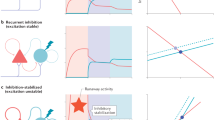
Abstract
Integrator circuits in the brain show persistent firing that reflects the sum of previous excitatory and inhibitory inputs from external sources. Integrator circuits have been implicated in parametric working memory, decision making and motor control. Previous work has shown that stable integrator function can be achieved by an excitatory recurrent neural circuit, provided synaptic strengths are tuned with extreme precision (better than 1% accuracy). Here we show that integrator circuits can function without fine tuning if the neuronal units have bistable properties. Two specific mechanisms of bistability are analyzed, one based on local recurrent excitation, and the other on the voltage-dependence of the NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) channel. Neither circuit requires fine tuning to perform robust integration, and the latter actually exploits the variability of neuronal conductances.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miyashita, Y. & Chang, H.S. Neuronal correlate of pictorial short-term memory in the primate temporal cortex. Nature 331, 68–70 (1988).
Gnadt, J.W. & Andersen, R.A. Memory related motor planning activity in posterior parietal cortex of macaque. Exp. Brain Res. 70, 216–220 (1988).
DeSouza, J.F. et al. Eye position signal modulates a human parietal pointing region during memory-guided movements. J. Neurosci. 20, 5835–5840 (2000).
Goldman-Rakic, P.S. Cellular basis of working memory. Neuron 14, 477–485 (1995).
Fuster, J.M. Memory in the Cerebral Cortex: An Empirical Approach to Neural Networks in the Human and Nonhuman Primate (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1995).
Romo, R., Brody, C.D., Hernandez, A. & Lemus, L. Neuronal correlates of parametric working memory in the prefrontal cortex. Nature 399, 470–473 (1999).
Wang, X.J. Synaptic reverberation underlying mnemonic persistent activity. Trends Neurosci. 24, 455–463 (2001).
Cannon, S.C., Robinson, D.A. & Shamma, S. A proposed neural network for the integrator of the oculomotor system. Biol. Cybern. 49, 127–136 (1983).
Fukushima, K., Kaneko, C.R. & Fuchs, A.F. The neuronal substrate of integration in the oculomotor system. Prog. Neurobiol. 39, 609–639 (1992).
Arnold, D.B. & Robinson, D.A. A learning network model of the neural integrator of the oculomotor. Biol. Cybern. 64, 447–454 (1991).
Robinson, D.A. Integrating with neurons. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 33–45 (1989).
Aksay, E., Baker, R., Seung, H.S. & Tank, D.W. Anatomy and discharge properties of pre-motor neurons in the goldfish medulla that have eye-position signals during fixations. J. Neurophysiol. 84, 1035–1049 (2000).
Seung, H.S., Lee, D.D., Reis, B.Y. & Tank, D.W. Stability of the memory of eye position in a recurrent network of conductance-based model neurons. Neuron 26, 259–271 (2000).
Seung, H.S. How the brain keeps the eyes still. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 13339–13344 (1996).
Seung, H.S., Lee, D.D., Reis, B.Y. & Tank, D.W. The autapse: a simple illustration of short-term analog memory storage by tuned synaptic feedback. J. Comput. Neurosci. 9, 171–185 (2000).
Wilson, H.R. & Cowan, J.D. Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophysical J. 12, 1–24 (1972).
Hopfield, J.J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2554–2558 (1982).
Wang, X.J. Synaptic basis of cortical persistent activity: the importance of NMDA receptors to working memory. J. Neurosci. 19, 9587–9603 (1999).
Koulakov, A.A. Properties of synaptic transmission and the global stability of delayed activity states. Network 12, 47–74 (2001).
Lisman, J.E., Fellous, J.M. & Wang, X.J. A role for NMDA-receptor channels in working memory. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 273–275 (1998).
Schiller, J. & Schiller, Y. NMDA receptor–mediated dendritic spikes and coincident signal amplification. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, 343–348 (2001).
Nowak, L., Bregestovski, P., Ascher, P., Herbet, A. & Prochiantz, A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurons. Nature 307, 462–465 (1984).
Mayer, M.L., Westbrook, G.L. & Guthrie, P.B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurons. Nature 309, 261–263 (1984).
Aksay, E., Gamkrelidze, G., Seung, H.S., Baker, R. & Tank, D.W. In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 184–193 (2001).
Godaux, E., Cheron, G. & Mettens, P. Ketamine induces failure of the oculomotor neural integrator in the cat. Neurosci. Lett. 116, 162–167 (1990).
Mettens, P., Cheron, G. & Godaux, E. NMDA receptors are involved in temporal integration in the oculomotor system of the cat. Neuroreport 5, 1333–1336 (1994).
Priesol, A.J., Jones, G.E., Tomlinson, R.D. & Broussard, D.M. Frequency-dependent effects of glutamate antagonists on the vestibulo-ocular reflex of the cat. Brain Res. 857, 252–264 (2000).
Taube, J.S., Muller, R.U. & Ranck, J.B. Jr. Head-direction cells recorded from the postsubiculum in freely moving rats. I. Description and quantitative analysis. J. Neurosci. 10, 420–435 (1990).
Blair, H.T. & Sharp, P.E. Anticipatory head direction signals in anterior thalamus: evidence for a thalamocortical circuit that integrates angular head motion to compute head direction. J. Neurosci. 15, 6260–6270 (1995).
Shadlen, M.N. & Newsome, W.T. Neural basis of a perceptual decision in the parietal cortex (area lip) of the rhesus monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 86, 1916–1936 (2001).
Lisman, J.E. A mechanism for memory storage insensitive to molecular turnover: a bistable autophosphorylating kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 3055–3057 (1985).
Petersen, C.C., Malenka, R.C., Nicoll, R.A. & Hopfield, J.J. All-or-none potentiation at CA3-CA1 synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4732–4737 (1998).
Cimino, A. & Hervagault, J.F. Irreversible tansitions in a model substrate cycle. An experimental illustration. FEBS Lett. 263, 199–205 (1990).
Novick, A. & Weiner, M. Enzyme induction as an all-or-none phenomenon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 43, 553–566 (1957).
McAdams, H.H. & Arkin, A. Simulation of prokaryotic genetic circuits. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 27, 199–224 (1998).
Segel, L.A., Jager, E., Elias, D. & Cohen, I.R. A quantitative model of autoimmune disease and T-cell vaccination: does more mean less? Immunol. Today 16, 80–84 (1995).
Pinsky, P. & Rinzel, J. Intrinsic and network rhythmogenesis in a reduced Traub model for CA3 neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 1, 39–60 (1994).
Kepecs, A. & Raghavachari, S. in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems Vol. 14 (eds. Dietterich, T. G., Becker, S. & Ghahramani, Z.) (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2002).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to C. Kaneko and H. Sompolinsky for encouragement and to S. Seung and his group for numerous helpful suggestions. A.A.K. and A. K. were supported by fellowships from the Swartz and Alfred P. Sloan Foundations. We also acknowledge grants NIH 461434 and NSF 450578.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koulakov, A., Raghavachari, S., Kepecs, A. et al. Model for a robust neural integrator. Nat Neurosci 5, 775–782 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn893
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn893
This article is cited by
-
An oscillatory mechanism for multi-level storage in short-term memory
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Robust working memory in a two-dimensional continuous attractor network
Cognitive Neurodynamics (2023)
-
Active intrinsic conductances in recurrent networks allow for long-lasting transients and sustained activity with realistic firing rates as well as robust plasticity
Journal of Computational Neuroscience (2022)
-
Spatial representability of neuronal activity
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A neural integrator model for planning and value-based decision making of a robotics assistant
Neural Computing and Applications (2021)