Abstract
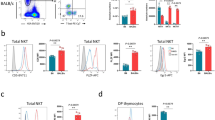
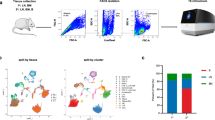
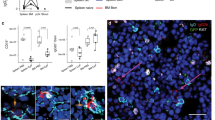
WHEN two populations of allogeneic lymphoid cells are cultured together, cellular interactions lead to blast transformation and proliferation of a portion of the cultured cells. In mice, this mixed leukocyte culture reaction (MLR) is under the independent control of two genetic systems: the multigenic major (H-2) histocompatibility system (MHS)1,2 and the unigenic (non-H-2) M locus3. The nature and cellular distribution of the gene products which mediate recognition of one cell (the stimulator cell) by another cell (the responder cell) are incompletely defined. The ‘recognising’ structure is likely to be a specific receptor present on thymus-derived (T) lymphocytes, since T cells are generally required as responder cells in MLR3–6, Recently it has been possible to distinguish, from these recognition sites, gene products which are expressed on the stimulator cells7 and which have been termed lymphocyte-activating determinants (LADs)3. Cell fractionation studies revealed that LADs of the MHS are expressed on both B and T lymphocytes8,9, whereas LADs of the M locus are preferentially if not exclusively expressed on B lymphocytes10. In this study we present evidence that LADs of the M locus as well as LADs of the MHS are also expressed on macrophages. These genetic determinants are shown to be stable in long term cultures and to induce specific one-way reactions in mixed lymphocyte–macrophage cultures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dutton, R. W., J. exp. Med., 123, 665–671 (1966).
Rychlikova, M., and Ivanyi, P., Folia Biol. (Praha), 15, 126–135 (1969).
Festenstein, H., Transplant. Rev., 15, 62–88 (1973).
Johnston, J. M., and Wilson, D. B., Cell. Immun., 1, 430–444 (1970).
Andersson, L. C., Nordling, S., and Håyry, P., J. exp. Med., 138, 324–328 (1973).
Plate, J. M. D., and McKenzie, I. F. C., Nature new Biol., 245, 247–249 (1973).
Abbasi, K., Festenstein, H., Verbi, W., and Roitt, I. M., Nature, 251, 227–229 (1974).
von Boehmer, H., J. Immun., 112, 70–78 (1974).
Lonai, P., and McDevitt, H., J. exp. Med., 140, 1317–1323 (1974).
von Boehmer, H., and Sprent, J., Nature, 249, 363–365 (1974).
Festenstein, H., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 129, 567–572 (1966).
Festenstein, H., Transplantation, 18, 555 (1974).
Halloran, P., Schirrmacher, V., and Festenstein, H., J. exp. Med., 140, 1348–1363 (1974).
Perlmann, P., and Perlmann, H., Cell. Immun., 1, 300 (1970).
Marshall, W. H., Rigo, S. J., and Melman, S., Lancet, i, 730–732 (1966).
Rode, H. N., and Gordon, J., Cell. Immun., 13, 87 (1974).
Greineder, D. K., and Rosenthal, A. S., J. exp. Med (in the press).
Wagner, H., and Wyss, C., Eur. J. Immun., 3, 549–555 (1973).
Dyminski, J. W., and Argyris, B. F., Transplantation, 11, 514–520 (1971).
Rosenthal, A. S., and Shevach, E. M., J. exp. Med., 138, 1194 (1973).
Twomey, J. J., Sharkey, O., Jr, Brown, J. A., Laughter, A. H., and Jordan, P. H., Jr, J. Immun., 104, 845–853 (1970).
Erb, P., and Feldmann, M., Nature, 254, 352 (1975).
Wagner, H., Feldmann, M., Schrader, J. W., and Boyle, W., J. exp. Med., 136, 331–343 (1972).
Feldmann, M., and Nossal, G. J. V., Transplant. Rev., 13, 3–34 (1972).
Wiener, E., and Bandieri, A., Eur. J. Immun., 4, 457–463 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SCHIRRMACHER, V., PEÑA-MARTINEZ, J. & FESTENSTEIN, H. Specific lymphocyte-activating determinants expressed on mouse macrophages. Nature 255, 155–156 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/255155a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/255155a0
This article is cited by
-
Multi-gene/allele control of Mls b of CBA/H
Immunogenetics (1989)
-
Multigene control of Mls c
Immunogenetics (1988)
-
H-2-linked genes determine the level of the primary in vitro anti-Mls response
Immunogenetics (1986)
-
Soluble Mlsa antigens: Stimulatory effect in vitro versus suppressive effect in vivo
Immunogenetics (1984)
-
Presence of HLA-D determinants on human macrophages
Nature (1976)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.