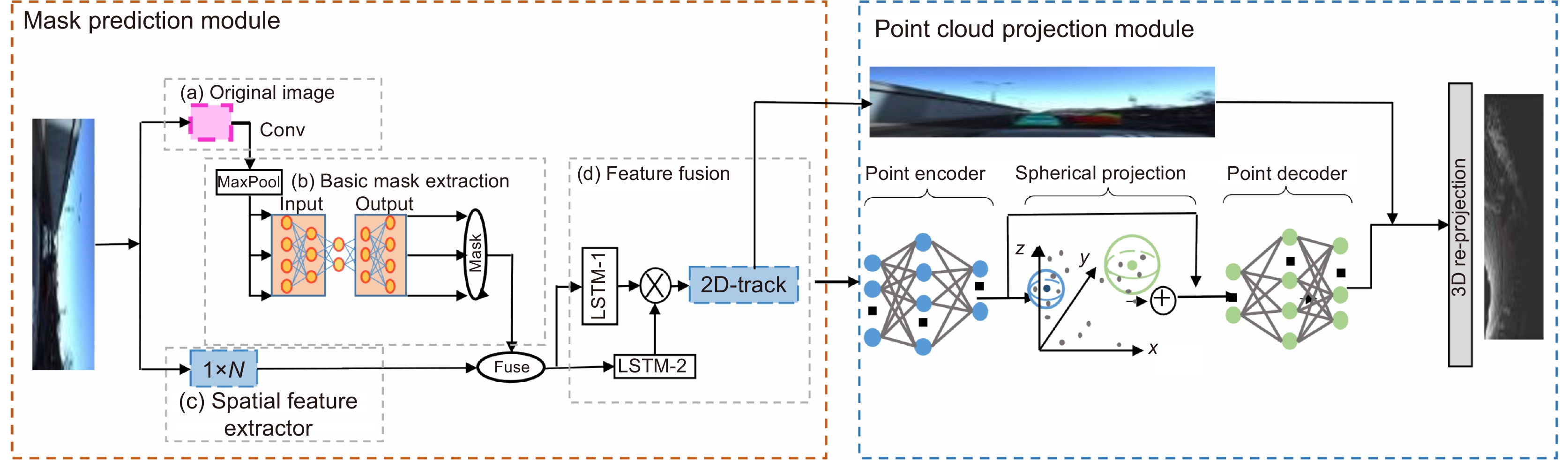
In this paper, the first mask input is added in front of the timing tracker to improve the accuracy of the initial target position. Secondly, the tracker dominated by a convolutional neural network is used for tracking, and the individual instance segmentation of each frame is optimized to increase the speed of the tracker, resulting in an improvement of the real-time effect. Finally, a verification layer is set to verify and compare the extracted sample mask output with the corresponding image output of the tracker, so as to reduce the tracking loss caused by the careless detection. After a two-dimensional video processing, the mask data is obtained, matched with the point cloud in the three-dimensional radar by the method of point cloud projection, and is projected into the three-dimensional point cloud to obtain the three-dimensional target tracking. The algorithm has three main contributions. Firstly, this paper takes the convolutional neural network target detection module as the basic module, does not directly use the example segmentation module for tracking, and extracts the mask of the first frame image. The mask information of the subsequent frame number can be extracted through the comparison and verification of the extraction of the prediction mask and the verification frame mask, which not only ensures the correct mask prediction, but also reduces the waste of a lot of computing power for extracting and tracking the mask information of each frame of the image. Secondly, this paper adds a gradient loss function of the prediction module to increase the control of the accuracy of the prediction mask and improve the correction ability of the algorithm for the prediction errors. Finally, this paper does not need to further process the point cloud image, but compares and matches the two-dimensional camera data with the three-dimensional point cloud radar data, and projects the two-dimensional tracked target mask data onto the corresponding point cloud image, so as to reduce the computational power of the algorithm and improve the real-time performance of the algorithm.
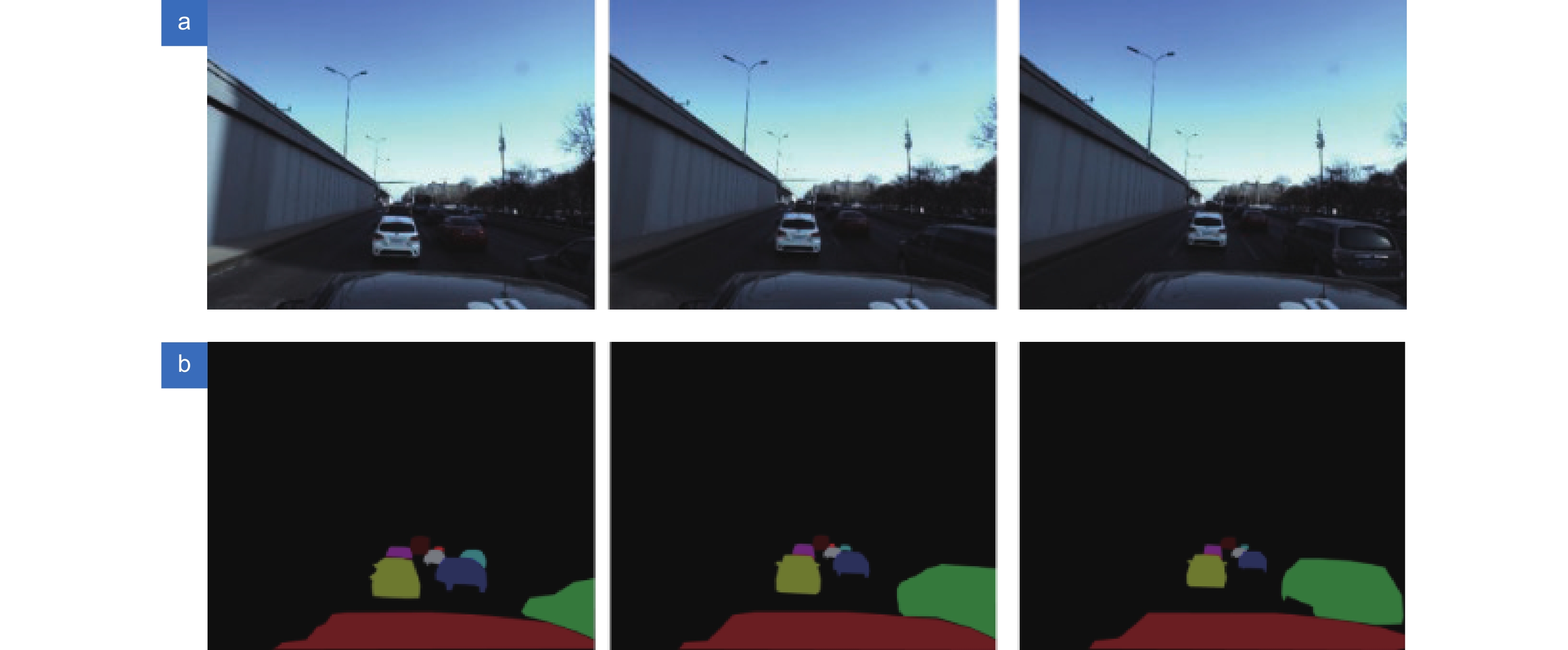
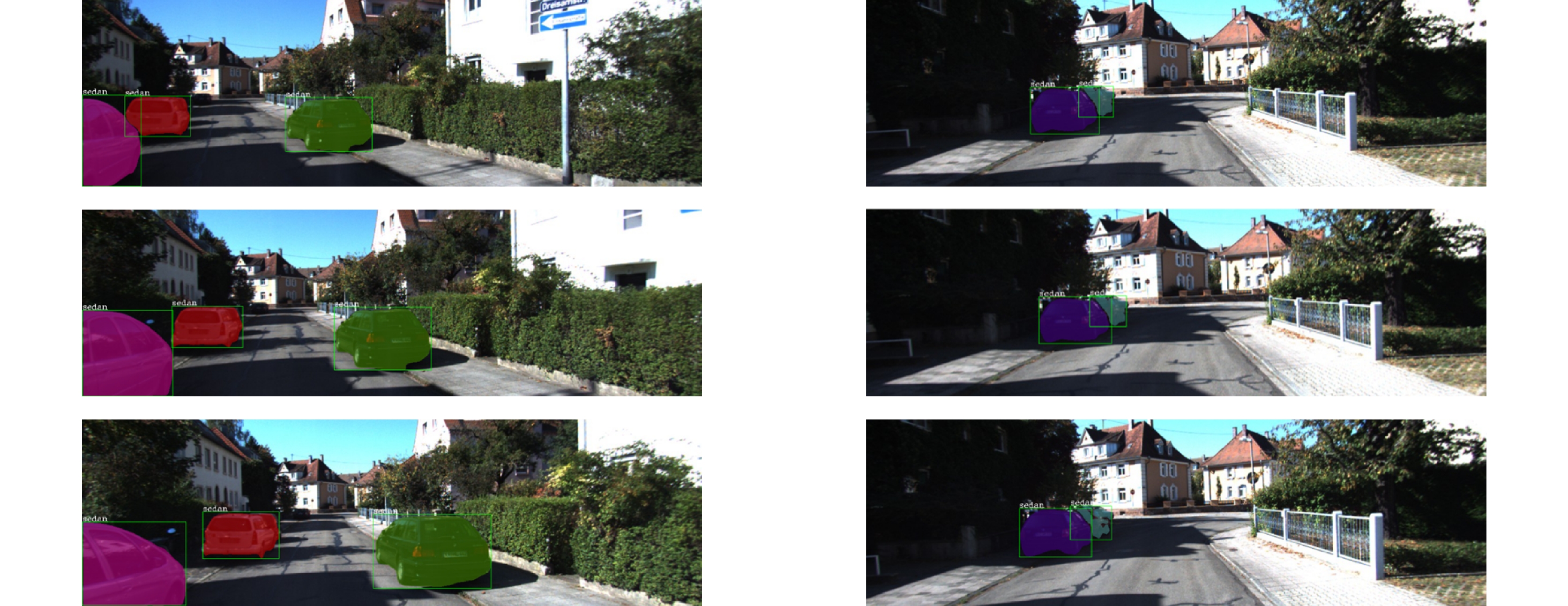
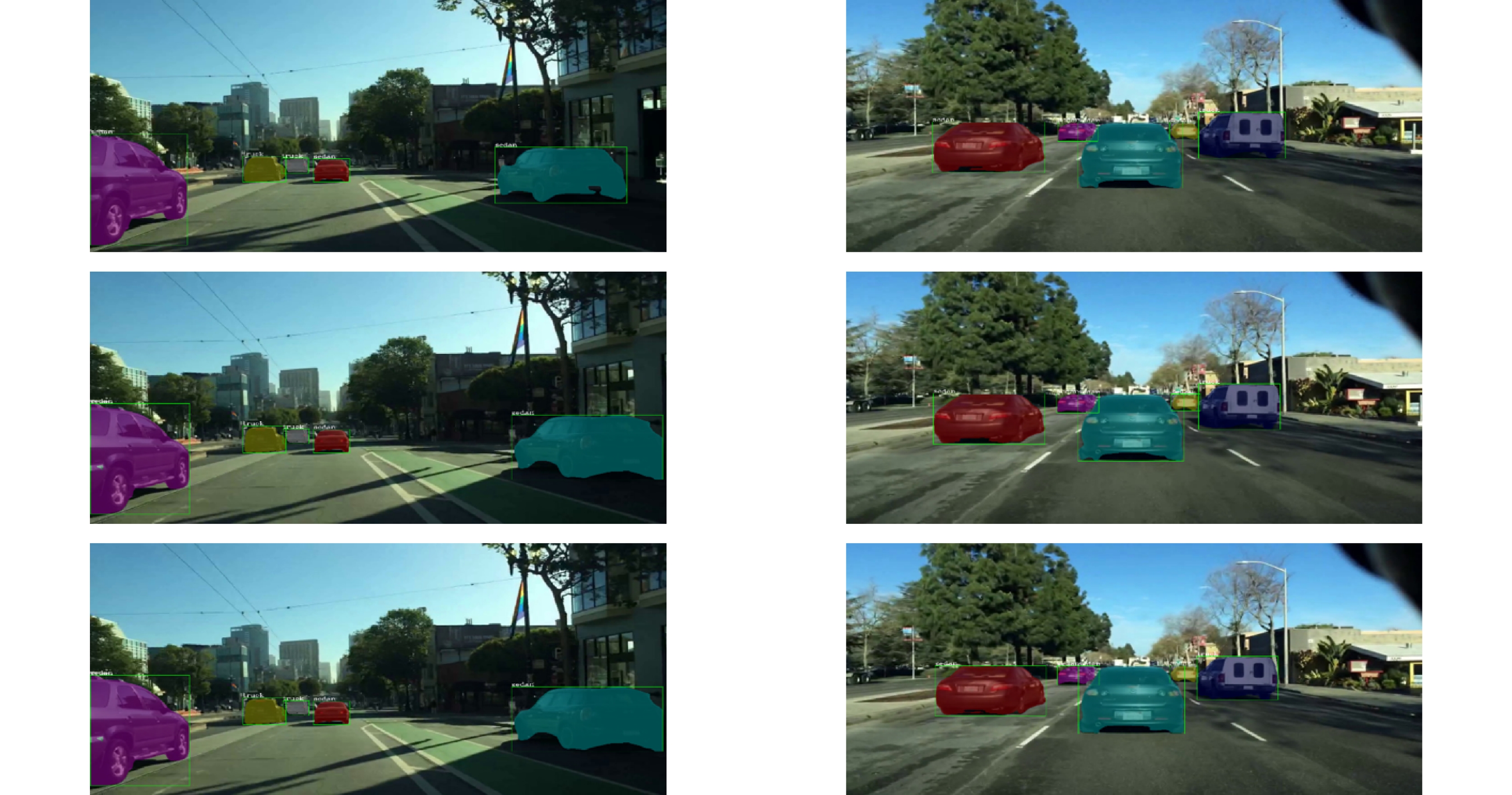
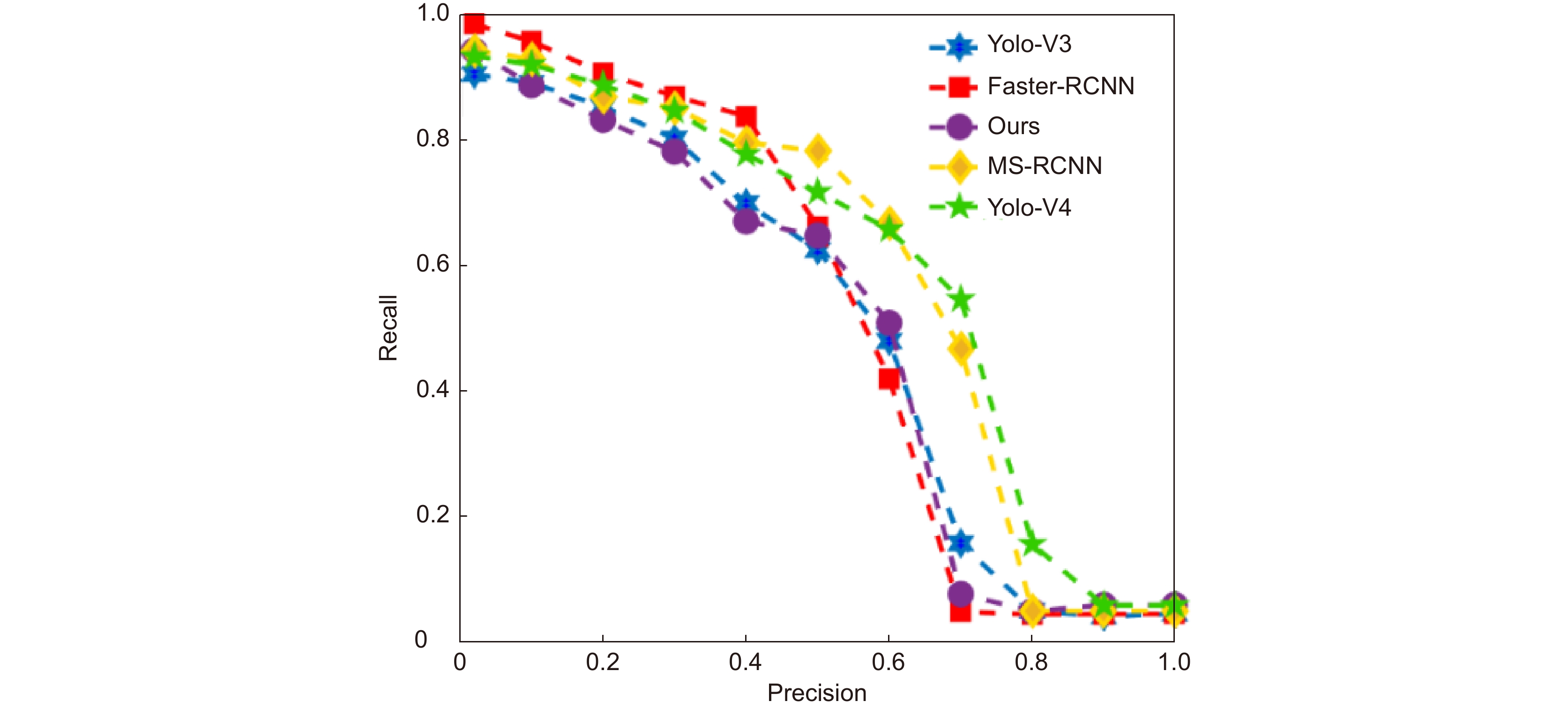
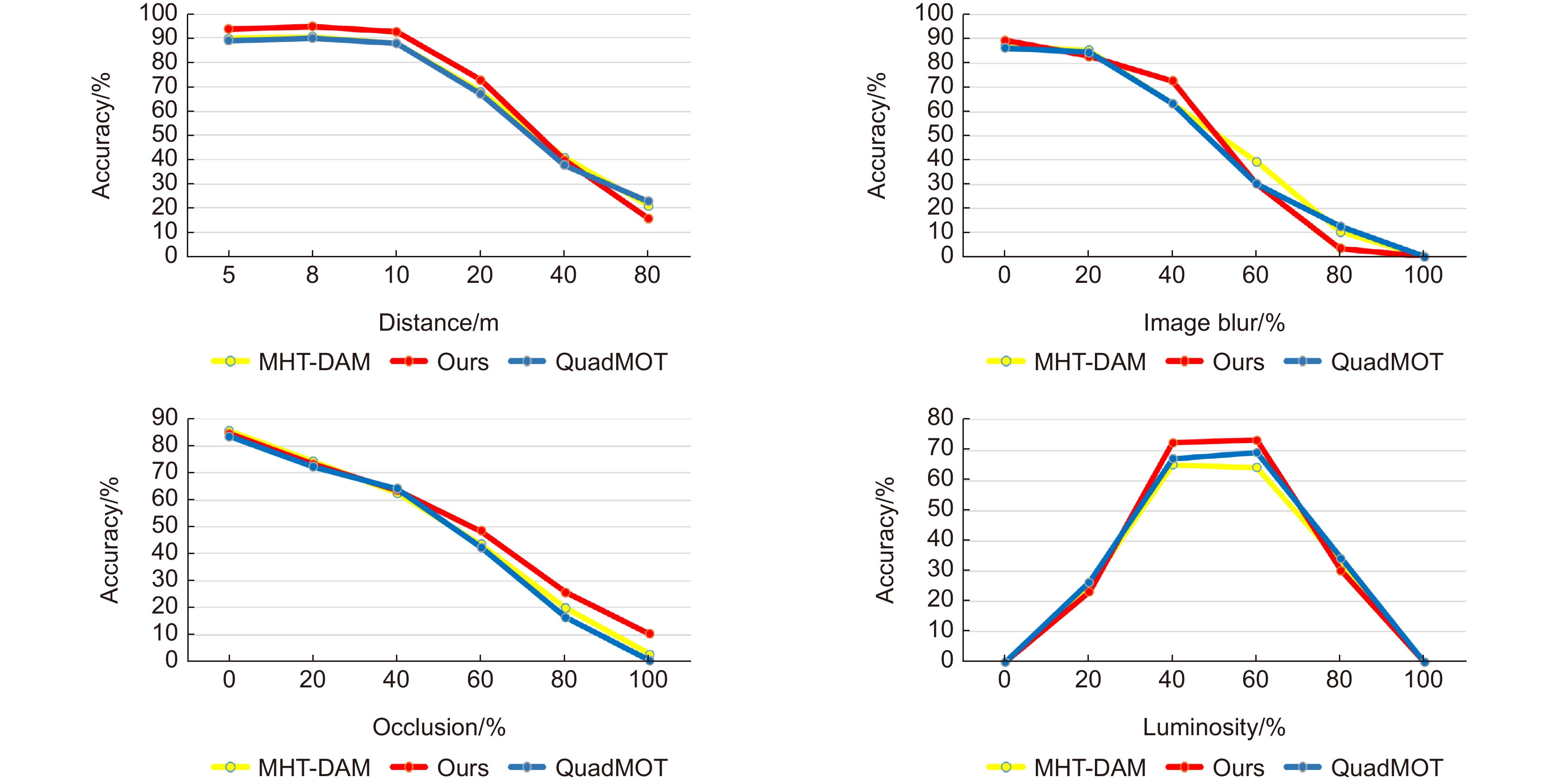
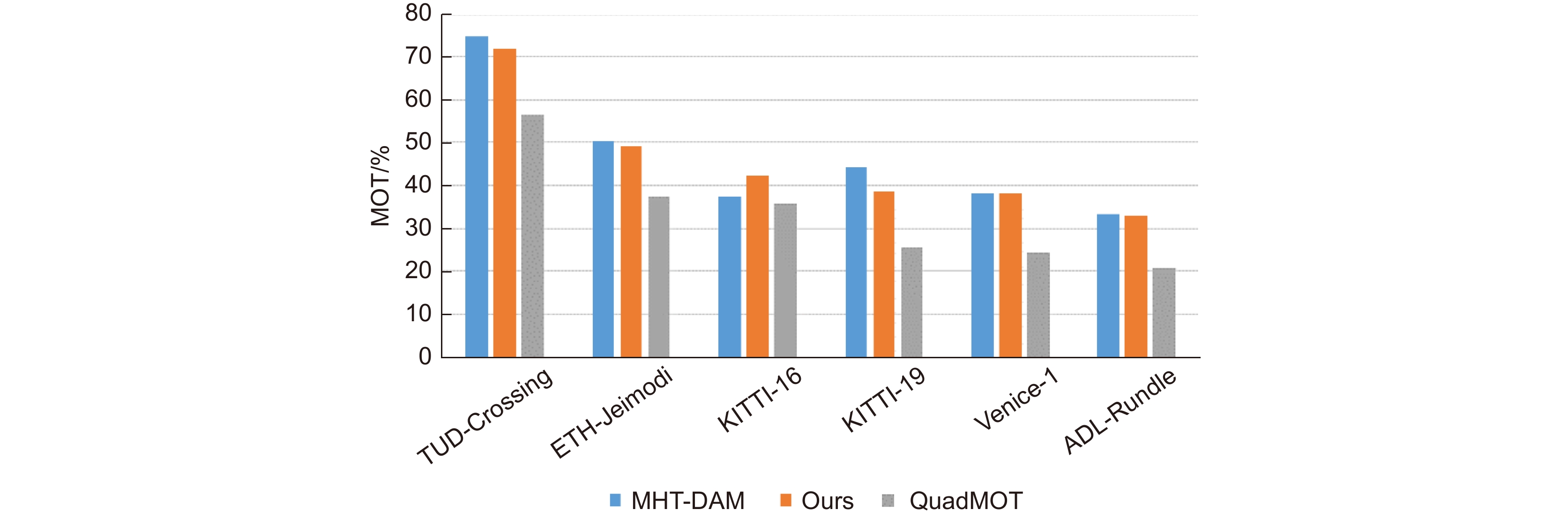
This paper is verified on the Apollo data set. The continuous road live screenshots are extracted from the data set to obtain the required set of time-series pictures, and the targets in the images are detected and tracked. Finally, the experiments show that the algorithm in this paper has an obvious effect on solving the occlusion problem. This paper has also been tested on the actual road, and the effect of medium and long-distance vehicle detection is good. The experiment shows that the algorithm can meet the real-time detection requirements under the actual road conditions.
-

-
表 1 本文与其他算法对比
Table 1. This algorithm is compared with other algorithms
Method Backbone ms rc Epochs AP AP50 AP75 APS APM APL APbb fps Mask R-CNN [19] R-50-FPN 12 34.6 56.5 36.6 15.3 36.3 49.7 38.0 8.6 Mask R-CNN R-101-FPN 12 36.2 58.6 38.5 16.4 38.4 52.0 40.1 8.1 Mask R-CNN R-101-FPN √ 36 38.1 60.9 40.7 18.4 40.2 53.4 42.6 8.7 YOLACT-700 [21] R-101-FPN √ √ 48 31.2 50.6 32.8 12.1 33.3 47.1 - 23.6 Ours R-50-FPN 12 33.6 54.5 35.4 15.1 35.9 47.3 38.2 16.7 Ours R-101-FPN √ 36 37.7 59.1 40.3 17.9 40.4 53.0 42.5 13.7 Ours-600 R-101-FPN √ 36 35.2 55.9 37.3 12.4 37.3 54.9 40.2 21.7 -
[1] Marvasti-Zadeh S M, Cheng L, Ghanei-Yakhdan H, et al. Deep learning for visual tracking: a comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst, 2022, 23(5): 3943−3968. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3046478
[2] Chiu H K, Li J, Ambruş R, et al. Probabilistic 3D multi-modal, multi-object tracking for autonomous driving[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2021: 14227–14233.
[3] Wu H, Han W K, Wen C L, et al. 3D multi-object tracking in point clouds based on prediction confidence-guided data association[J]. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst, 2022, 23(6): 5668−5677. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3055616
[4] Tao C B, He H T, Xu F L, et al. Stereo priori RCNN based car detection on point level for autonomous driving[J]. Knowl Based Syst, 2021, 229: 107346. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107346
[5] 吕晨, 程德强, 寇旗旗, 等. 基于YOLOv3和ASMS的目标跟踪算法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(2): 200175. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200175
Lv C, Cheng D Q, Kou Q Q, et al. Target tracking algorithm based on YOLOv3 and ASMS[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(2): 200175. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200175
[6] 鄂贵, 王永雄. 基于R-FCN框架的多候选关联在线多目标跟踪[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(1): 190136. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190136
E G, Wang Y X. Multi-candidate association online multi-target tracking based on R-FCN framework[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(1): 190136. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190136
[7] 金立生, 华强, 郭柏苍, 等. 基于优化DeepSort的前方车辆多目标跟踪[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2021, 55(6): 1056−1064. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008.973X.2021.06.005
Jin L S, Hua Q, Guo B C, et al. Multi-target tracking of vehicles based on optimized DeepSort[J]. J Zhejiang Univ (Eng Sci), 2021, 55(6): 1056−1064. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008.973X.2021.06.005
[8] Jiang M X, Deng C, Shan J S, et al. Hierarchical multi-modal fusion FCN with attention model for RGB-D tracking[J]. Inf Fusion, 2019, 50: 1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.014
[9] Muller N, Wong Y S, Mitra N J, et al. Seeing behind objects for 3D multi-object tracking in RGB-D sequences[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 6067–6076.
[10] He J W, Huang Z H, Wang N Y, et al. Learnable graph matching: Incorporating graph partitioning with deep feature learning for multiple object tracking[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 5295–5305.
[11] Zhan X H, Pan X G, Dai B, et al. Self-supervised scene de-occlusion[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 3783–3791.
[12] Yuan D, Chang X J, Huang P Y, et al. Self-supervised deep correlation tracking[J]. IEEE Trans Image Proc, 2021, 30: 976−985. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3037518
[13] Luo C X, Yang X D, Yuille A. Self-supervised pillar motion learning for autonomous driving[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 3182–3191.
[14] Han T D, Xie W D, Zisserman A. Video representation learning by dense predictive coding[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, 2019: 1483–1492.
[15] Wang Q, Zheng Y, Pan P, et al. Multiple object tracking with correlation learning[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 3875–3885.
[16] Tian Z, Shen C H, Chen H, et al. FCOS: fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 9626–9635.
[17] Ying H, Huang Z J, Liu S, et al. EmbedMask: embedding coupling for one-stage instance segmentation[Z]. arXiv: 1912.01954, 2019. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1912.01954.
[18] 曹春林, 陶重犇, 李华一, 等. 实时实例分割的深度轮廓段落匹配算法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(11): 210245. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210245
Cao C L, Tao C B, Li H Y, et al. Deep contour fragment matching algorithm for real-time instance segmentation[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2021, 48(11): 210245. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.210245
[19] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2980–2988.
[20] Kim C, Li F X, Rehg J M. Multi-object tracking with neural gating using bilinear LSTM[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 208–224.
[21] Bolya D, Zhou C, Xiao F Y, et al. YOLACT: real-time instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 9156–9165.
[22] Redmon J, Farhadi A. Yolov3: an incremental improvement[Z]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.02767.
[23] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015: 91–99.
[24] Tu Z G, Cao J, Li Y K, et al. MSR-CNN: applying motion salient region based descriptors for action recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2016: 3524–3529.
[25] Yang L J, Fan Y C, Xu N. Video instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 5187–5196.
[26] Voigtlaender P, Krause M, Osep A, et al. MOTS: multi-object tracking and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 7934–7943.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: