Abstract
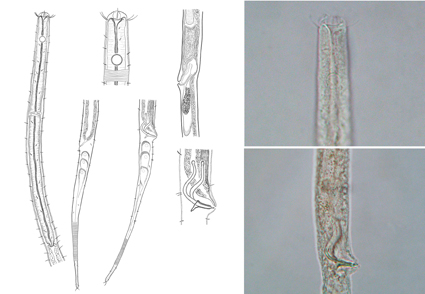
A new ice-associated species of Xyalidae family, Daptonema gelida sp. n., is described from the first-year fast sea ice of the Ermolinskaya Inlet, White Sea, Russia. The new species of Daptonema is a morphologically distinct species from other species of the genus. Daptonema gelida sp. n. is characterized by (1) elongated, slender body, (2) short, evenly distributed throughout the body somatic setae, (3) circular amphideal fovea, (4) thin and strongly curved, L-shaped spicules with round-shaped manubrium, (5) gubernaculum with short dorsal-caudal apophysis by triangular-shaped outline, (6) post-vulval uterine sac present, and (7) two short terminal setae. We barcoded partial 18S rRNA gene sequences from the new sympagic species. Phylogenetic reconstructions showed that the specimen of Daptonema gelida sp. n. formed a distinct lineage with high support among other Daptonema species and was genetically related to D. carnulentum, D. setosum, D. hirsutum, Metadesmolaimus sp. and Daptonema spp. We provided a list of valid Daptonema species, including key morphological characteristics of males, and additionally reviewed 30 species inquirenda.
References
- Alekseev, V.M. (1984) Daptonema inversum sp. n. and comments on the status of the subgenus Pseudotheristus (Nematoda, Xyalidae). Zoologicheskiy Zhurnal, 63, 1420−1423. [in Russian]
- Allgén, C. (1928) Neue oder wenig bekannte freilebende marine Nematoden von der schwedischen Westküste. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 77, 281–307.
- Allgén, C.A. (1929) Freilebende marine Nematoden aus den Umgebungen der Staatlichen Zoologischen Station Kristineberg an der Westküste Schwedens. Capita Zoologica, 2 (8), 1−52.
- Allgén, C.A. (1932) Weitere Beitrage zur Kenntnis der marinen Nematodenfauna der Campbellinsel. Nyt Magazin for Naturvidenskaberne, 70, 97–198.
- Allgén, C.A. (1933) Freilebende Nematoden aus dem Trondhjemsfjord. Capita Zoologica, 4 (2), 1–162.
- Allgén, C.A. (1935) Die freilebenden Nematoden des Öresunds. Capita Zoologica, 6 (3), 1−192.
- Allgén, C.A. (1947) West American nematodes (Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen’s Pacific Expedition 1914−16 75). Meddeleiser fra Dansk naturhisforisk Forening i Kjøbenhavn, 110, 65–219.
- Allgén, C.A. (1948) Zur Kenntnis norwegischer Nematoden. XIII. Ueber zwei weitere freilebende Nematoden von der Insel Storfosen. Det Kongelige Norske Videnskabers Selskabs Forhandlinger, 20 (16), 59−61.
- Allgén, C.A. (1951) Pacific Freeliving Marine Nematodes. (Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen’s Pacific Expedition 1914−16. LXXVI). Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra Dansk Naturhistorisk Forening Kebenhavn, 113, 263–411.
- Allgén, C.A. (1959) Freeliving marine nematodes. In: Further zoological results of the Swedish Antarctic expedition, 1901−1903 under the direction of Dr. Otto Nordenskjold. V (2). P.A. Norstedt & Söner, Stockholm, 293 pp.
- Aryuthaka, C. & Kito, K. (2012) Two new species of the genus Daptonema Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda: Xyalidae) found in the monospecific Halophila ovalis patches within an intertidal mixed-species seagrass bed on the coast of the Andaman Sea, Thailand. Zootaxa, 3350 (1), 34−46. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3350.1.2
- Aryuthaka, C. & Kito, K. (2018) Two new species of the genus Daptonema Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda: Xyalidae) found in an intertidal seagrass bed on the coast of the Andaman Sea, Thailand, with reference to the taxonomic status of the genus Trichotheristus Wieser, 1956. Zootaxa, 4394 (1), 77. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4394.1.4
- Bastian, H.C. (1865) Monograph on the Anguillutidae, or Free Nematoids, marine, land, and freshwater, with descriptions of 100 new species. Transactions of the Linnean Society, 25, 73−180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1865.tb00179.x
- Benson, D.A., Cavanaugh, M., Clark, K., Karsch-Mizrachi, I., Lipman, D.J., Ostell, J. & Sayers, E.W. (2012) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Research, 41, D36−D42. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1195
- Bhadury, P., Austen, M.C., Bilton, D.T., Lambshead, P.J.D., Rogers, A.D. & Smerdon, G.R. (2006) Development and evaluation of a DNA-barcoding approach for the rapid identification of nematodes. Marine ecology Progress Series, 320, 1−9. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps320001
- Blome, D. & Riemann, F. (2000) Antarctic sea ice nematodes, with description of Geomonhystera glaciei sp. nov. (Monhysteridae). Mitteilungen aus dem Hamburgischen Zoologischen Museum und Institut, 96, 15−20.
- Bluhm, B.A., Swadling, K.M. & Gradinger, R. (2017) Sea ice as a habitat for macrograzers. In: Thomas, D.N. (Ed.), Sea Ice. Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, pp. 394−414. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118778371.ch16
- Boucher, G. & Helléouët, M.N. (1977) Nématodes des sables fins infralittoraux de la Pierre Noire (Manche occidentale). III. Araeolaimida et Monhysterida. Bulletin du Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, 427, 85−122.
- Bütschli, O. (1873) Beiträge zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden. Nova Acta der Kaiserlich Leopoldinisch-Carolinischen Deutschen Akademie der Natutforscher, 36, 1−144.
- Bütschli, O. (1874) Zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden, insbesondere der des Kieler Hafens. Abhandlungen der Senckenbergischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft, IX Bd.,1−56.
- Chitwood, B.G. (1951) North American marine nematodes. Texas Journal of Science, 3, 627−672.
- Cobb, N.A. (1914) Antarctic marine free-living nematodes of the Shackleton expedition. Contribution to a Science of Nematology, 1, 1–33.
- Cobb, N.A. (1920) One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contributions to a Science of Nematology, 9, 217−343.
- Cobb, N.A. (1930) Marine free-living nemas. Scientific Reports of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911−1914), Series C: Zoology & Botany, 6 (7), 1–28.
- Coomans, A. & Eyualem, A. (2006) Order Monhysterida. In: Eyualem-Abebe, Traunspurger, W. & Andrássy, I. (Eds.), Freshwater nematodes: ecology and taxonomy. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp. 574−603. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851990095.0574
- Cunha, B.P., Brito, S. & Fonseca, G. (2013) Zygonemella: the forgotten genus of the family Xyalidae (Nematoda). Zootaxa, 3669 (2), 179−183. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3669.2.10
- De Coninck, L.A. & Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. (1933) The freeliving marine nemas of the Belgian Coast. II. With general remarks on the structure and the system of nemas. Mémoires du Musée Royal d’Histoire Naturelle de Belgique, 58, 3−163
- de Man, J.G. (1881) Die einheimischen, frei in der reinen Erde und im süssen Wasser lebenden Nematoden. Tijdschrift van der Nederlandsche Dierkundige Vereeniging, 5, 1–104.
- de Man, J.G. (1888) Sur quelques nématodes libres de la mer du Nord, nouveaux ou peu connus. Mémoires de la Société Zoologique de France, 1, 1−51. [http://biostor.org/reference/61577]
- de Man, J.G. (1890) Quatrième note sur les nématodes libres de la mer du Nord et de la Manche. Mémoires de la Société Zoologique de France, 3, 169−194. [https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/10111370]
- Ditlevsen, H. (1911) Danish freeliving nematodes. Videnskabelige Meddelelser Dansk Naturhistorisk Forening, 63, 213−256.
- Ditlevsen, H. (1918) Marine freeliving nematodes from Danish waters. Vidensk. Meddeleiser fra Dansk Naturhisforisk Forening i Kjøbenhavn, 70 (7), 147−214.
- Ditlevsen, H. (1928) Free-living marine nematodes from Greenland waters. Meddelelser om Gronland, 23, 199−250.
- Eicken, H., Bluhm, B., Collins, R.E., Gradinger, R., Haas, C., Ingham, M., Mahoney, A., Nicolaus, M. & Perovich, D. (2014) Field techniques in sea-ice research. In: Cold regions science and marine technology. Eolss Publishers, Paris, pp. 1–45. pp. [https://globalcryospherewatch.org/bestpractices/docs/SeaIceFieldTechniques_Eicken_140301_s.pdf]
- Fadeeva, N.P. & Belogurov, O.I. (1987) Structure of the Cephalic End of Nematodes of the Family Xyalidae and a Description of Three Species. The Soviet Journal of Marine Biology, 13 (1), 9−17.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1922a) Encore sur les Nematodes de la Mer Noire. Trudy Stavropolskago Sel’skokhozyaistvennago Instituta, 1, 83−184.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1922b) Sur les Nématodes libres de la mer d’Azov. Trudy Stavropolskago Sel’skokhozyaistvennago Instituta, 1 (7), 185−208.
- Filipjev, I.N. (1929) Classification of free-living Nematoda and relations to parasitic forms. Journal of Parasitology Urbana, 15, 281−282.
- Floyd, R.M., Rogers, A.D., Lambshead, P.J.D. & Smith, C.R. (2005) Nematode-specific PCR primers for the 18S small subunit rRNA gene. Molecular Ecology Notes, 5, 611−612. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01009.x
- Fonseca, G. & Bezerra, T.N. (2014) Order Monhysterida. In: Shmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Ed.), Handbook of Zoology Gastrotricha, Cyclioneura and Gnathifera. Vol. 2. Nematoda, De Gruyter, Hamburg, pp. 435−465.
- Gagarin, V.G. & Gusakov, V.A. (2014) Daptonema salinae sp. n. from highly mineralized rivers of Lake Elton basin, Russia. International Journal of Nematology, 24, 18−22.
- Gagarin, V.G. & Lemzina, L.V. (1980) A new species of free-living nematodes from the Monhysteridae. Zoologicheskiy Zhurnal, 59, 139−141. [in Russian]
- Gagarin, V.G. & Lemzina, L.V. (1981) Two new species of free-living nematodes of the genus Cylindrolaimus from the Issyk-kul Lake. Zoologicheskiy Zhurnal, 60, 773−775. [in Russian]
- Gagarin, V.G. & Thanh, N.V. (2014) Two new species of the family Xyalidae Chitwood, 1951 (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from the coast of Vietnam. International Journal of Nematology, 24 (2), 108−116.
- Gagarin, V.G. (1993) Free-living nematodes in freshwaters of Russia and adjacent lands (Orders Monhysterida, Araeolaimida, Chromadorida, Enoplida, Mononchida). Gidrometeoizdat, St. Petersburg, 352 pp. [in Russian]
- Gagarin, V.G. & Thanh, N.V. (2005) Free-living nematodes from some water bodies of northern Vietnam. Biologiya Vnutrennih Vod, 1, 18−23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12212-008-1003-4
- Gagarin, V.G. & Thanh, N.V. (2010) Two new species of the family Xyalidae Chitwood, 1951 (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from littoral zone of South China Sea. International Journal of Nematology, 20 (1), 1−6.
- Gagarin, V.G. & Thu, N.T. (2008) Three new species of the genus Daptonema (Nematoda, Xyalidae) from the Red River Delta (Vietnam). Zoologischeskii Zhurnal, 87 (5), 515−523. [in Russian]
- Gagarin, V.G. (1987) Two new species of the family Monhysteridae (Nematoda). Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 66 (3), 454−456. [in Russian]
- Gagarin, V.G. (2000) New species of nematodes from waterbodies of Russian Arctica. Biologia Vnuttrennikh Vod, 3, 9−15. [in Russian]
- Gagarin, V.G. (2018) An annotated checklist of the free-living nematodes from mangrove thickets of Vietnam. Zootaxa, 4403 (2), 261–288. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4403.2.3
- Gagarin, V.G. (2001) New species of free-living nematodes from Biwa Lake and Inflowing Stream (Honshu Island, Japan). Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 80 (1), 12−25. [in Russian]
- Gagarin, V.G. (2021a) Two nematode species new to science of genus Daptonema (Nematoda, Monhysterida) found in artificial reservoirs in Vietnam. Inland Water Biology, 14, 247−255. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082921030068
- Gagarin, V.G. (2021b) Two new species of free-living nematodes (Nematodes, Monhysterida) from the Mouth of the Cấm River, Vietnam. Inland Water Biology, 14 (1), 1−9. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1995082921010028
- Gagarin, V.G., Gusakov, V.A. & Dinh, C.N. (2021) Two new species of free-living nematodes (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from Mekong River mouth, Vietnam. Amurian Zoological Journal, XIII, 4, 536−549. https://doi.org/10.33910/2686-9519-2021-13-4-536-549
- Gagarin, V.G., Thanh, N.V & Thu, N.T. (2005) Daptonema salvum sp. n. and D. rigidum sp. n. (Nematoda: Monhysterida) from Chu River, Vietnam. International Journal of Nematology, 15 (2), 210.
- Galtsova, V.V. (1976) Free-living marine nematodes as components of the meiofauna of the Chupa Bay, White Sea. Issledovaniya Fauny Morei (Nematody i ikh rol’ v meiobentose), 15 (23), 165−270. [in Russian]
- Gerlach, S.A. & Riemann, F. (1973/1974) The Bremerhaven Checklist of Aquatic Nematodes: A catalog of Nematoda Adenophorea excluding the Dorylaimida. Part I. Veroffentlichungen des Instituts fur Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, Supplement 4 Heft, 1, 1−404.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1951) Freilebende nematoden aus der verwandtschaft der gattung Theristus. Zoologische Jahrbücher, 80, 379−406.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1952) Nematoden aus dem Küstengrundwasser. Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur, in Kommission bei F. Steiner, Wiesbaden, 6, 315−372.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1953a) Die Nematodenbesiedlung des Sandstandes und des Kustengrundwassers an der italienischen Kuste. 1. Systematischer Teil. Archivio Zoologico Italiano, 37, 517−640.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1953b) Freilebende marine Nematoden aus dem Küstengrundwasser und aus dem Brackwasser der Chilenischen Küste. Lunds universitets års-skrift. Acta Universitatis Lundensis, 2, 49 (10), 1−37.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1956) Diagnosen neuer Nematoden aus der Kieler Bucht. Kieler Meeresforsch, 12, 85−109.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1957) Die Nematodenfauna Des Sandstrandes an Der Küste von Mittelbrasilien (Brasilianische Meeres‐Nematoden IV). Mitteilungen aus dem Museum für Naturkunde in Berlin. Zoologisches Museum und Institut für Spezielle Zoologie, Berlin, 33 (2), 411−459. https://doi.org/10.1002/mmnz.19570330206
- Gerlach, S.A. (1959) Neue Meeres-nematoden aus dem Supralitoral der deutschen Küsten. Internationele Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie, 44, 463−467. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.19590440125
- Gerlach, S.A. (1964) Freilebende Nematoden aus dem Roten Meer. Kieler Meeresforsch, 20 (Sonderheft), 18−34.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1965) Freilebende Meersenematoden aus der Gezeitenzone von Spitzbergen. Veroffentlichungen des Instituts fur Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, Band IX, 109−172.
- Guo, W., Meng, Z & Wang, C. (2023) Two New Nematode Species, Desmolaimus magnus sp. nov.(Monhysterida, Linhomoeidae) and Metadesmolaimus robustus sp. nov.(Monhysterida, Xyalidae), from the Yellow Sea, China with Phylogenetic Analyses within Linhomoeidae and Xyalidae. Diversity, 15 (11), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15111130
- Gusakov, V.A., Gagarin, V.G. & Dinh, C.N. (2023) Daptonema brzeskii sp. n. and D. rivale sp. n. (Nematoda, Monhysterida, Xyalidae) from Mekong River Mouth, Vietnam. Inland Water Biology, 16, 404−412. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082923030094
- Hodda, M. (2022) Phylum Nematoda: a classification, catalogue, and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. Zootaxa, 5114 (1), 1−289. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5114.1.1
- Hopper, B.E. (1969) Marine nematodes of Canada. II. Marine nematodes from the Minas Basin-Scots Bay area of the Bay of Fundy, Nova Scotia. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 47 (4), 671−690. https://doi.org/10.1139/z69-114
- Huang, M., Sun, J. & Huang, Y. (2019) Daptonema parabreviseta sp. nov. (Xyalidae, Nematoda) from the Jiaozhou Bay of the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 37 (1), 273−277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-7362-3
- Huang, Y. & Zhang, Z. (2006) Two new species of free-living marine nematodes (Trichotheristus articulatus sp. n. and Leptolaimoides punctatus sp. n.) from the Yellow Sea. Russian Journal of Nematology, 14 (1), 43−50.
- Huang, Y. & Zhang, Z. (2010) Two new species of Xyalidae (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 90 (2), 391−397. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315409000794
- Juario, J.V. (1974) Neue freilebende Nematoden aus dem Sublitoral der Deutschen Bucht [New Free-living Nematodes from the Sublittoral Zone of the German Bight]. Veroffentlichungen des Instituts fuer Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, 14, 275−303.
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B., Wong, T., Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L. (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Methods, 14 (6), 587−589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
- Kearse, M., Moir, R., Wilson, A., Stones-Havas, S., Cheung, M., Sturrock, S., Buxton, S., Cooper, A., Markowitz, S., Duran, C., Thierer, T., Ashton, B., Meintjes, P. & Drummond, A. (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics, 28 (12), 1647−1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
- Kreis, H.A. (1929) Freilebende marine Nematoden von der Nordwest-Küste Frankreichs (Trébeurden Côtes du Nord). Capita Zoologica, II, 7, 1−98.
- Lanfear, R., Frandsen, P.B., Wright, A.M., Senfeld, T. & Calcott, B. (2016) PartitionFinder 2: new methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 772−773. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw260
- Leduc, D. & Zhao, Z.Q. (2021) Molecular characterization of free-living nematodes from Kermadec Trench (Nematoda: Aegialoalaimidae, Xyalidae) with description of Aegialoalaimus tereticauda n. sp. Zootaxa, 4949 (2), 341−352. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4949.2.7
- Leduc, D. & Zhao, Z.Q. (2023) The Marine Biota of Aotearoa New Zealand. Ngâ toke o Parumoana: common free-living Nematoda of Pâuatahanui Inlet, Te-Awarua-o-Porirua Harbour, Wellington. NIWA Biodiversity Memoir, 135, 1–212.
- Leduc, D. (2015) One new genus and five new nematode species (Monhysterida, Xyalidae) from Tonga and Kermadec Trenches, Southwest Pacific. Zootaxa, 3964 (5), 501−525. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3964.5.1
- Letunic, I. & Bork, P. (2021) Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, W293−W296. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab301
- Long, P.K., Tu, N.D. & Gagarin, V.G. (2020/2021) Daptonema paramonovi sp. n. (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from a Mangrove Habitat in Vietnam. Biology Bulletin, 48, 1170−1175. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359021080203
- Li, T., Ban, S & Huang, Y. (2023) Two new species of Xyalidae Chitwood, 1951 (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from Chinese Sea Area. Zootaxa, 5369 (2), 255−268. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5369.2.5
- Lorenzen, S. (1971) Die Nematodenfauna im Verklappungsgebiet für Industrieabwasser nordwestlich von Helgoland: I. Araeolaimida und Monhysterida. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 187 (3), 223−248.
- Lorenzen, S. (1973) Freilebende Meersenematoden aus dem Sublitoral der Nordsee und der Kieler Bucht. Veroffentlichungen des Instituts fur Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, 14, 103−130.
- Lorenzen, S. (1977) Revision det Xyalidae (freilebende nematoden) auf der grundlage einer kritischen analyse von 56 Aarten aus Nord- und Ostsee. Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, 16, 197−261.
- Lorenzen, S. (1979) Marine Monhysteridae (sensu stricto, Nematodes) von der südchilenischen Küste und aus den küstenfernen Sublitoral der Nordsee. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Environment, 14, 203−214. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650527909360556
- Meldal, B.H., Debenham, N.J., De Ley, P., De Ley, I.T., Vanfleteren, J.R., Vierstraete, A.R., Bert, W., Borgonie, G., Moens, T., Tyler, P.A., Austen, M.C., Blaxter, M.L., Rogers, A.D. & Lambshead, P.J.D. (2007) An improved molecular phylogeny of the Nematoda with special emphasis on marine taxa. Molecular phylogenetics and evolution, 42 (3), 622−636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2006.08.025
- Murphy, D.G. (1965) Chilean marine nematodes. Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, 9, 173−203.
- Nemys eds. (2024) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available from: https://nemys.ugent.be (accessed 13 January 2024) https://doi.org/10.14284/366
- Neres, P.F., Fonseca-Genevois, V.G., Torres, R.A., Fonseca Cavalcanti, M., Castro, F.J.V., Silva, N.R.R., Rieger, T.T. & Decraemer, W. (2010) Morphological and molecular taxonomy of a new Daptonema (Nematoda, Xyalidae) with comments on the systematics of some related taxa. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 158 (1), 1−15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00528.x
- Nguyen, T.T., Thanh, N.V. & Gagarin, V.G. (2004) Two new brackish water nematode species of the genus Daptonema Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda: Monhysterida) from Can Gio mangrove. Proceedings of the National Conference of Life Sciences, Thai Nguyen University, 23 September 2004, 249−252.
- Pasotti, F., De Troch, M., Raes, M & Vanreusel, A. (2012) Feeding ecology of shallow water meiofauna: insights from a stable isotope tracer experiment in Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biology, 35, 1629−1640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-012-1203-6
- Pastor de Ward, C.T. (1985) Nematodes de la Ria Deseado (Monhysteroidea, Xyalidae), Santa Cruz, Argentina. II. Physis, Seccion A, 43 (105), 113−130.
- Pavljuk, O.N. (1984) New species of marine free-living nematodes in the Sea of Japan and comments to the genus Halanonchus. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 63 (8), 1144−1149. [in Russian]
- Pitusi, V., Søreide, J.E., Hassett, B.T., Marquardt, M. & Andreasen, M.H. (2021) The occurrence of Nematoda in coastal sea ice on Svalbard (European Arctic) determined with the 18S small subunit rRNA gene. Polar Biology, 44 (6), 1153−1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-021-02863-y
- Phuong, N.T.X., Judith, C.K., Man, P.T., Gagarin, V.G. & Tu, N.D. (2016) Description of the new species of free-livings nematodes Daptonema securum sp. nov. from artificial reservoirs in Vietnam. Amurian Zoological Journal, 8 (4), 225−232. https://doi.org/10.33910/1999-4079-2016-8-4-225-232
- Platt, H.M. (1973) Freeliving marine nematodes from Strangford Lough, Northern Ireland. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 14 (3), 295−321.
- Rieger, R. & Ott, J. (1971) Gezeitenbedingte Wanderungen von Turbellarien und Nematoden eines nordadriatischen Sandstrandes. Vie Milieu, 22, Supplement I, 425−447.
- Riemann, F. (1966) Die interstitielle Fauna im Elbe-Aestuar. Verbreitung und Systematik. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Supplement l, 31, 1−279.
- Riemann, F. (1979) Nematoden aus dem Brackwasser des Weser-Ästuars und Beschreibung von drei Monhysteroidea. Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven, 17, 213−223.
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., Van Der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic biology, 61 (3), 539−542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Ryss, A.Y. (2003) Express technique to prepare permanent collection slides of nematodes. Zoosystematica Rossica, 11 (2), 257−260. https://doi.org/10.31610/zsr/2002.11.2.257
- Schneider, G. (1906) Beitrag zur Kenntnis der im Uferschlamm des Finnischen Meerbusens freilebenden Nematoden. Acta Societatis Pro Fauna Et Flora Fennica, 27 (7), 1−40.
- Schulz, E. (1932) Beitrage zur Kenntnis mariner Nematoden aus der Kileler Bucht. Zoologische Jahrbucher, Abteilung für Systematik, Öcologie und Biologie der Tiere, 62, 331−430.
- Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. (1950) The freeliving marine nemas of the Mediterranean: I. The bay of Villefranche. Vol. 37. Mémoires de l’Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Deuxième Série, 1–220.
- Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. & De Coninck, L.A. (1933) Diagnoses of new Belgian marine nematodes. Bulletin du Musée Royal d’Histoire Naturelle de Belgique, 9, 1−15.
- Schuurmans Stekhoven, J.H. (1935) Nematoda: Systematischer Teil, Nematoda Errantia. Die Tierwelt der Nord- und Ostsee, 28, 1−173.
- Schuurmans, S. (1935) Additional notes to my monographs on the free-living marine nemas of the Belgian coast. I and II. Written in collaboration with W. Adam and LA de Coninck, with some remarks on the ecology of Belgian nemas. Musée royal d’histoire naturelle de Belgique, Bruxelles, 72 pp.
- Seinhorst, J.W. (1966) Killing nematodes for taxonomic study with hot f. a. 4:1. Nematologica, 12, 175. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529266X00239
- Steiner, G. (1916) Freilebende Nematoden aus der Barentssee. Zoologische Jahrbücher, 39, 511–664.
- Sun, Y., Huang, Y., Tang, H., Zang, Y., Xiao, H. & Tang, X. (2019) Two new free-living nematode species of the family Xyalidae from the Laizhou Bay of the Bohai Sea, China. Zootaxa, 4614 (2), 383−394. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4614.2.7
- Tchesunov, A.V. & Miljutin, D.M. (2006) Three new free-living nematode species (Monhysterida) from the Arctic abyss, with revision of the genus Eleutherolaimus Filipjev, 1922 (Linhomoeidae). Russian Journal of Nematology, 14 (1), 57−75.
- Tchesunov, A.V., Kaljakina, N.M. & Bubnova, E.N. (2008) A catalogue of biota of the White Sea Biological Station of the Moscow State University. KMK Scientific Press Ltd., Moscow, 384 pp. [in Russian]
- Tchesunov, A.V. & Portnova, D.A. (2005) Free-living nematodes in seasonal coastal ice of the White Sea. Description of Hieminema obliquorum gen. et sp. n. (Nematoda, Monhysteroidea). Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 84, 899−914. [in Russian]
- Tchesunov, A.V. & Riemann, F. (1995) Arctic sea ice nematodes (Monhysteroidea), with descriptions of Cryonema crassum gen. n., sp. n. and C. tenue sp. n. Nematologica, 41 (1−4), 35−50. https://doi.org/10.1163/003925995X00035
- Tchesunov, A.V. (1980) New Data on Free-Living Nematodes of the Superfamily Monhysteroidea of the Caspian Sea. Zoologischeskii Zhurnal, 59 (7), 973−985. [in Russian]
- Tchesunov, A.V. (1986) A new free-living nematode connected with sea Arctic ice. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 65, 1782−1787. [in Russian]
- Tchesunov, A.V. (1990a) Long-hairy Xyalidae (Nematoda, Chromadoria, Monhysterida) in the White Sea: new species, new combinations and status of the genus Trichotheristus. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 69, 5−19. [in Russian]
- Tchesunov, A.V. (1990b) New taxa of marine free-living nematodes of the Family Xyalidae Chitwood, 1951 (Nematoda, Chromadorida, Monhysterida) from the White Sea. Fauna, biology and systematics of freeliving lower worms. Rybinsk, Russia, Institute of Inland Water Biology, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Proceedings, 64, 101−117.
- Tchesunov, A.V. (2006) Biology of marine nematodes. KMK Scientific Press Ltd, Moscow, 296 pp. [in Russian]
- Thanh, N.V. & Gagarin, V.G. (2004) Two new free-living brackish water nematode species of the genus Daptonema Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda: Monhysterida) recorded from Can Gio mangrove. National Conference of Life Sciences Thai Nguyen University, 2004, 229−232. [in Vietnamese]
- Thanh, N.V., Hoang, L.P. & Gagarin, V.G. (2005) The new species Daptonema pumilus sp. nov. (Nematoda: Monhysterida) in Vietnam. Academia Journal of Biology, 27 (3), 1−4. https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7160/v27n3.5261
- Thanh, N.V & Gagarin, V.G. (2009) Three species of monhysterids (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from mangrove forest of the Me Kong river estuary, Vietnam. Academia Journal of Biology, 31 (2), 8−15. https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7160/v31n2.808
- Thanh, N.V. & Gagarin, V.G. (2009) Three species of monhysterids (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from mangrove forest of the Me Kong river estuary, Vietnam. Vietnam Journal of Biology, 31 (2), 8−15.
- Timm, R.W. (1952) A survey of the marine nematodes of Chesapeake Bay, Maryland. Contr. Chesapeake Biological Laboratories, 95, 1−70.
- Timm, R.W. (1957) New marine nematodes from St. Martin’s Island. Pakistan Journal of Scientific Research, 9 (4), 133−138.
- Timm, R.W. (1961) The marine nematodes of the Bay of Bengal. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Science, 1 (1), 25−88.
- Tsalolikhin, S.J. (2002) Some species of freshwater nematodes from Singapore and Japan. Zoosystematica Rossica, 10, 231−239. https://doi.org/10.31610/zsr/2001.10.2.231
- Tsalolikhin, S.Y. (1985) Nematodes of fresh and brackish waters in Mongolia. (Joint Soviet-Mongolian biological expedition). Nauka, Lenigrad, 115 pp. [in Russian]
- Tsalolikhin, S.Y. (2017) Identification key to the intracontinental species of the genus Daptonema (Nematoda: Monhysterida: Xyalidae) with descriptionof the new species D. borkini sp. nov. Proceedings of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 321, 89−97. https://doi.org/10.31610/trudyzin/2017.321.1.89
- Tu, N.D., Gagarin, V.G., Thanh, N.V., Phuong, N.T.X. & Hien, N.T. (2014) Two new nematode species of the genus Daptonema Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda, Xyalidae) from mangrove forest estuary of the Red River (Vietnam). Inland Water Biology, 7, 125−133. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082914020114
- Vanhove, S., Beghyn, M., Van Gansbeke, D., Bullough, L.W. & Vincx, M. (2000) A seasonally varying biotope at Signy Island, Antarctic: implications for meiofaunal structure. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 202, 13−25. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps202013
- Venekey, V., Gheller, P.F., Maria, T.F., Brustolin, M.C., Kandratavicius, N., Vieira, D.C., Brito, S., Souza, G.S. & Fonseca, G. (2014) The state of the art of Xyalidae (Nematoda, Monhysterida) with reference to the Brazilian records. Marine Biodiversity, 44, 367−390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-014-0226-3
- Vincx, M. & Coomans, A. (1983) Daptonema williamsi sp.n. (Nematoda, Xyalidae) from the Solomon Islands. Zoologica Scripta, 12 (4), 237−244. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.1983.tb00507.x
- Vitiello, P. (1967) Nématodes libres marins de Roscoff. I. Déscription de cinq espèces nouvelles. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 8, 403−416.
- Vitiello, P. (1970/1971a) Nématodes libres marins des vases profondes du Golfe du Lion. III. Monhysterida, Araeolaimida, Desmodorida. Téthys, 2, 647−690.
- Vitiello, P. (1971b) Nématodes nouveaux des vases terrigènes cotières des côtes provençales. Téthys, 2 (4), 859−875.
- Wang, C., An, L. & Huang, Y. (2018) Two new species of Xyalidae (Monhysterida, Nematoda) from the East China Sea. Zootaxa, 4514 (4), 583−592. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4514.4.11
- Warwick, R.M. (1970) Fourteen new species of the free-living marine nematodes from the Exe estuary. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Zoology, 19, 139−177. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.24086
- Wieser, W. & Hopper, B.E. (1967) Marine nematodes of the east coast of North America. I. Florida. Bulletin Museum of Comparative Zoology, 135, 239−344.
- Wieser, W. (1956) Free-living marine nematodes. III. Axonolaimoidea and Monhysteroidea. Acta Universitatis Lund, Neue Folge 2, 52 (13), 1−115.
- Wieser, W. (1959) Free-living nematodes and other small invertebrates of Puget Sound beaches. University of Washington Publications in Biology, 19, 1−179.
- Wu, J. & Liang, Y. (2000) Inland fee-living nematodes in China: A historical review of taxonomic studies with descriptions of Aphanonchus orientalis sp. nov. (Chromadorida: Leptolaimidae) and Daptonema limnobia sp. nov. (Monhysterida: Xyalidae). Annales Zoologici, 50, 307−319.
- Yoder, M., Tandingan De Ley, I., King, I.W., Mundo-Ocampo, M., Mann, J., Blaxter, M., Poiras, L. & De Ley, P. (2006) DESS: a versatile solution for preserving morphology and extractable DNA of nematodes. Nematology, 8 (3), 367−376. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854106778493448