Abstract
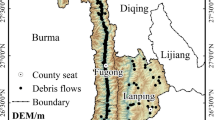
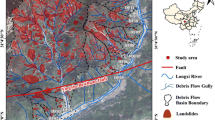
Jiuzhaigou is situated on a mountain-canyon region and is famous for frequent tectonic activities. An abundance of loose co-seismic landslides and collapses were produced on gullies after the Jiuzhaigou Earthquake on August 8, 2017, which was served as material source for debris flow in later years. Debris flow appears frequently which are seriously endangering the safety of people’s lives and properties. Even the earliest debris flow appeared in areas where no case ever reported before. The debris flow susceptibility evaluation (DFSE) is used for predicting the areas prone to debris flow, which is urgently required to avoid hazards and help to guide the strategy of preventive measures. Therefore, this work employs debris flow in Jiuzhaigou to reveal the characteristics of disaster-pregnant environment and to explore the application of machine learning in DFSE. Some new viewpoints are suggested: (i) Material density factor of debris flow is first adopted in this work, and it is proved to be a critical factor for triggering debris flows by sensitivity analysis method. (ii) Deep neural network and convolutional neural network (CNN) achieve relatively good area under the curve (AUC) values and are 0.021–0.024 higher than traditional machine learning methods. (iii) Watershed units combined with CNN-based model can achieve more accurate, reliable and practical susceptibility map. This work provides an idea for prevention of debris flow in mountainous lands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Amari, S., Wu, S., 1999. Improving Support Vector Machine Classifiers by Modifying Kernel Functions. Neural Networks, 12(6): 783–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-6080(99)00032-5
Apté, C., Damerau, F., Weiss, S. M., 1994. Automated Learning of Decision Rules for Text Categorization. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 12(3): 233–251. https://doi.org/10.1145/183422.183423
Barbu, A., She, Y. Y., Ding, L. J., et al., 2017. Feature Selection with Annealing for Computer Vision and Big Data Learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39(2): 272–286. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2544315
Blais-Stevens, A., Behnia, P., 2016. Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping Using a Qualitative Heuristic Method and Flow-R along the Yukon Alaska Highway Corridor, Canada. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 16(2): 449–462. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-16-449-2016
Bregoli, F., Medina, V., Chevalier, G., et al., 2015. Debris-Flow Susceptibility Assessment at Regional Scale: Validation on an Alpine Environment. Landslides, 12(3): 437–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0493-x
Bui, D. T., Pradhan, B., Lofman, O., et al., 2012. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment in the Hoa Binh Province of Vietnam: A Comparison of the Levenberg-Marquardt and Bayesian Regularized Neural Networks. Geomorphology, 171/172: 12–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j-geomorph.2012.04.023
Can, T., Nefeslioglu, H. A., Gokceoglu, C., et al., 2005. Susceptibility Assessments of Shallow Earthflows Triggered by Heavy Rainfall at Three Catchments by Logistic Regression Analyses. Geomorphology, 72(1/2/3/4): 250–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.05.011
Carrara, A., Crosta, G., Frattini, P., 2008. Comparing Models of Debris-Flow Susceptibility in the Alpine Environment. Geomorphology, 94(3/4): 353–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.10.033
Chaabani, C., Chini, M., Abdelfattah, R., et al., 2018. Flood Mapping in a Complex Environment Using Bistatic TanDEM-X/TerraSAR-X InSAR Coherence. Remote Sensing, 10(12): 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121873
Chang, M., Tang, C., Zhang, D. D., et al., 2014. Debris Flow Susceptibility Assessment Using a Probabilistic Approach: A Case Study in the Longchi Area, Sichuan Province, China. Journal of Mountain Science, 11(4): 1001–1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2747-9
Chen, Y., Qin, S. W., Qiao, S. S., et al., 2020. Spatial Predictions of Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping Using Convolutional Neural Networks in Jilin Province, China. Water, 12(8): 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082079
Cheng, J. J., Cao, C., Qin, S. W., et al., 2018. Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping Using an Improved Information Value Model Based on a Combined Weighting Method for Jilin Province, China. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 27: 9706–9716.
Conoscenti, C., Ciaccio, M., Caraballo-Arias, N. A., et al., 2015. Assessment of Susceptibility to Earth-Flow Landslide Using Logistic Regression and Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines: A Case of the Belice River Basin (Western Sicily, Italy). Geomorphology, 242: 49–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.09.020
Cui, P., Chen, X. Q., Zhu, Y. Y., et al., 2011. The Wenchuan Earthquake (May 12, 2008), Sichuan Province, China, and Resulting Geohazards. Natural Hazards, 56(1): 19–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-009-9392-1
Delen, D., 2010. A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Techniques for Student Retention Management. Decision Support Systems, 49(4): 498–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.06.003
Delen, D., Tomak, L., Topuz, K., et al., 2017. Investigating Injury Severity Risk Factors in Automobile Crashes with Predictive Analytics and Sensitivity Analysis Methods. Journal of Transport & Health, 4: 118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jth.2017.01.009
Di, B. F., Zhang, H. Y., Liu, Y. Y., et al., 2019. Assessing Susceptibility of Debris Flow in Southwest China Using Gradient Boosting Machine. Scientific Reports, 9: 12532. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48986-5
Dixon, B., Candade, N., 2008. Multispectral Landuse Classification Using Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines: One or the Other, or Both?. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29(4): 1185–1206. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160701294661
Dou, J., Yunus, A. P., Bui, D. T., et al., 2019. Assessment of Advanced Random Forest and Decision Tree Algorithms for Modeling Rainfall-Induced Landslide Susceptibility in the Izu-Oshima Volcanic Island, Japan. Science of the Total Environment, 662: 332–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.221
Gao, R. Y., Wang, C. M., Liang, Z., 2021. Comparison of Different Sampling Strategies for Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping: A Case Study Using the Centroids of the Scarp Area, Flowing Area and Accumulation Area of Debris Flow Watersheds. Journal of Mountain Science, 18(6): 1476–1488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6471-y
Gong, X. L., Chen, K. T., Chen, X. Q., et al., 2020. Characteristics of a Debris Flow Disaster and Its Mitigation Countermeasures in Zechawa Gully, Jiuzhaigou Valley, China. Water, 12(5): 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051256
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A., 2016. Deep Learning: Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning Series. The MIT Press, Cambridge Guzzetti, F., Carrara, A., Cardinali, M., et al., 1999. Landslide Hazard Evaluation: a Review of Current Techniques and Their Application in a Multi-Scale Study, Central Italy. Geomorphology, 31(1/2/3/4): 181–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(99)00078-1
Hinton, G., Deng, L., Yu, D., et al., 2012. Deep Neural Networks for Acoustic Modeling in Speech Recognition: The Shared Views of Four Research Groups. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 29(6): 82–97. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597
Hong, H. Y., Panahi, M., Shirzadi, A., et al., 2018. Flood Susceptibility Assessment in Hengfeng Area Coupling Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System with Genetic Algorithm and Differential Evolution. Science of the Total Environment, 621: 1124–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.114
Horton, P., Jaboyedoff, M., Rudaz, B., et al., 2013. Flow-R, a Model for Susceptibility Mapping of Debris Flows and Other Gravitational Hazards at a Regional Scale. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 13(4): 869–885. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-869-2013
Hou, S. S., Cao, P., Li, A., et al., 2021. Debris Flow Hazard Assessment of the Eryang River Watershed Based on Numerical Simulation. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 861(6): 062002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/861/6/062002
Hu, X. D., Hu, K. H., Tang, J. B., et al., 2019. Assessment of Debris-Flow Potential Dangers in the Jiuzhaigou Valley Following the August 8, 2017, Jiuzhaigou Earthquake, Western China. Engineering Geology, 256: 57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.05.004
Huang, F. M., Zhang, J., Zhou, C. B., et al., 2020b. A Deep Learning Algorithm Using a Fully Connected Sparse Autoencoder Neural Network for Landslide Susceptibility Prediction. Landslides, 17(1): 217–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01274-9
Huang, H., Shi, S. W., Yang, S., 2020a. Study on the Damage of the August 8, 2017 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake to Debris Flow Mitigation Engineering in the National Park. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(9): 1773–1786 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Huang, W. B., Ding, M. T., Wang, D., et al., 2022. Evaluation of Landslide Susceptibility Based on Layer Adaptive Weighted Convolutional Neural Network Model along Sichuan-Tibet Traffic Corridor. Earth Science, 47(6): 2015–2030. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx. 2021.243 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Jiang, B., Ren, Q., Dai, F., et al., 2020. Parallel Multi-Task Cascade Convolution Neural Network Optimization Algorithm for Real-Time Dynamic Face Recognition. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 14(10): 4117–4135. https://doi.org/10.3837/tiis.2020.10.011
Kang, S., Lee, S. R., 2018. Debris Flow Susceptibility Assessment Based on an Empirical Approach in the Central Region of South Korea. Geomorphology, 308: 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.01.025
Kappes, M. S., Malet, J. P., Remaître, A., et al., 2011. Assessment of Debris-Flow Susceptibility at Medium-Scale in the Barcelonnette Basin, France. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 11(2): 627–641. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-11-627-2011
Kavzoglu, T., Colkesen, I., Sahin, E. K., 2019. Machine Learning Techniques in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Survey and a Case Study. Landslides: Theory, Practice and Modelling. Springer, Cham. 283–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77377-3_13
Kavzoglu, T., Sahin, E. K., Colkesen, I., 2014. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis, Support Vector Machines, and Logistic Regression. Landslides, 11(3): 425–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0391-7
King, G., Zeng, L. C., 2001. Logistic Regression in Rare Events Data. Political Analysis, 9(2): 137–163. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pan.a004868
Klose, M., 2015. Landslide Databases as Tools for Integrated Assessment of Landslide Risk. Springer, Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20403-1
Komac, M., 2006. A Landslide Susceptibility Model Using the Analytical Hierarchy Process Method and Multivariate Statistics in Perialpine Slovenia. Geomorphology, 74(1/2/3/4): 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.07.005
Lay, U. S., Pradhan, B., Yusoff, Z. B. M., et al., 2019. Data Mining and Statistical Approaches in Debris-Flow Susceptibility Modelling Using Airborne LiDAR Data. Sensors, 19(16): 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163451
Le Cun, Y., 1989. Generalization and Network Design Strategies. Connectionism in Perspective, 19: 143–155
Le Cun, Y., Ranzato, M., 2013. Deep Learning Tutorial. Tutorials in International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’13). Citeseer. 1–29
Li, W. B., Fan, X. M., Huang, F. M., et al., 2021. Uncertainties of Landslide Susceptibility Modeling under Different Environmental Factor Connections and Prediction Models. Earth Science, 46(10): 3777–3795 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, Y. C., Chen, J. P., Li, Z. H., et al., 2021. A Case Study of Debris Flow Risk Assessment and Hazard Range Prediction Based on a Neural Network Algorithm and Finite Volume Shallow Water Flow Model. Environmental Earth Sciences, 80(7): 275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09580-z
Li, Y. W., Wang, X. M., Mao, H., 2020. Influence of Human Activity on Landslide Susceptibility Development in the Three Gorges Area. Natural Hazards, 104(3): 2115–2151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04264-6
Li, Y. W., Xu, L. R., Zhang, L. L., et al., 2022. Study on Development Patterns and Susceptibility Evaluation of Coseismic Landslides within Mountainous Regions Influenced by Strong Earthquakes. Earth Science, Online. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2022.224 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liang, W. J., Zhuang, D. F., Jiang, D., et al., 2012. Assessment of Debris Flow Hazards Using a Bayesian Network. Geomorphology, 171/172: 94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.05.008
Liang, Z., Wang, C. M., Zhang, Z. M., et al., 2020. A Comparison of Statistical and Machine Learning Methods for Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 34(11): 1887–1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01851-8
Liu, C. N., Dong, J. J., Peng, Y. F., et al., 2009. Effects of Strong Ground Motion on the Susceptibility of Gully Type Debris Flows. Engineering Geology, 104(3/4): 241–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.10.012
Lobo, J. M., Jiménez-Valverde, A., Real, R., 2008. AUC: A Misleading Measure of the Performance of Predictive Distribution Models. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 17(2): 145–151. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2007.00358.x
Ma, C., Hu, K. H., Zou, Q., et al., 2013. Characteristics of Clustering Debris Flows in Wenchuan Earthquake Zone. Journal of Mountain Science, 10(6): 953–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2410-5
Marcus, G., 2018. Deep Learning: A Critical Appraisal.: arXiv: 1801.00631. https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.00631
Minaee, S., Kalchbrenner, N., Cambria, E., et al., 2022. Deep Learning: Based Text Classification: A Comprehensive Review. ACM Computing Surveys, 54(3): 1–40. https://doi.org/10.1145/3439726
Mojaddadi, H., Pradhan, B., Nampak, H., et al., 2017. Ensemble Machine-Learning-Based Geospatial Approach for Flood Risk Assessment Using Multi-Sensor Remote-Sensing Data and GIS. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 8(2): 1080–1102. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1294113
Moraci, N., Mandaglio, M. C., Gioffrè, D., et al., 2017. Debris Flow Susceptibility Zoning: An Approach Applied to a Study Area. Rivista Italiana di Geotecnica, 51(2): 47–62. https://doi.org/10.19199/2017.2.0557-1405.047
Nguyen, A. D., Kim, J., Oh, H., et al., 2018. Deep Visual Saliency on Stereoscopic Images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 28(4): 1939–1953. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2879408
Oh, H. J., Lee, S., 2011. Integration of Ground Subsidence Hazard Maps of Abandoned Coal Mines in Samcheok, Korea. International Journal of Coal Geology, 86(1): 58–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2010.11.009
Oprea, S., Martinez-Gonzalez, P., Garcia-Garcia, A., et al., 2022. A Review on Deep Learning Techniques for Video Prediction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 44(6): 2806–2826. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3045007
Pal, M., 2005. Random Forest Classifier for Remote Sensing Classification. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26(1): 217–222. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160412331269698
Peterson, A. T., Papeş, M., Soberón, J., 2008. Rethinking Receiver Operating Characteristic Analysis Applications in Ecological Niche Modeling. Ecological Modelling, 213(1): 63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2007.11.008
Pham, B. T., Prakash, I., Khosravi, K., et al., 2019. A Comparison of Support Vector Machines and Bayesian Algorithms for Landslide Susceptibility Modelling. Geocarto International, 34(13): 1385–1407. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1489422
Platt, J., 1999. Probabilistic Outputs for Support Vector Machines and Comparisons to Regularized Likelihood Methods. Advances in Large Margin Classifiers, 10(3): 61–74
Qian, H., Zhou, R., Ma, S. H., et al., 1999. South Segment of Minjiang Fault and Diexi Earthquake in 1933. Earthquake Research in China, 15(4): 333–338 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Qing, F., Zhao, Y., Meng, X. M., et al., 2020. Application of Machine Learning to Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping along the China–Pakistan Karakoram Highway. Remote Sensing, 12(18): 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182933
Rammer, W., Seidl, R., 2019. Harnessing Deep Learning in Ecology: An Example Predicting Bark Beetle Outbreaks. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01327
Rampasek, L., Goldenberg, A., 2016. TensorFlow: Biology’s Gateway to Deep Learning?. Cell Systems, 2(1): 12–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2016.01.009
Saltelli, A., 2002. Making Best Use of Model Evaluations to Compute Sensitivity Indices. Computer Physics Communications, 145(2): 280–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-4655(02)00280-1
Schmidhuber, J., 2015. Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview. Neural Networks, 61: 85–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003
She, J., Zhou, X., Liu, F., et al., 2020. Preliminary Results and Analyses of Post-Earthquake Geological Hazards in Jiuzhaigou Based on Airborne Lidar and Imagery. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 43: 541–545. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-xliii-b3-2020-541-2020
Shieh, C. L., Chen, Y. S., Tsai, Y. J., et al., 2009. Variability in Rainfall Threshold for Debris Flow after the Chi-Chi Earthquake in Central Taiwan, China. International Journal of Sediment Research, 24(2): 177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6279(09)60025-1
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., et al., 2014. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1): 1929–1958
Sujatha, E. R., 2020. A Spatial Model for the Assessment of Debris Flow Susceptibility along the Kodaikkanal-Palani Traffic Corridor. Frontiers of Earth Science, 14(2): 326–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-019-0775-7
Sun, J. B., Yue, H., Shen, Z. K., et al., 2018. The 2017 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake: A Complicated Event Occurred in a Young Fault System. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(5): 2230–2240. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017gl076421
Sun, X. H., Chen, J. P., Han, X. D., et al., 2020. Application of a GIS-Based Slope Unit Method for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping along the Rapidly Uplifting Section of the Upper Jinsha River, South-Western China. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 79(1): 533–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01572-5
Tehrany, M. S., Pradhan, B., Jebur, M. N., 2015. Flood Susceptibility Analysis and Its Verification Using a Novel Ensemble Support Vector Machine and Frequency Ratio Method. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 29(4): 1149–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1021-9
Thamba, N. B., Aravind, A., Rakesh, A., et al., 2018. Application of EMD, ANN and DNN for Self-Aligning Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Archives of Acoustics, 43(2): 163–175. https://doi.org/10.24425/122364
Tu, J. V., 1996. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Artificial Neural Networks Versus Logistic Regression for Predicting Medical Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 49(11): 1225–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-4356(96)00002-9
Vinayakumar, R., Soman, K. P., Poornachandran, P., 2017. Applying Convolutional Neural Network for Network Intrusion Detection. 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI). September 13–16, 2017, Udupi, India. IEEE. 1222–1228. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2017.8126009
Wang, G. L., 2013. Lessons Learned from Protective Measures Associated with the 2010 Zhouqu Debris Flow Disaster in China. Natural Hazards, 69(3): 1835–1847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0772-1
Wang, W. P., Yin, Y. P., Zhu, S. N., et al., 2019. Dynamic Analysis of a Long-Runout, Flow-Like Landslide at Areletuobie, Yili River Valley, Northwestern China. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 78(5): 3143–3157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1322-6
Wang, Z. L., Lai, C. G., Chen, X. H., et al., 2015. Flood Hazard Risk Assessment Model Based on Random Forest. Journal of Hydrology, 527: 1130–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.06.008
Xiong, K., Adhikari, B. R., Stamatopoulos, C. A., et al., 2020. Comparison of Different Machine Learning Methods for Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping: A Case Study in the Sichuan Province, China. Remote Sensing, 12(2): 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020295
Yi, Y. N., Zhang, Z. J., Zhang, W. C., et al., 2020. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Multiscale Sampling Strategy and Convolutional Neural Network: A Case Study in Jiuzhaigou Region. CATENA, 195: 104851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104851
Yin, Y. P., Cheng, Y. L., Liang, J. T., et al., 2016. Heavy-Rainfall-Induced Catastrophic Rockslide-Debris Flow at Sanxicun, Dujiangyan, after the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 Earthquake. Landslides, 13(1): 9–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0554-9
Zhang, T. Y., Li, Y. N., Wang, T., et al., 2022. Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Models and Novel Deep Learning-Based Algorithm for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Geoscience Letters, 9(1): 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40562-022-00236-9
Zhang, W., Chen, J. P., Wang, Q., et al., 2013. Susceptibility Analysis of Large-Scale Debris Flows Based on Combination Weighting and Extension Methods. Natural Hazards, 66(2): 1073–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0539-0
Zhang, Y. H., Ge, T. T., Tian, W., et al., 2019. Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping Using Machine-Learning Techniques in Shigatse Area, China. Remote Sensing, 11(23): 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232801
Zhang, Y. Q., Yang, N., Shi, W., et al., 2008. Neotectonics of Eastern Tibet and Its Control on the Wenchuan Earthquake. Acta Geologica Sinica. 82(12):1668–1678 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, Y. Y., Huang, C., Huang, C., et al., 2022. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Typical Debris Flow Sources after an Earthquake. Landslides, 19(9): 2263–2275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01883-x
Zhao, B., Wang, Y. S., Luo, Y. H., et al., 2018. Landslides and Dam Damage Resulting from the Jiuzhaigou Earthquake (8 August 2017), Sichuan, China. Royal Society Open Science, 5(3): 171418. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.171418
Zhao, D. Z., Qu, C. Y., Shan, X. J., et al., 2018. InSAR and GPS Derived Coseismic Deformation and Fault Model of the 2017 Ms7.0 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake in the Northeast Bayanhar Block. Tectonophysics, 726: 86–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2018.01.026
Zhao, W. Y., You, Y., Chen, X. Q., et al., 2020. Case Study on Debris-Flow Hazard Mitigation at a World Natural Heritage Site, Jiuzhaigou Valley, Western China. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 11(1): 1782–1804. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2020.1810784
Zhou, R. J., Pu, X. H., He, Y. L., et al., 2000. Recent Activity of Minjiang Fault Zone, Uplift of Minshan Block and Their Relationship with Seismicity of Sichuan. Seismology and Geology, 22: 285–294 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhou, W., Tang, C., 2014. Rainfall Thresholds for Debris Flow Initiation in the Wenchuan Earthquake-Stricken Area, Southwestern China. Landslides, 11(5): 877–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0421-5
Zhou, W., Tang, C., Van Asch, T. W. J., et al., 2016. A Rapid Method to Identify the Potential of Debris Flow Development Induced by Rainfall in the Catchments of the Wenchuan Earthquake Area. Landslides, 13(5): 1243–1259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0631-0
Zhu, H., Wen, X. Z., 2009. Stress Triggering Process of the 1973 to 1976 Songpan, Sichuan, Sequence of Strong Earthquakes. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(4): 994–1003 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu, L., Huang, L. H., Fan, L. Y., et al., 2020. Landslide Susceptibility Prediction Modeling Based on Remote Sensing and a Novel Deep Learning Algorithm of a Cascade-Parallel Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors, 20(6): 1576. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061576
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42172322, U2268213 and 42007419), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1505403), Natural Sciences Funding Project of Hunan Province (No. 2020JJ5981), Excellent Youth Fund Project of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 21B0226) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (No. 2022ZZTS0646). The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1803-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Xu, L., Shang, Y. et al. Debris Flow Susceptibility Evaluation in Meizoseismal Region: A Case Study in Jiuzhaigou, China. J. Earth Sci. 35, 263–279 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1803-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1803-1