No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Optimal stopping under g-Expectation with 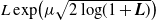 ${L}\exp\bigl(\mu\sqrt{2\log\!(1+\textbf{L})}\bigr)$-integrable reward process
${L}\exp\bigl(\mu\sqrt{2\log\!(1+\textbf{L})}\bigr)$-integrable reward process
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 September 2022
Abstract
In this paper we study a class of optimal stopping problems under g-expectation, that is, the cost function is described by the solution of backward stochastic differential equations (BSDEs). Primarily, we assume that the reward process is
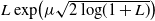 $L\exp\bigl(\mu\sqrt{2\log\!(1+L)}\bigr)$
-integrable with
$L\exp\bigl(\mu\sqrt{2\log\!(1+L)}\bigr)$
-integrable with
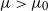 $\mu>\mu_0$
for some critical value
$\mu>\mu_0$
for some critical value
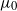 $\mu_0$
. This integrability is weaker than
$\mu_0$
. This integrability is weaker than
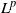 $L^p$
-integrability for any
$L^p$
-integrability for any
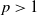 $p>1$
, so it covers a comparatively wide class of optimal stopping problems. To reach our goal, we introduce a class of reflected backward stochastic differential equations (RBSDEs) with
$p>1$
, so it covers a comparatively wide class of optimal stopping problems. To reach our goal, we introduce a class of reflected backward stochastic differential equations (RBSDEs) with
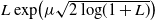 $L\exp\bigl(\mu\sqrt{2\log\!(1+L)}\bigr)$
-integrable parameters. We prove the existence, uniqueness, and comparison theorem for these RBSDEs under Lipschitz-type assumptions on the coefficients. This allows us to characterize the value function of our optimal stopping problem as the unique solution of such RBSDEs.
$L\exp\bigl(\mu\sqrt{2\log\!(1+L)}\bigr)$
-integrable parameters. We prove the existence, uniqueness, and comparison theorem for these RBSDEs under Lipschitz-type assumptions on the coefficients. This allows us to characterize the value function of our optimal stopping problem as the unique solution of such RBSDEs.
Keywords
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of Applied Probability Trust
References
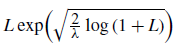 $L\exp\bigl(\sqrt{\frac{2}{\lambda}\log(1+L)}\bigr)$
-integrable terminal values. Electron. Commun. Prob. 23, 27.Google Scholar
$L\exp\bigl(\sqrt{\frac{2}{\lambda}\log(1+L)}\bigr)$
-integrable terminal values. Electron. Commun. Prob. 23, 27.Google Scholar




