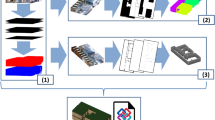
Abstract
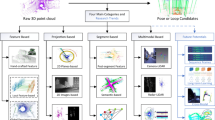
The manipulation of deformable linear objects (DLOs) is an important task in many fields, which raises demands for the perception of DLOs in real situation. In this paper, we propose a cylindrical fitting reconstruction method for DLOs with only one frame of point clouds captured by a depth camera. The point clouds are first processed by operation space filtering and outlier removal to eliminate the interference. To accurately segment the specific object from the complex background, the PointSIFT module is inserted into PointNet++ architecture and fine-tuned on our dataset. To reconstruct the flexible DLOs in 3D space, an improved adaptive K-means algorithm which accommodates to the unknown length and curvature is designed. The adaptive K-means algorithm distributes the point clouds into appropriate number of cylindrical clusters. To achieve the main axis of the cylinders, we construct the point clouds covariance matrix. By applying principal component analysis (PCA), three orthogonal dimensions and the PCA bounding box are obtained. Afterward, an octree-based directional constraints is designed to sort the center points of DLOs with arbitrary curvature. The proposed framework achieves an average error of less than 1 mm during a manipulation experiment in a simulation live-line maintenance site.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The cable dataset generated during the current study is shot in private scene and involves other technology privacy. So they are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bo, G., Qingquan, L., Xianfeng, H., et al.: An improved method for power-line reconstruction from point cloud data. Remote Sens. 8(1), 36 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010036
Borum, A., Matthews, D., Bretl, T.: State estimation and tracking of deforming planar elastic rods. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4127–4132. IEEE (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2014.6907459
Bretl, T., McCarthy, Z.: Equilibrium configurations of a Kirchhoff elastic rod under quasi-static manipulation. In: Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics X, pp. 71–87. Springer, Berlin (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36279-8_5
Caldwell, T.M., Coleman, D., Correll, N.: Optimal parameter identification for discrete mechanical systems with application to flexible object manipulation. In: 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp 898–905. IEEE (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2014.6942666
Chen, W., Liu, J., Tang, Y., et al.: Automatic spray trajectory optimization on Bézier surface. Electronics 8(2), 168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8020168
Cretu, A.M., Petriu, E.M., Payeur, P., et al.: Deformable object segmentation and contour tracking in image sequences using unsupervised networks. In: 2010 Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision, pp. 277–284. IEEE (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/CRV.2010.43
Dai, A., Chang, A.X., Savva, M., et al.: Scannet: richly-annotated 3d reconstructions of indoor scenes. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2432–2443. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA, USA (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.261
Fan, Z., Guo, L., Chen, Y., et al.: CPC: cable parameters calculation based on 3D point cloud. In: International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, pp. 264–271. Springer, Berlin (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13841-6_25
Gao, H., Ye, C., Lin, W., et al.: Complex workpiece positioning system with nonrigid registration method for 6-DoFs automatic spray painting robot. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 51(12), 7305–7313 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2020.2980424
Hu, Q., Yang, B., Xie, L., et al.: Learning semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds with random sampling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3083288
Lee, M.J., Jeon, Y.J., Son, G.E., et al.: Grain boundary conformed volumetric mesh generation from a three-dimensional voxellated polycrystalline microstructure. Met. Mater. Int. 24(4), 845–859 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0083-x
Li, P., Wang, R., Wang, Y., et al.: Evaluation of the ICP algorithm in 3D point cloud registration. IEEE Access 8, 68030–68048 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986470
Qi, C.R., Su, H., Mo, K., et al.: Pointnet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 652–660 (2017). arXiv:1612.00593
Qi, C.R., Yi, L., Su, H., et al.: Pointnet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Rostami, M., Oussalah, M., Farrahi, V.: A novel time-aware food recommender-system based on deep learning and graph clustering. IEEE Access 10, 52508–52524 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3175317
Saberi-Movahed, F., Rostami, M., Berahmand, K., et al.: Dual regularized unsupervised feature selection based on matrix factorization and minimum redundancy with application in gene selection. Knowl. Based Syst. 256, 109,884-109,900 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109884
Sanchez, J., Corrales, J.A., Bouzgarrou, B.C., et al.: Robotic manipulation and sensing of deformable objects in domestic and industrial applications: a survey. Int. J. Robotics Res. 37(7), 688–716 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0278364918779698
Wei, W., Hui, Z., Yu, G., et al.: Peg-in-hole assembly in live-line maintenance based on generative mapping and searching network. Robotics Auton. Syst. 143(103), 797 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2021.103797
Wu, P., Li, W., Yan, M.: 3D scene reconstruction based on improved ICP algorithm. Microprocess. Microsyst. 75(103), 064 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103064
Xie, Y., Tian, J., Zhu, X.X.: Linking points with labels in 3D: a review of point cloud semantic segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 8(4), 38–59 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2019.2937630
Yan, M., Zhu, Y., Jin, N., et al.: Self-supervised learning of state estimation for manipulating deformable linear objects. IEEE Robotics Autom. Lett. 5(2), 2372–2379 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2020.2969931
Zhao, H., Jiang, L., Fu, C.W., et al.: Pointweb: enhancing local neighborhood features for point cloud processing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5565–5573 (2019)
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(61973167).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yiman Zhu designed and implemented the method. Xiao Xiao wrote the original draft. Wei Wu did visualization and investigation. Yu Guo was responsible for conceptualization, resources, review and editing, project administration and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Xiao, X., Wu, W. et al. 3D Reconstruction of deformable linear objects based on cylindrical fitting. SIViP 17, 2617–2625 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02478-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02478-8