Abstract
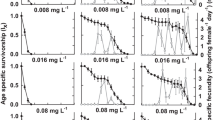
An attempt to evaluate aluminum toxicity to living organisms was undertaken in the study. A laboratory experiment was conducted to determine aluminum bioaccumulation and toxicity in Chironomus and Chaoborus larvae and in Cyprinus carpio L. roe depending on aluminum concentration in water reflecting natural chemical composition. Water was examined for temperature, pH, electrical conductivity, dissolved oxygen, color, nitrate nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, sulfates by spectrophotometric method; total hardness and chlorides by titration method; and calcium, magnesium, sodium by flame atomic absorption spectrometry, total aluminum by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Determination of aluminum levels in water, roe, and zooplankton was carried out after mineralization using electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Aluminum bioaccumulation factor in roe was determined with respect to concentration in water. Moreover, acute toxicity (LC50) was calculated. In the roe experiment, aluminum concentration in water at the end of the experiment was 0.0635–0.1283 mgAl∙dm−3. The lowest values were noted for the control sample and the highest for water with 0.03 mgAl∙dm−3 aluminum content. The final aluminum level in roe was, like in water, the highest in roe treated with 0.03 mgAl∙dm−3 (18.95 mgAl∙kg−1), and the lowest in roe treated with 3.00 mgAl∙dm−3 (6.96 mgAl∙kg−1). Aluminum bioaccumulation in roe was the strongest in the control. Survival rate ranged from 2.00 to 97.00%, which shows higher sensitivity of roe to aluminum concentration. LC50 value for Chaoborus was 0.6464 mgAl⋅dm−3, and for Chironomus 0.2076 mgAl⋅dm−3 indicating that Chironomus is more sensitive to aluminum toxic effects. Concentration of 3.0 mgAl∙dm−3 caused the highest mortality. Aluminum in both species at each concentration reached the highest levels after one day (24 h), 254.58 mg⋅kg−1 for Chaoborus and 3107 mg⋅kg−1 for Chironomus. After another day, aluminum levels decreased. This demonstrated the differential accumulation of aluminum depending on the species, which predisposes Chironomus as a better indicator organism. This type of research is important from the point of view of aquaculture, which is a targeted activity with a high degree of economic importance, but is also important for aquatic organisms living in natural conditions. Fish reproduction takes place in both types of waters, so all these reservoirs regardless of their source of destination should be inspected.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Markert BA, Breure AM, Zechmeister HG (2003) Bioindicators & Biomonitors, Principles, Concepts and Applications. Elsevier
Skibniewska E, Skibniewski M (2019) Aluminium, Al. In: Kalisińska E. Mammals and birds as bioindicators of trace element contaminations in terrestrial environments. An Ecotoxicological Assessment of the Northern Hemisphere. Springer, Switzerland, pp 413-462. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00121-6
Howells GD, Brown DJA, Sadler K (1983) Effects of acidity, calcium, and aluminium on fish survival and productivity—a review. J Sci Food Agric 34(6):559–570. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740340606
Kolada A, Pasztaleniec A, Bielczyńska A, Ochocka A, Kutyła S, Zalewska T, Drgas N, Krzymiński W, Szoszkiewicz K, Gebler D, Borowiec P, Panek P (2018) Physicochemical indicators in the assessment of the ecological status of surface waters - verification of environmental standards. Warsaw: Chief Inspectorate for Environmental Protection - its a book published by Polish Chief Inspectorate for Environmental Protection
Dinis F, Liu H, Liu Q, Wang X, Xu M (2021) Ecological risk assessment of cadmium in karst lake sediments based on Daphnia pulex ecotoxicology. Minerals 11:650. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060650
Gonçalves AMM, Castro BB, Pardal MA, Gonçalves F (2007) Salinity effects on survival and life history of two freshwater cladocerans (Daphnia magna and Daphnia longispina). Ann Limnol-Int J Lim 43(1):13–20. https://doi.org/10.1051/limn/2007022
Herrmann J (1987) Aluminum impact on freshwater invertebrates at low pH: a review. In: Landner. L. (eds) Speciation of Metals in Water. Sediment and Soil Systems. Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences 11:57–175. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0019700
Lutnicka H, Fochtman P, Bojarski B, Ludwikowska A, Formicki G (2014) The influence of low concentration of cypermethrin and deltamethrin on phyto- and zooplankton of surface waters. Folia Biol (Kraków) 62(3):251–257. https://doi.org/10.3409/fb62_3.251
Łaszczyca P, Francikowski J, Guzik J, Nikiel A, Kłosok M, Michalczyk K, Augustyniak M, Migula P (2012) Usefulness of ecotoxicological biotests for assessing the biological state of waters on the example of the Goczałkowice dam reservoir. Kosmos 61(3):381–392
Rosenberg DM (1992) Freshwater biomonitoring and Chironomidae. Neth J Aquatic Ecol 26(2–4):101–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02255231
Senze M, Kowalska-Góralska M, Białowąs H (2015) Evaluation of the aluminium load in the aquatic environment of two small rivers in the Baltic Sea catchment area. J Elementol 20(4):987–998. https://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2015.20.1.757
Vorobieva OV, Isakova EF, Zaec MA, Merzelikin AY, Samoilova TA (2020) Toxicity of aluminum ions to Daphnia magna straus depending on the hardness of natural and artificial water. Mosc Univ Biol Sci Bull 75(4):231–236. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392520040124
Vuorinen M, Vuorinrn PJ, Hoikka J, Peuranen S (1993) Lethal and sublethal threshold values of aluminium and acidity to pike (Esox lucius), whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus pallasi), pike perch (Stizostedion lucioperca) and roach (Rutilus rutilus) yolk-sac fry. Sci Total Environ 134(2):953–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(05)80102-0
Weenink EFJ, Kraak MHS, van Teulingen C, Kuijt S, van Herk MJ, Sigon CAM, Piel T, Sandrini G, Leon-Grooters M, de Baat ML, Huisman J, Visser PM (2022) Sensivity of phytoplankton, zooplankton and macroinvertebrates to hydrogen peroxide treatments of cyanobacterial blooms. Water Res 225:119169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119169
Alvarado C, Cortez-Valladolid DM, Herrera-López EJ, Godínez X (2021) Metal bioaccumulation by carp and catfish cultured in Lake Chapala, and weekly intake assessment. Appl Sci 11(13):6087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136087
Al-Weher SM (2008) Levels of heavy metal Cd, Cu and Zn in three fish species collected from the northern Jordan Valley, Jordan. Jordan J Biol Sci 1(1):41–46
Bajzik P, Golian J, Židek R, Krall M, Walczycka M, Tkaczewska J (2012) Identification of the common carp (Cypronus carpio) species using real-time PCR methods. Żywność Nauka Technologia Jakość 5(84):166–176
Bekhit AED, Morton JD, Dawson Ch (2008) Effect of processing conditions on trace elements in fish roe from six commercial New Zealand fish species. J Agric Food Chem 56(12):4846–4853. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8005646
Cabejszek I, Stasiak M (1960) Studies on the toxic effect of some metals on the water biocensois - Daphnia Magna employed as index. Roczniki PZH 11(6):533–540
Caglar M, Canpolat O, Selamoglu Z (2019) Determination of some heavy metal levels in three freshwater fish in Keban Dam Lake (Turkey) for public consumption. Iran J Fish Sci 18(1):188–198. https://doi.org/10.22092/ijfs.2018.117890
Gurganari L, Dastageer G, Mushtaq R, Khwaja S, Uddin S, Baloch MI, Hasni S (2022) Assessment of heavy metals in cyprinid fishes: rivers of district Khuzdar Balochistan Pakistan. Braz J Biol 84:e256071. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.256071
Huang Y, Zhang D, Xu Z, Yuan S, Li Y, Wang L (2017) Effect of overlying water pH, dissolved oxygen and temperature on heavy metal release from river sediments under laboratory conditions. Arch Environ Prot 43(2):28–36. https://doi.org/10.1515/aep-2017-0014
Kowalska-Góralska M, Senze M, Łuczyńska J, Czyż K (2020) Effects of the ionic and nanoparticle forms of Cu and Ag on these metals’ bioaccumulation in the eggs and fry of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss W.). Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:6392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176392
Ługowska K, Kondera E (2020) Developmental anomalies in ide (Leuciscus idus L.) larvae caused by copper and cadmium. Roczniki Nauk Pol Tow Zoot 16(3):37–51. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0014.3996
Moghadasi M, Heshmati A, Vahidinia A (2021) Measurement of heavy metals (nickel, chromium, and cobalt) in wild and farmed carps (Cyprinus carpio) of Hamadan Province). Avicenna J Environ Health Eng 8(2):97–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03641-z
Nzeve JK, Kitur E (2019) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) of Masigna Dam, Kenya. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 13(8):23–28
Öztürk M, Özözen G, Minareci O, Minareci E (2009) Determination of heavy metals in fish, water and sediments of Asvar Dam Lake in Turkey. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 6(2):73–80
Pynnönen K (1995) Effect of pH, hardness and maternal pre-exposure on the toxicity of Cd, Cu and Zn to the glochidial larvae of a freshwater clam Anodonta cygnea. Wat Res 29(1):247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)00126-R
Regaldo L, Reno U, Gervasio S, Troiani H, Gagneten AM (2014) Effects of metal on Daphnia magna and cladocerans representatives of the Argentinean Fluvial Littoral. J Environm Biol 35:689–697
Sahiti H, Bislimi K, Rexhepi A, Dalo E (2020) Metal accumulation and effect of vitamin C and E in accumulated heavy metals in different tissues in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) treated with heavy metals. Pol J Environ Stud 29(1):799–805. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/103354
Sarosiek B, Pietrusewicz M, Radziwoniuk J, Glogowski J (2009) The effect of copper, zinc, mercury and cadmium on some sperm enzyme activities in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Reproductive Biol 9(3):295–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1642-431X(12)60033-3
Ullah S, Hassan S, Dhama K (2016) Level of heavy metals in two highly consumed fish species at District Lowe Dir, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Pak J Biol Sci 19(3):115–121. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2016.115.121
Vičarová P, Dočekalová H, Ridošková A, Pelcová P (2016) Heavy metals in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) from three reservoirs in the Czech Republic. Czech J Food Sci 34(5):422–428. https://doi.org/10.17221/100/2016-CJFS
Zahidah J, Aprilliani IM (2017) Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in various fish meat from Cirata Da, West Java, Indonesia. AACL Bioflux 10(2):241–246
Ociepa-Kubicka A, Ociepa E (2012) Toxic effects of heavy metals on plants, animals and humans. Inż Ochr Środ 15(2):169–180
Barabasz W, Albińska D, Jaśkowska M, Lipiec J (2002) Ecotoxicology of aluminium. Polish J Environ St 11(3):199–203
Kabata-Pendias A (2010) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press
Borkowska B (1988) Aluminium toxicity (Al). Wiadomości Bot 32(3):157–166
Gworek B (2006) Aluminium in the natural environment and its toxicity. Ochrona Środ Zas Natur 29:27–38
Hamda A, Javed M, Jabeen G (2011) Acute toxicity of aluminium to the fish (Catla catla, Labeo rohita and Cirrhina mrigala). Pak Vet J 32(1):85
Howells G, Dalziel TRK, Reader JP, Solbé JF (1994) Aluminium and freshwater fish water quality criteria. In: Water quality for freshwater fish. Environmental topics vol 6
Srinivasan PT, Viraraghavan T (2002) Characterisation and concentration profile of aluminium during drinking-water treatment. Water 28(1):99–106. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v28i1.4873
Wold LA, Moore BC, Dasgupta N (2005) Life-history responses of Daphnia pulex with exposure to aluminum sulfate. Lake Reserv Manag 21(4):383–390. https://doi.org/10.1080/07438140509354443
Ljubojević D, Dorđević V, Ćirković M (2017) Evaluation of nutritive quality of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ Sci 85 012013 https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/85/1/012013
Steffens W, Wirth M (2007) Influence of nutrition on the lipid quality of pond fish: common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and tench (Tinca tinca). Aquacult Int 15:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-007-9088-z
Szarek J, Skibniewska KA, Guziur J (2008) Technology of fish production and carp quality. Influence of the type of fish production and quality of water environment on some breeding and patomorphologic parameters of consumption carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). ElSet, Olsztyn. pp 106
Adams WJ, Cardwell AS, DeForest DK, Gensemer RW, Santore RC, Wang N, Nordheim E (2018) Aluminium bioavailability and toxicity to aquatic organisms: introduction to the special section. Environ Toxicol Chem 37(1):34–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3879
Gensemer RW, Playle RC (1999) The bioavailability and toxicity of aluminum in aquatic environments. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 29(4):315–450
Botté A, Zaidi M, Guery J, Fichet D, Leignel V (2002) Aluminium in aquatic environments: abundance and ecotoxicological impacts. Aquat Ecol 56(3):751–773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-021-09936-4
Dietrich D, Schlatter C (1989) Aluminium toxicity to rainbow trout at low pH. Aquat Toxicol 15:197–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(89)90036-2
Kalff J (2002) Limnology. Inland water ecosystems. Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River. New Jersey, pp 536
Kluczka J, Zołotajkin M, Ciba J (2012) Speciation of aluminium in the water and bottom sediment of fish-breeding ponds. Archives Environ Prot 38(1):83–96. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10265-012-0007-7
Kotowski M, Saczuk M (1997) Aluminium in water and soil environment. Ekoinżynieria 2:22–29
Kotowski M, Wieteska E, Pawłowski L, Kozak Z (1994) Characterization of the occurrence of various forms of aluminum in selected elements of the environment in Poland. pp. 99 Warsaw: Chief Inspectorate for Environmental Protection - its a book published by Polish Chief Inspectorate for Environmental Protection
Kubiak J, Machula S, Stepanowska K, Biernaczyk M (2013) The influence of the content of aluminium on the biocenosis of the waters of lakes with poorly urbanized reception basins. Inżynieria Ekol 35:95–105
Miller TE, Iqbal N, Reader SM, Mahmood A, Cant KA, King IP (1997) A cytogenetic approach to the improvement of aluminium tolerance in wheat. New Phytol 137:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00821.x
Zuziak J, Jakubowska M (2016) Aluminium in the environment and its influence on living organisms. Analit 2:110–120
Pasieczna A (2012) Geochemical atlas. National Geological Institute-National Research Institute. https://mapgeochem.pgi.gov.pl/atlas-polski/atlas-geochemiczny-polski/atlas-geochemiczny-polski/
Senze M, Kowalska-Góralska M, Czyż K (2022) Aluminum bioaccumulation in reed canary grass (Phalaris arundinacea L) from rivers in southwestern Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19052930
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1999) Biogeochemistry of trace elements. pp.400. Scientific Publishing House PWN, Warsaw
Market B (1992) Presence and significance of naturally occurring chemical elements of the periodic system in the plant organism and consequences for future investigations on inorganic environmental chemistry in ecosystems. Vegetatio 103:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00033413
Gaillardet J, Viers J, Dupré B (2014) Trace elements in river waters. Treatise Geochem (Second Edition) 7:195–235
Luoma SN, Rainbow PS, DiLeo J (2008) Metal contamination in aquatic environments. Science and Lateral Management pp 573. Cambridge University Press
Mandeng EPB, Bidjeck LMB, Bessa AME, Ntomb YD, Wadjou JW, Doumo EPE, Dieudonne LB (2019) Contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals, and uranium of sediments in two watershed in Abiete-Toko gold district, Southern. Cameroon Heliyon 5:e02591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02591
Siregar AS, Sulistyo I, Prayogo NA (2020) Heavy metal contamination in water, sediments and Planiliza subviridis tissue in the Donan River, Indonesia. J Water Land Developm 45(4–6):157–164
Walton JR (2011) Bioavailable aluminium: Its metabolism and effects on the environment. Encycl Environ Health 343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52272-6.00334-2
Cánovas CR, Olias M, Vazquez-Suñé E, Ayora C, Nieto JM (2012) Influence of releases from a fresh water reservoirs on the hydrochemistry of the Tinto River (SW Spain). Sci Total Environm 416:418–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.11.079
Dixon E, Gardner M (1998) Reactive aluminium in UK Surface waters. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 10(1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.3184/095422998782775899
Guibaud G, Gauthier C (2003) Study of aluminium concentration and speciation of surface water in four catchments in the Limousin region (France). J Inorg Biochem 97(1):16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0162-0134(03)00254-x
John DA, Leventhal JS (1995) Bioavailability of metals. In: Preliminary compilation of descriptive geoenvironmental mineral deposit models. ed. du Bray EA. U.S. Department of the Interior. U.S. Geological Survey. Denver. Colorado 10–18
Regulation of the Minister of Maritime Affairs and Inland Navigation of July 12, 2019 on substances particularly harmful to the aquatic environment and conditions, to be met when discharging wastewater into waters or into the ground, as well as when discharging rainwater or snowmelt into waters or into water facilities. Journal of Laws. 2019, item 1311. - its Polish law act
Water Law (2017) Official Journal of the Laws of 20 July 2017. Item 1566 - its Polish law act
Ciszewski D, Malik I, Wardas M (2004) Geomorphological influences on heavy metal migration in fluvial deposits: the Mała Panew River valley (southern Poland). Przegląd Geol 52:163–174
Korzeniewski K (1986) Hydrochemistry. pp. 226 WSP Słupsk
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lake and river ecosystems. Academic Press. New York, London
Closset M, Cailliau K, Slaby S, Marin M (2022) Effects of Aluminium Contamination on the Nervous System of Freshwater Aquatic Vertebrates: A Review. Int J Mol Sci 23:31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010031
Wren CD, Stephenson GL (1991) The effect of acidification on the accumulation and toxicity of metals to freshwater invertebrates. Environ Pollut 71(2–4):205–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(91)90033-s
Bengtsson BE (1978) Use of a harpacticoid copepod in toxicity tests. Marine Pollution Bull 9(9):238–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(78)90378-8
Muramoto S (1981) Influence of complexans (NTA, EDTA) on the toxicity of aluminum chloride and sulfate to fish at high concentrations. Bull Environm Contam Toxicol 27:221–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01611011
Petrich SM, Reish DJ (1979) Effects of aluminium and nickel on survival and reproduction in Polychaetous Annelids. Bull Environm Contam Toxicol 23:698–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01770027
Gostomski F (1990) The toxicity of aluminium to aquatic species in the US. Environ Geochem Health 12:51–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734047
Neville CM, Campbell PGC (1988) Possible mechanisms of aluminium toxicity in a dilute, acidic environment to fingerlings and older life stages of salmonids. Water Air Soil Pol 42:311–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279276
Sparling DW, Lowe TP (1996) Environmental hazards of aluminium to plants, invertebrates, fish, and wildlife. Re Environ Contam Toxicol 145:1–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-2354-2_1
Zioła A, Frankowski M, Siepak M (2007) Analysis of aluminium in surface water samples and fractionation of aluminium from bottom sediment samples. Ochrona Środ Zas Natur 31:338–347
Kuklina I, Kouba A, Buřič M, Horká I, Ďuriš Z, Kozák P (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals in crayfish and fish from selected Czech reservoirs. Biomed Res Int. Article ID 306103https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/306103
Wojda R (2006) Carp. Farming and breeding. pp. 457. Inland Fisheries Institute Publishing House. Olsztyn
Mackie GL (1989) Tolerances of five benthic invertebrates to hydrogen ions and metals (Cd, Pb, Al). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056206
Havas M (1985) Aluminum bioaccumulation and toxicity to Daphnia magna in soft water and low pH. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42(11):1696–1852. https://doi.org/10.1139/f85-218
Quiroz-Vázquez P, Sigee DC, White KN (2010) Bioavailability and toxicity of aluminium in a model planktonic food chain (Chlamydomonas – Daphnia) at neutral pH. Limnologica 40:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2009.10.007
Świderska-Bróż M (1987) Sorption phenomena in natural waters and in water treatment processes. Ochrona Środ 521(2–3):9–14
Bieniarz K, Epler P, Chyb J (2008) Hydrozoology textbook for students of fisheries. Publishing house of the University of Agriculture in Krakow
Kurek J, Cwynar LC, Weeber RC, Jeffries DS, Smol JP (2010) Ecological distributions of Chaoborus species in small, shallow lake from the Canadian Boreal Shield ecozone. Hydrobiol 652:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0333-5
Sweetman JN, Smol JP (2006) Reconstructing fish populations using Chaoborus (Diptera: Chaoboridae) remains – a reveiw. Quat Sci Rev 25:2013–2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.01.007
Armitage PD, Cranson PS, Pinder LCV (1995) The chironomidae. Biology and ecology of non-biting midges. Springer, Dordrecht
Havas M, Hutchinson TC (1982) Aquatic invertebrates from the smoking hills. N.W.T.: effect of pH and metals on mortality. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 39(6):890–903. https://doi.org/10.1139/f82-120
Havas M, Likens GE (1985) Toxicity of aluminum and hydrogen ions to Daphnia catawba, Holopedium gibberum, Chaoborus punctipennis, and Chironomus anthrocinus from Mirror Lake. New Hampshire. Can J Zool 63(5):1114–1119. https://doi.org/10.1139/z85-168
Kownacki A (2010) Chironomidae (Diptera, Insecta) of the Tatra National Park - distribution, ecology, zoogeography. Science and management of the Tatra area and its surroundings. Zakopane 2:113–118
Polish Standard (1977) PN-77/C-04584 – determination of temperature - positions 98-108 - these are Polish standards
Polish Standard (1982) PN-82/C-04576.08 - nitrate nitrogen by spectrophotometric method.
Polish Standard (1999) PN-EN 27888:1999 - determination of electrical conductivity, conductometric method.
Polish Standard (1999c) PN-EN 25814:1999 – determination of dissolved oxygen by electrochemical method.
Polish Standard (1999d) PN-EN 26777:1999 – nitrite nitrogen by spectrophotometric method
Polish Standard (2004) PB/LC/04 - sulfates by spectrophotometric method.
Polish Standard (2012) PN-EN ISO 10523:2012 - determination of pH, potetiometric method.
Polish Standard (2012) PN-EN ISO 7887:2012+Ap1:2015–06 pt. 7 - determination of color by spectrophotometric method - its Polish standard
Polish Standard (1994) PN-ISO 9297:1994 – chlorides by titration method.
Polish Standard (1999b) PN-ISO 6059:1999 - determination of total hardness. titration method.
Polish Standard (2002b) PN-EN ISO 7980:2002 – calcium, magnesium, sodium by flame atomic absorption spectrometry.
Polish Standard (2002a) PN-EN ISO 12020:2002 - total aluminium by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry.
Polish Standard (1998) PB-10/I - Research Procedure - VARIAN Analytical Methods. - its Polish standard
Jezierska B, Witeska M (2001) Metal toxicity to fish. Wydawnictwo Akademii Podlaskiej, Siedlce, pp 318.
Reed LJ, Muench H (1938) A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am J Epidemiol 27(3):493–497
Dziewulska K, Kirczuk L, Czerniawski R, Kowalska-Góralska M (2021) Survival of embryos and fry of sea trout (Salmo trutta m. trutta) growing from eggs exposed to different concentrations of selenium during egg swelling. Animals 11(10):2921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11102921
OECD (1992) Test Guideline 203. Fish, acute toxicity test. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals - items 112 and 113 - commonly available gudelines
OECD (2004) Test Guidelines 218. Sediment-water chironomid toxicity test using spiked sediment. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals
Koivisto S, Ketola M (1995) Effects of copper on life-history traits of Daphnia pulex and Bosmina longirostris. Aquatic Toxicol 32:255–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(94)00094-7
Regulation of the Commission (EU) No 283/2013 of March 1, 2013 establishing data requirements for active substances. In accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market. 3.4.2013 Official Journal of the European Union L 93/1. - its legal act
Wayne G, Landis, Ming-Ho Yu (1995) Introduction to environmental toxicology. Impact of chemicals upon ecological systems. Lewis Publisher CRC Press. Boca Raton, p 512. https://doi.org/10.1201/b12447
Traczewska TM (2011) Biological methods for assessing environmental contamination. Publishing house of the Wrocław University of Technology. Wrocław, pp 214
Slaninova A, Machova J, Svobodova Z (2014) Fish kill caused by aluminium and iron contamination in a natural pond used for fish rearing: a case report. Vet Med 59(11):573–581
Kenaga EE (1982) Predictability of chronic toxicity from acute toxicity of chemicals in fish and aquatic invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 1(4):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620010410
Herrmann J, Frick K (1995) Do stream invertebrates accumulate aluminium at low pH conditions? Water Air Soil Poll 85:407–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00476863
Wickham P, van de Walle E, Planas D (1987) Comparative effects of mine wastes on the benthos of an acid and an alkaline pond. Environ Poll 44(2):83–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(87)90019-4
Hooper HL, Connon R, Callaghan A, Fryer G, Yarwood-Buchanan S, Biggs J, Maund SJ, Hutchinson TH, Sibly RM (2008) The ecological niche of Daphnia magna characterized using population growth rate. Ecology 89(4):1015–1022. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-0559.1
Pérez-Fuentetaja A, Goodberry F (2016) Daphnia’s challenge: survival and reproduction when calcium and food are limiting. J Plankton Res 38(6):1379–1388. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbw077
Brun NR, Fields PD, Horsfield S, Mirbahai L, Ebert D, Colbourne JK, Fent K (2019) Mixtures of aluminum and indium induce more than additive phenotypic and toxicogenimic responses in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 53(3):1639–1649. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05457
Sapkale PH, Singh RK, Desai AS (2011) Optimal water temperature and pH for development of eggs and growth of spawn of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). J Appl Animal Res 39(4):339–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.2011.620269
Correia TG, Narcizo AM, Bianchini A, Moreira RG (2010) Aluminum as an endocrine disruptor in female Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 151:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.02.002
Myllynena K, Ojutkangasa E, Nikinmaac M (1997) River water with high iron concentration and low pH causes mortality of lamprey roe and newly hatched larvae. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 36(1):43–48. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1996.1484
Holopainen IJ, Oikari A (1992) Ecophysiological effects of temporary acidification on crucian carp. Carassius carassius (L.): a case history of a forest pond in eastern Finland. Ann Zool Fennici 29:29–38
Poléo ABS, Østbye K, Øxnevad SA, Andersen RA, Heibo E, Vøllestad LA (1997) Toxicity of acid aluminium-rich water to seven freshwater fish species: a comparative laboratory study. Environ Poll 96(2):129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(97)00033-x
Poléo ABS, Schjolden J, Sørensen J, Nilsson G (2017) The high tolerance to aluminium in crucian carp (Carassius carassius) is associated with its ability to avoid hypoxia. PLoS ONE 12(6):e0179519. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179519
Eshun-Wilson F, Wolf R, Andersen T, Hessen DO, Sperfeld E (2020) UV radiation affects antipredatory defense traits in Daphnia pulex. Ecology Evol 10:14082–14097. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.6999
Polish Standard (2005) PN-EN ISO 5667–3:2005 – guidelines for the preservation and handling of samples
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S., and M.K.-G.; methodology, M.S.; software, M.K.-G.; validation, M.S., and K.C.; formal analysis, M.S. and M.K.-G.; investigation, M.S. and M.K.-G.; resources, M.S.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, K.C.; visualization, M.S., M.K.-G. and K.C.; supervision, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Senze, M., Kowalska-Góralska, M. & Czyż, K. Effect of Aluminum Concentration in Water on Its Toxicity and Bioaccumulation in Zooplankton (Chaoborus and Chironomus) and Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Roe. Biol Trace Elem Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04062-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04062-2