Abstract
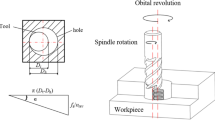
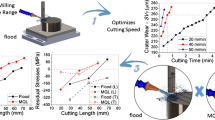
Hole milling is strenuous in the Titanium Alloy grade 5. Ti6Al4V has extraordinary metallurgical properties, so it has popularity in the Aerospace, Automobile, and Ship-building industry. The lower heat absorbing ability, springiness, and chemically activeness at higher temperatures, strain hardening consensuses, poor tool life, and damaged surface texture. This is a common issue in Ti6Al4V machining allows penurious machinability. This investigation focuses on the effect of cooling strategies like a typical flood, Minimum Quantity Cooling Lubrication, and novel Hybrid Tri-nano Flood Coolant with popular cutting inserts in Hole milling. A total L9 orthogonal arrays performance quantifying in terms of the Crater, Flank wear, and Average Surface Roughness value (Ra) at a sidewall and bottom of the Hole. Analysis of Variance manifests that the Tool type and Coolant are more significant for wear control and superior surface quality in the Ti6Al4V Hole milling by balanced Lubri-Cooling. Optimum results were acquired by adapting the 65 m/min cutting speed, Axial Depth of Cut is 0.6 mm, and Hybrid Tri-nano Flood Coolant through PVD-TiAlN + TiN coated inserts. However, the Radial Depth of Cut is 45% of the tool diameter, and the Ramp angle should be 1.24° constant through the hole milling. All these shearing parameters in the hole milling of Ti6Al4V under the Helical milling Computer Aided Milling tool path revamp.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shyha, I., Gariani, S., El-Sayed, M., Huo, D.: Analysis of microstructure and chip formation when machining Ti–6Al–4V. Metals (Basel) 8(3), 185 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030185
Liu, H., Zhang, J., Xu, X., Zhao, W.: Experimental study on fracture mechanism transformation in chip segmentation of Ti–6Al–4V alloys during high-speed machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 257, 132–140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.02.040
Kishawy, A.H., H.A.: Machining of titanium alloys. In: Davim, J.P. (ed.) Materials Forming, Machining and Tribology. pp. 31–62. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-43902-9
Gariani, S., Shyha, I., Inam, F., Huo, D.: Experimental analysis of system parameters for minimum cutting fluid consumption when machining Ti–6Al–4V using a novel supply system. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 95(5–8), 2795–2809 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1216-y
Motyka, M., Kubiak, K., Sieniawski, J., Ziaja, W.: Phase transformations and characterization of α + β titanium alloys. Compr. Mater. Process. 2(May), 7–36 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-096532-1.00202-8
Peters, M., Hemptenmacher, J., C.L.: Titanium and titanium alloys edited by presented at the (2003)
Joshi, V.A., Group, F., Features, F., Joshi, V.A., Group, F., Features, F.: TITANIUM. Presented at the (2006)
Patil, A.S., Ingle, S.V., More, Y.S., Mathe, M.S.: Machining challenges in Ti–6Al–4V—a review. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 5(4), 6–23 (2015)
Fernández-Vidal, S.R., Mayuet, P., Rivero, A., Salguero, J., Del Sola, I., Marcos, M.: Analysis of the effects of tool wear on dry helical milling of Ti6Al4V alloy. Procedia Eng. 132, 593–599 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.12.536
Li, H., He, G., Qin, X., Wang, G., Lu, C., Gui, L.: Tool wear and hole quality investigation in dry helical milling of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 71(5–8), 1511–1523 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5570-0
Qin, X., Gui, L., Li, H., Rong, B., Wang, D., Zhang, H., Zuo, G.: Feasibility study on the minimum quantity lubrication in high-speed helical milling of Ti–6Al–4V. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 6(7), 1222–1233 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1299/jamdsm.6.1222
Festas, A.J., Pereira, R.B., Ramos, A., Davim, J.P.: A study of the effect of conventional drilling and helical milling in surface quality in titanium Ti–6Al–4V and Ti–6AL–7Nb alloys for medical applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(3), 2361–2369 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05047-8
Barman, A., Adhikari, R., Bolar, G.: Evaluation of conventional drilling and helical milling for processing of holes in titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. Mater. Today Proc. 28, 2295–2300 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.573
Akula, S., Nayak, S.N., Bolar, G., Managuli, V.: Comparison of conventional drilling and helical milling for hole making in Ti6Al4V titanium alloy under sustainable dry condition. Manuf. Rev. 8, 12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1051/mfreview/2021010
Ahmed, T., Rack, H.J.: Phase transformations during cooling in α+β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 243(1–2), 206–211 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00802-2
Polishetty, A., Littlefair, G., Praveen Kumar, K.: Machinability assessment of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. Res. 941–944, 1985–1990 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.941-944.1985
Sharma, S., Meena, A.: Microstructure attributes and tool wear mechanisms during high-speed machining of Ti–6Al–4V. J. Manuf. Process. 50(December 2019), 345–365 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.12.029
Khawarizmi, R.M., Lu, J., Nguyen, D.S., Bieler, T.R., Kwon, P.: The effect of Ti–6Al–4V microstructure, cutting speed, and adiabatic heating on segmented chip formation and tool life. Jom 74(2), 526–534 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-05091-1
Zang, J., Zhao, J., Li, A., Pang, J.: Serrated chip formation mechanism analysis for machining of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V based on thermal property. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 98(1–4), 119–127 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0451-6
Gonsalves, J.A., Nayak, S.N., Bolar, G.: Experimental investigation on the performance of helical milling for hole processing in AZ31 magnesium alloy. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 34(5), 366–374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2020.10.004
Yuan, C.G., Pramanik, A., Basak, A.K., Prakash, C., Shankar, S.: Drilling of titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V)—a review. Mach. Sci. Technol. 25(4), 637–702 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2021.1925295
Sharif, S., Abd, E., Sasahar, H.: Machinability of titanium alloys in drilling. In: Nurul Amin, A.K.M. (ed.) Titanium Alloys—Towards Achieving Enhanced Properties for Diversified Applications, pp. 1–25 (2012)
Puerta-Morales, F.J., Gomez, J.S., Fernandez-Vidal, S.R.: Study of the influence of helical milling parameters on the quality of holes in the UNS R56400 alloy. Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030845
Ge, J., Chen, G., Su, Y., Zou, Y., Ren, C., Qin, X., Wang, G.: Effect of cooling strategies on performance and mechanism of helical milling of CFRP/Ti–6Al–4 V stacks. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 35(2), 388–403 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2020.12.003
Olvera, D., De Lacalle, L.N.L., Urbikain, G., Lamikiz, A., Rodal, P., Zamakona, I.: Hole making using ball helical milling on titanium alloys. Mach. Sci. Technol. 16(2), 173–188 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2012.673958
Pereira, R.B.D., Brandão, L.C., de Paiva, A.P., Ferreira, J.R., Davim, J.P.: A review of helical milling process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 120, 27–48 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2017.05.002
Chen, G., Zou, Y., Qin, X., Liu, J., Feng, Q., Ren, C.: Geometrical texture and surface integrity in helical milling and ultrasonic vibration helical milling of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 278(July 2019), 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116494
Mughal, K., Mughal, M.P., Farooq, M.U., Qaiser Saleem, M., Haber Guerra, R.: Helical milling of CFRP/Ti6Al4V stacks using nano fluid based minimum quantity lubrication (NF-MQL): investigations on process performance and hole integrity. Materials (Basel) 16, 566(2), 1–25 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020566
Patil, A.S., Sunnapwar, V.K., Bhole, S., K., Ray, M.P., More, Y.S.: Effective cooling methods for Ti6Al4V CNC milling: a review. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 7(4), 1–51 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2022.2094073
Sharma, V.S., Singh, G., Sorby, K.: A review on minimum quantity lubrication for machining processes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 30(8), 935–953 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.994759
Dhal, A.K., Panda, A., Kumar, R., Sahoo, A.K.: Different machining environments impact analysis for Ti–6Al–4V alloy (Grade 5) turning process: a scoping review. In: Materials Today: Proceedings. pp. 2342–2347. Elsevier Ltd. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.432
Gupta, M.K., Song, Q., Liu, Z., Sarikaya, M., Jamil, M., Mia, M., Kushvaha, V., Singla, A.K., Li, Z.: Ecological, economical and technological perspectives based sustainability assessment in hybrid-cooling assisted machining of Ti–6Al–4 V alloy. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 26, e00218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2020.e00218
Park, K.H., Suhaimi, M.A., Yang, G.D., Lee, D.Y., Lee, S.W., Kwon, P.: Milling of titanium alloy with cryogenic cooling and minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 18(1), 5–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-017-0001-z
Pramanik, A., Littlefair, G.: Machining of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V)-theory to application. Mach. Sci. Technol. 19(1), 1–49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2014.991031
Outeiro, J., Cheng, W., Chinesta, F., Ammar, A.: Modelling and optimization of machining of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy using machine learning and design of experiments methods. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 6(3), 1–22 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp6030058
Kucharska, B., Czarniak, P., Kulikowski, K., Krawczyńska, A., Rożniatowski, K., Kubacki, J., Szymanowski, K., Panjan, P., Sobiecki, J.R.: Comparison study of PVD coatings: TiN/AlTiN, TiN and TiAlSiN used in wood machining. Materials (Basel). 15(20), 1–15 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207159
Koseki, S., Inoue, K., Sekiya, K., Morito, S., Ohba, T., Usuki, H.: Wear mechanisms of PVD-coated cutting tools during continuous turning of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Precis. Eng. 47, 434–444 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.09.018
Yousfi, M., Outeiro, J.C., Nouveau, C., Marcon, B., Zouhair, B.: Tribological Behavior of PVD hard coated cutting tools under cryogenic cooling conditions. Procedia CIRP. 58, 561–565 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.269
Yang, S.B., Ni, H.C., Zhu, G.H.: Study of the effect of tool wear on cutting Ti6Al4V process. Adv. Mater. Res. 690–693, 2030–2035 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.690-693.2030
Sarwar, M., Haider, J.: Characteristics and machining performance of TiN and TiAlN coatings on a milling cutter. AIP Conf. Proc. 1315(1), 1005–1010 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3552310
Dongre, G., Shaikh, J., Dhakad, L., Rajurkar, A., Gaigole, P.: Analysis for machining of Ti6Al4V alloy using coated and non-coated carbide tools. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Communication Signal Processing 2016 (ICCASP 2016), Vol. 137, pp 134–141 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2991/iccasp-16.2017.22
Sarwar, M., Haider, J., Chinesta, F., Chastel, Y., El Mansori, M.: Characteristics and machining performance of TiN and TiAlN coatings on a milling cutter. In: International Conference on Advances in Materals and Processing Technologies (AMPT2010). pp. 1005–1010. AIP Publishing, Paris, France (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3552310.
Gobivel, K., Vijay Sekar, K.S.S.: Investigation on the effect of TiN and Al2O3 coated tools in the Machining of Ti–6Al–4 V alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 62, 920–924 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.071
Patil, A.S., Sunnapwar, V.K., Bhole, K.S., Oza, A.D., Shinde, S.M., Ramesh, R.: Effective machining parameter selection through fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS for 3D finish milling of Ti6Al4V. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2013, 1–16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-00993-z
Patil, A.S., Sunnapwar, V.K., Bhole, K.S., More, Y.S.: Experimental investigation and fuzzy TOPSIS optimisation of Ti6Al4V finish milling. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 8(4), 3706–3729 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2021.1971002
Jamil, M., Khan, A.M., Hegab, H., Gupta, M.K., Mia, M., He, N., Zhao, G., Song, Q., Liu, Z.: Milling of Ti–6Al–4V under hybrid Al2O3-MWCNT nanofluids considering energy consumption, surface quality, and tool wear: a sustainable machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 107(9–10), 4141–4157 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05296-9
Jamil, M., He, N., Huang, X., Zhao, W., Khan, A.M., Iqbal, A.: Thermophysical, tribological, and machinability characteristics of newly developed sustainable hybrid lubri-coolants for milling Ti–6Al–4V. J. Manuf. Process. 73(October 2021), 572–594 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.10.051
Jamil, M., Khan, A.M., Hegab, H., Gong, L., Mia, M., Gupta, M.K., He, N.: Effects of hybrid Al2O3-CNT nanofluids and cryogenic cooling on machining of Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102(9–12), 3895–3909 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03485-9
Chang, W.-R., Hirvonen, M., Grönqvist, R.: The effects of cut-off length on surface roughness parameters and their correlation with transition friction. Saf. Sci. 42(8), 755–769 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2004.01.002
Kore, N.B., Ravi, K., Patil, S.B.: A simplified description of FUZZY TOPSIS method for multi criteria decision making. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 4(5), 2395–2456 (2017)
Balioti, V., Tzimopoulos, C., Evangelides, C.: Multi-criteria decision making using TOPSIS method under fuzzy environment. Appl. Spillw. Select. Proc. 2(11), 637 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110637
Chen, C.-T.: Extensions of the TOPSIS for group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 114(1), 1–9 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(97)00377-1
Vega, A., Aguarón, J., García-Alcaraz, J., Moreno-Jiménez, J.M.: Notes on dependent attributes in TOPSIS. Procedia Comput. Sci. 31, 308–317 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2014.05.273
Parida, A.K., Routara, B.C.: Multiresponse optimization of process parameters in turning of GFRP using TOPSIS method. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 1–10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/905828
Chakraborty, S.: TOPSIS and modified TOPSIS: a comparative analysis. Decis. Anal. J. 2(2021), 100021 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2021.100021
Wang, T.C., Lee, H.D.: Developing a fuzzy TOPSIS approach based on subjective weights and objective weights. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(5), 8980–8985 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.11.035
Kumar, R.: Comparative performance analysis of coated carbide insert in turning of Ti–6Al–4V ELI grade alloy under dry, minimum quantity lubrication and spray impingement cooling environments. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (Ref 11) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06183-4
Dargusch, M.S., Sun, S., Kim, J.W., Li, T., Trimby, P., Cairney, J.: Effect of tool wear evolution on chip formation during dry machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 126, 13–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2017.12.003
Luo, M., Wang, J., Wu, B., Zhang, D.: Effects of cutting parameters on tool insert wear in end milling of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 30(1), 53–59 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3901/CJME.2016.0405.045
Nowakowski, L., Skrzyniarz, M., Blasiak, S., Bartoszuk, M.: Influence of the cutting strategy on the temperature and surface flatness of the workpiece in face milling. Materials (Basel). 13(20), 1–16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204542
Astakhov, V.P., Davim, J.P.: Tools (geometry and material) and tool wear. In: Machining: Fundamentals and Recent Advances, pp. 29–57 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84800-213-5_2
Saini, A., Pabla, B.S., Dhami, S.S.: Developments in cutting tool technology in improving machinability of Ti6Al4V alloy: a review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 230(11), 1977–1989 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405416640176
Ross, N.S., Mia, M., Anwar, S.G.M., Saleh, M., Ahmad, S., Sworna, N., Mia, M., Anwar, S., Manimaran, G., Saleh, M., Ahmad, S.: A hybrid approach of cooling lubrication for sustainable and optimized machining of Ni-based industrial alloy. J. Clean. Prod. 321(July), 1–18 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128987
Tiwari, P.K., Raj, S., Kumar, R., Panda, A., Sahoo, A.K.: Machinability improvement investigation in face milling of Ti–3Al–2.5V alloys using TiAlN coated carbide insert under dual nozzle minimum quantity lubrication cooling environment. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process. Mech. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/09544089221132449
Joshi, S., Pawar, P., Tewari, A., Joshi, S.S.: Tool wear mechanisms in machining of three titanium alloys with increasing β-phase fraction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 228(9), 1090–1103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414522796
Li, A., Zhao, J., Hou, G.: Effect of cutting speed on chip formation and wear mechanisms of coated carbide tools when ultra-high-speed face milling titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Adv. Mech. Eng. 9(7), 168781401771370 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814017713704
Liu, Q., Xu, J., Yu, H.: Experimental study on the influence of tool wear on the cutting process of Ti6Al4V. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1838(1), 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1838/1/012026
Sivalingam, V., Sun, J., Selvam, B., Murugasen, P.K., Yang, B., Waqar, S.: Experimental investigation of tool wear in cryogenically treated insert during end milling of hard Ti alloy. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41(2), 110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1612-3
Cui, X., Li, C., Ding, W., Chen, Y., Mao, C., Xu, X., Liu, B., Wang, D., Li, H.N., Zhang, Y., Said, Z., Debnath, S., Jamil, M., Ali, H.M., Sharma, S.: Minimum quantity lubrication machining of aeronautical materials using carbon group nanolubricant: from mechanisms to application. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 1–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2021.08.011
Bai, X., Li, C., Dong, L., Yin, Q.: Experimental evaluation of the lubrication performances of different nanofluids for minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) in milling Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 101(9–12), 2621–2632 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3100-9
Acknowledgment
Authors are grateful to Mr. Rajesh Gurhale, Supra Techno Services, Authorized Distributors for Seco Tools India Ltd. Pune for technical support. Also, Special thanks to the Institute of Pharmacy, MET’s Bhujbal Knowledge City, Adgaon, Nashik, for availing the facility for preparing Hybrid Tri-nano suspension for conducting the present research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
There is no conflict of interest. The authors are solely responsible for the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, A.S., Sunnapwar, V.K. & Bhole, K.S. Effect of hybrid tri-nano flood cooling environment and shearing parameters on surface quality with tool health in helical milling of Ti6Al4V. Int J Interact Des Manuf (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01286-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01286-9