Abstract
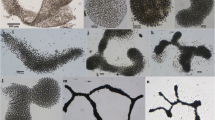
Cyanobacteria containing neurotoxic saxitoxin synthesis genes were found in the coastal zone of Lake Baikal near the village of Turka for the first time. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the sequences of saxitoxin synthesis genes belong to the genus Anabaena Bory. Saxitoxin concentration in the water according to ELISA was 1.93 ± 0.64 mg/L. The genetic and taxonomic composition of the bacterial community of the central part of Lake Baikal was characterized using 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing. It was established that the phylum Cyanobacteria dominated in the composition of summer bacterioplankton in both littoral and pelagic zones of the lake, but higher species diversity was found in the plankton of littoral zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballot, A., Fastner, J., and Wiedner, C., Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin-producing cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon gracile in Northeast Germany, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 76, pp. 1173–1180.
Belykh, O.I., Gladkikh, A.S., Sorokovikova, E.G., Tikhonova, I.V., Potapov, S.A., and Fedorova, G.A., Microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in reservoirs of Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine, Khim. Interesakh Ustoich. Razvit. 2013, vol. 21, pp. 363–378.
Belykh, O.I., Pomazkina, G.V., Tikhonova, I.V., and Tomberg, I.V., Characteristics of Lake Baikal summer phytoplankton and autotrophic picoplankton in 2005, Algologiya, 2007, no. 3, pp. 380–396.
Belykh, O.I. and Sorokovikova, E.G., Autotrophic picoplankton in Lake Baikal: abundance, dynamics, and distribution, Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manage., 2003, vol. 3, pp. 251–261.
Belykh, O.I., Sorokovikova, E.G., Fedorova, G.A., Kaluzhnaya, O.V., Korneva, E.S., Sakirko, M.V., and Sherbakova, T.A., Presence and genetic diversity of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria (Anabaena and Microcystis) in Lake Kotokel (Russia, Lake Baikal region), Hydrobiologia, 2011, vol. 671, pp. 241–252.
Burch, M.D., Effective doses, guidelines and regulations, in Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs, Hudnell, H.K., Ed., 2008, ch. 36. http://www.epa.gov/cyano_habs_symposium/monograph/Ch36.pdf
Chorus, I., Current approaches to cyanotoxin risk assessment, risk management, and regulations in different countries, 2012. http://www.uba.de/uba-info-medien-e/4390.html
Chorus, I. and Bartram, J., Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: a Guide to their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management, London: E. & F.N. Spoon, 1999.
Cusick, K. and Sayler, G., Overview on the marine neurotoxin, saxitoxin: genetics, molecular targets, methods of detection and ecological functions, Mar. Drugs, 2013, vol. 11, pp. 991–1018.
Deeds, J.R., Landsberg, J.H., Etheridge, S.M., Pitcher, G.C., and Longan, S.W., Non-traditional vectors for paralytic shellfish poisoning, Mar. Drugs, 2008, vol. 6, pp. 308–348.
Doucette, G.J., Cembella, A.D., Martin, J.L., Michaud, J., Cole, T.V.N., and Rolland, R.M., PSP toxins in North Atlantic right whales (Eubalaena glacialis) and their zooplankton prey in the Bay of Fundy, Canada, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 2006, vol. 306, pp. 303–313.
Gollerbakh, M.M., Kosinskaya, E.K., and Polyanskii, V.I., Opredelitel’ presnovodnykh vodoroslei SSSR (Guidance to Identification of Freshwater Algae in the Soviet Union), Moscow: Sovetskaya Nauka, 1953, vol. 2.
Ibelings, B.W. and Chorus, I., Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: a review, Environ. Pollut., 2007, vol. 150, pp. 177–192.
Kleinteich, J., Wood, S.A., Puddick, J., Schleheck, D., Küpper, F.C., and Dietrich, D., Potent toxins in Arctic environments — presence of saxitoxins and an unusual microcystin variant in Arctic freshwater ecosystems, Chem. Biol. Interact., 2013, vol. 206, pp. 423–431.
Lepisto, L., Rapala, J., Lyra, C., Berg, K.A., Erkomaa, K., and Issakainen, J., Occurrence and toxicity of cyanobacterial blooms dominated by Anabaena lemmermannii P. Richter and Aphanizomenon spp. in boreal lakes in 2003, Algol. Stud., 2005, vol. 117, pp. 315–328.
Mnogoletnie dannye o rezhime i resursakh poverkhnostnykh vod sushi (Long-Term Data on Regime and Resources of Inland Surface Waters), Leningrad: Gidrometeoizdat, 1986, vol. 1, no. 14.
Parfenova, V.V., Gladkikh, A.S., and Belykh, O.I., Comparative analysis of biodiversity in the planktonic and biofilm bacterial communities in Lake Baikal, Microbiology (Moscow), 2013, vol. 82, no. 1, pp. 91–101.
Popovskaya, G.I. and Belykh, O.I., Massovye, endemichnye i indikatornye vidy planktonnykh vodoroslei ozera Baikal (Widespread, Endemic, and Indicator Species of Planktonic Algae from the Baikal Lake), Irkutsk: Irkut. Gos. Univ., 2002.
Rajaniemi, P., Komarek, J., Willame, R., Hrouzek, P., Kastovska, K., Hoffmann, L., and Sivonen, K., Taxonomic consequences from the combined molecular and phenotype evaluation of selected Anabaena and Aphanizomenon strains, Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl., 2005, vol. 159, pp. 371–391.
Rapala, J., Robertson, A., Negri, A.P., Berg, K.A., Tuomi, P., Lyra, C., Erkomaa, K., Lahti, K., Hoppu, K., and Lepisto, L., First report of saxitoxin in Finnish lakes and possible associated effects on human health, Environ. Toxicol., 2005, vol. 20, pp. 331–340.
Shimaraev, M.N. and Domysheva, V.M., Trends in hydrological and hydrochemical processes in Lake Baikal under conditions of modern climate change, in Climatic Change and Global Warming of Inland Waters. Impacts and Mitigation for Ecosystems and Societies, Goldman, C., Kumagai, M., and Robarts, R.D., New York: Wiley, 2013, pp. 43–66.
Smith, J.L., Boyer, G.L., and Zimba, P.V., A review of cyanobacterial odorous and bioactive metabolites: impacts and management alternatives in aquaculture, Aquaculture, 2008, vol. 280, pp. 5–20.
Steffen, M.M., Li, Z., Effler, T.C., Hauser, L.J., Boyer, G.L., and Wilhelm, S.W., Comparative metagenomics of toxic freshwater cyanobacteria bloom communities on two continents, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 8, p. e44002. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044002
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., and Kumar, S., MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2013, vol. 30, pp. 2725–2729.
Wiese, M., D’Agostino, P.M., Mihali, T.K., Moffitt, M.C., and Neilan, B.A., Neurotoxic alkaloids: saxitoxin and its analogs, Mar. Drugs, 2010, vol. 8, pp. 2185–2211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belykh, O.I., Gladkikh, A.S., Sorokovikova, E.G. et al. Saxitoxin-Producing cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 8, 186–192 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S199542551502002X
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S199542551502002X