Abstract
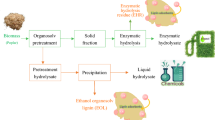
In this study, a mild-temperature two-step dilute acid and alkaline pretreatment (DA-AL) process was developed to generate highly digestible cellulose pulp from sugarcane bagasse for producing fermentable sugars by novel thermophilic cellulases derived from Phomopsis stipata SC 04. First, DA pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse at 2% (w/v) H2SO4 and 121 °C for 71 min, followed by AL pretreatment at 2.2% (w/v) NaOH and 110 °C for 100 min led to the pulp containing 86% cellulose. The cellulose pulp was hydrolyzed by the immobilized P. stipata cellulase on Ca-alginate beads, following optimization of immobilization conditions. The results showed that mixing the cellulase extract and sodium alginate solutions at a volume ratio of 1:4 led to the highest immobilization efficiencies of 99.83% for β-glucosidase and 97.52% for endoglucanase while the enzyme leakage was the lowest. The use of the immobilized cellulases led to a cellulose digestibility of 30% in the initial batch and recycling of the immobilized cellulases reduced cellulose digestibility to 18% after s recycling for two times (a total of third rounds). Overall, this study provides useful information in the use of a mild pretreatment process to produce highly digestible cellulose pulp and in the immobilization of thermophilic cellulases to produce fermentable sugars from pretreated biomass.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baruah J, Nath BK, Sharma R, Kumar S, Deka RC, Baruah DC, Kalita E (2018) Recent trends in the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for value-added products. Front Energy Res. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2018.00141
Bilal M, Iqbal HMN (2019) Naturally-derived biopolymers: potential platforms for enzyme immobilization. Int J Biol Macromol 130:462–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.152
Cardoso CL, Moraes MCD, Cass QB (2009) Imobilização de enzimas em suportes cromatográficos: uma ferramenta na busca por substâncias bioativas. Quím Nova 32:175–187
Chandel AK, Garlapati VK, Singh AK, Antunes FAF, da Silva SS (2018) The path forward for lignocellulose biorefineries: bottlenecks, solutions, and perspective on commercialization. Bioresour Technol 264:370–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.06.004
Chapman J, Ismail AE, Dinu CZ (2018) Industrial applications of enzymes: recent advances, techniques, and outlooks. Catalysts 8:238
Chen X et al (2020) The inhibitory effect of xylan on enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose is dependent on cellulose ultrastructure. Cellulose 27:4417–4428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03087-9
de Assumpção SMN, Pontes LAM, de Carvalho LS, Campos LMA, de Andrade JCF, da Silva EG (2016) Pré-tratamento combinado H2SO4/H2O2/NaOH para obtenção das frações lignocelulósicas do bagaço da cana-de-açúcar. Rev Virtual Quim 8:803–822. https://doi.org/10.5935/1984-6835.20160059
de Cassia PJ et al (2015) Thermophilic fungi as new sources for production of cellulases and xylanases with potential use in sugarcane bagasse saccharification. J Appl Microbiol 118:928–939. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12757
de Cassia Pereira J, Travaini R, Paganini Marques N, Bolado-Rodríguez S, Bocchini Martins DA (2016) Saccharification of ozonated sugarcane bagasse using enzymes from Myceliophthora thermophila JCP 1–4 for sugars release and ethanol production. Bioresour Technol 204:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.12.064
de Oliveira RL, Dias JL, da Silva OS, Porto TS (2018) Immobilization of pectinase from Aspergillus aculeatus in alginate beads and clarification of apple and umbu juices in a packed bed reactor. Food Bioprod Process 109:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2018.02.005
Dussán KJ, Silva DDV, Perez VH, da Silva SS (2016) Evaluation of oxygen availability on ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate in a batch bioreactor using two strains of xylose-fermenting yeast. Renew Energy 87:703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.10.065
Flórez Pardo LM, Salcedo Mendoza JG, López Galán JE (2019) Influence of pretreatments on crystallinity and enzymatic hydrolysis in sugar cane residues. Braz J Chem Eng 36:131–141
Galbe M, Wallberg O (2019) Pretreatment for biorefineries: a review of common methods for efficient utilisation of lignocellulosic materials. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:294. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1634-1
Giese EC, Pierozzi M, Dussán KJ, Chandel AK, da Silva SS (2013) Enzymatic saccharification of acid–alkali pretreated sugarcane bagasse using commercial enzyme preparations. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:1266–1272. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.3968
Hassanpour M, Abbasabadi M, Gebbie L, Te’o VSJ, O’Hara IM, Zhang Z (2020a) Acid-catalyzed glycerol pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse: understanding the properties of lignin and its effects on enzymatic hydrolysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:10380–10388. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01832
Hassanpour M et al (2020b) Mild fractionation of sugarcane bagasse into fermentable sugars and β-O-4 linkage-rich lignin based on acid-catalysed crude glycerol pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 318:124059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124059
Hassanpour M, Abbasabadi M, Strong J, Gebbie L, Te’o VSJ, O’Hara IM, Zhang Z (2020c) Scale-up of two-step acid-catalysed glycerol pretreatment for production of oleaginous yeast biomass from sugarcane bagasse by Rhodosporidium toruloides. Biores Technol 313:123666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123666
Hosseini SH, Hosseini SA, Zohreh N, Yaghoubi M, Pourjavadi A (2018) Covalent immobilization of cellulase using magnetic poly(ionic liquid) support: improvement of the enzyme activity and stability. J Agric Food Chem 66:789–798. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03922
Houfani AA, Anders N, Spiess AC, Baldrian P, Benallaoua S (2020) Insights from enzymatic degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose to fermentable sugars—a review. Biomass Bioenergy 134:105481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105481
Hu J, Arantes V, Saddler JN (2011) The enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates by the addition of accessory enzymes such as xylanase: is it an additive or synergistic effect? BiotecHnol Biofuels 4:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-4-36
Illanes A (2011) Whey upgrading by enzyme biocatalysis. Electron J Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol14-issue6-fulltext-11
Ingle AP, Rathod J, Pandit R, da Silva SS, Rai M (2017) Comparative evaluation of free and immobilized cellulase for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass for sustainable bioethanol production. Cellulose 24:5529–5540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1517-1
Jesionowski T, Zdarta J, Krajewska B (2014) Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: a review. Adsorption 20:801–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-014-9623-y
Johnson E (2016) Integrated enzyme production lowers the cost of cellulosic ethanol. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 10:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1634
Karp SG, Woiciechowski AL, Soccol VT, Soccol CR (2013) Pretreatment strategies for delignification of sugarcane bagasse: a review. J Braz Arch Biol Technol 56:679–689. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132013000400019
Keerti, Gupta A, Kumar V, Dubey A, Verma AK (2014) Kinetic characterization and effect of immobilized thermostable β-glucosidase in alginate gel beads on sugarcane juice. ISRN Biochem 2014:178498. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/178498
Kumar AK, Sharma S (2017) Recent updates on different methods of pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks: a review. Bioresour Bioprocess 4:7–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0137-9
Laluce C, Roldan IU, Pecoraro E, Igbojionu LI, Ribeiro CA (2019) Effects of pretreatment applied to sugarcane bagasse on composition and morphology of cellulosic fractions. Biomass Bioenerg 126:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.03.002
Li X, Zheng Y (2017) Lignin-enzyme interaction: mechanism, mitigation approach, modeling, and research prospects. Biotechnol Adv 35:466–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.03.010
Liu G, Zhang J, Bao J (2016) Cost evaluation of cellulase enzyme for industrial-scale cellulosic ethanol production based on rigorous aspen plus modeling. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1497-1
Mahajan R, Gupta V, Sharma J (2010) Comparison and suitability of gel matrix for entrapping higher content of enzymes for commercial applications. Indian J Pharm Sci 72:223–228. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.65010
Marques NP et al (2018) Cellulases and xylanases production by endophytic fungi by solid state fermentation using lignocellulosic substrates and enzymatic saccharification of pretreated sugarcane bagasse. Ind Crops Prod 122:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.05.022
Mohamad NR, Marzuki NHC, Buang NA, Huyop F, Wahab RA (2015) An overview of technologies for immobilization of enzymes and surface analysis techniques for immobilized enzymes. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29:205–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2015.1008192
Motamedi E, Sadeghian Motahar SF, Maleki M, Kavousi K, Ariaeenejad S, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Hosseini Salekdeh G (2021) Upgrading the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass by immobilization of metagenome-derived novel halotolerant cellulase on the carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03727-8
Nakanishi SC, Nascimento VM, Rabelo SC, Sampaio ILM, Junqueira TL, Rocha GJM (2018) Comparative material balances and preliminary technical analysis of the pilot scale sugarcane bagasse alkaline pretreatment to 2G ethanol production. Ind Crops Prod 120:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.04.064
Nath P, Maibam PD, Singh S, Rajulapati V, Goyal A (2021) Sequential pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse by alkali and organosolv for improved delignification and cellulose saccharification by chimera and cellobiohydrolase for bioethanol production. 3 Biotech 11:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02600-y
Obeng EM, Adam SNN, Budiman C, Ongkudon CM, Maas R, Jose J (2017) Lignocellulases: a review of emerging and developing enzymes, systems, and practices. Bioresour Bioprocess 4:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0146-8
Olofsson J, Barta Z, Börjesson P, Wallberg O (2017) Integrating enzyme fermentation in lignocellulosic ethanol production: life-cycle assessment and techno-economic analysis. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0733-0
Questell-Santiago YM, Galkin MV, Barta K, Luterbacher JS (2020) Stabilization strategies in biomass depolymerization using chemical functionalization. Nat Rev Chem 4:311–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-0187-y
Rehbein P, Raguz N, Schwalbe H (2019) Evaluating mechanical properties of silica-coated alginate beads for immobilized biocatalysis. Biochem Eng J 141:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2018.10.028
Reis ALS, Damilano ED, Menezes RSC, de Morais Jr MA (2016) Second-generation ethanol from sugarcane and sweet sorghum bagasses using the yeast Dekkera bruxellensis. Ind Crops Prod 92:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.08.007
Rocha GJM, Nascimento VM, Silva VFND, Corso DLS, Gonçalves AR (2014) Contributing to the environmental sustainability of the second generation ethanol production: delignification of sugarcane bagasse with sodium hydroxide recycling. Ind Crops Prod 59:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.05.002
Roth JCG, Hoeltz M, Benitez LB (2020) Current approaches and trends in the production of microbial cellulases using residual lignocellulosic biomass: a bibliometric analysis of the last 10 years. Arch Microbiol 202:935–951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01796-9
Samaratunga A, Kudina O, Nahar N, Zakharchenko A, Minko S, Voronov A, Pryor SW (2015) Impact of enzyme loading on the efficacy and recovery of cellulolytic enzymes immobilized on enzymogel nanoparticles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:2872–2882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1463-4
Sánchez-Ramírez J et al (2017) Cellulases immobilization on chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles: application for Agave Atrovirens lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1670-1
Silva DF, Carvalho AFA, Shinya TY, Mazali GS, Herculano RD, Oliva-Neto P (2017) Recycle of Immobilized endocellulases in different conditions for cellulose hydrolysis. Enzyme Res 2017:4362704. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4362704
Singh R, Liu H, Shanklin J, Singh V (2021) Hydrothermal pretreatment for valorization of genetically engineered bioenergy crop for lipid and cellulosic sugar recovery. Biores Technol 341:125817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125817
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2012) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Lab Anal Proced 1617:1–16
Sun S, Chen W, Tang J, Wang B, Cao X, Sun S, Sun R-C (2016) Synergetic effect of dilute acid and alkali treatments on fractional application of rice straw. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:217. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0632-9
Téllez-Luis SJ, Ramı́rez JA, Vázquez M (2002) Mathematical modelling of hemicellulosic sugar production from sorghum straw. J Food Eng 52:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0260-8774(01)00117-0
Tian S-Q, Zhao R-Y, Chen Z-C (2018) Review of the pretreatment and bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass from wheat straw materials. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 91:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.113
Van Dyk JS, Pletschke BI (2012) A review of lignocellulose bioconversion using enzymatic hydrolysis and synergistic cooperation between enzymes—factors affecting enzymes, conversion and synergy. Biotechnol Adv 30:1458–1480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.03.002
Viet TQ, Minh NP, Dao DTA (2013) Immobilization of cellulase enzyme in calcium alginate gel and its immobilized stability. Am J Res Commun 1:254–267
Won K, Kim S, Kim K-J, Park HW, Moon S-J (2005) Optimization of lipase entrapment in Ca-alginate gel beads. Process Biochem 40:2149–2154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.08.014
Yassin MA, Gad AAM, Ghanem AF, Abdel Rehim MH (2019) Green synthesis of cellulose nanofibers using immobilized cellulase. Carbohyd Polym 205:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.040
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the researcher Luis Carlos Bertolino and the Center of Mineral Technology (CETEM) for the SEM analysis, as well as professor Dr Angela Regina Araujo from the Center of Bioassays, Biosynthesis and Ecophysiology of Natural Products, IQ/UNESP, for having granted the fungus Phomopsis stipata SC 04. The authors also thank the Unesp-PROPe Research Office, for financial support through the First Projects Program (09/2016-PROPe).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SGCA; GFM; and KJD Methodology and synthesis: GFM and SGCA Physicochemical characterization, data organization, and analysis: SGCA; ECG; DDVS. Writing original draft preparation: MGS, DDVS; KJD. Writing, review, and editing: MH; ZZ; DDVS; KJD. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Almeida, S.G.C., de Mello, G.F., do Santos, M.G. et al. Saccharification of acid–alkali pretreated sugarcane bagasse using immobilized enzymes from Phomopsis stipata. 3 Biotech 12, 39 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03101-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03101-2