Abstract
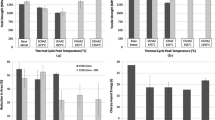
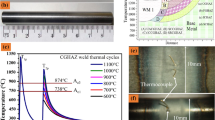
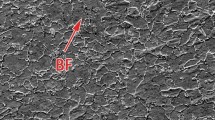
The influence of weld thermal simulation on the transformation kinetics and heat-affected zone (HAZ) microstructure of two high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, HSLA-80 and HSLA-100, has been investigated. Heat inputs of 10 kJ/cm (fast cooling) and 40 kJ/cm (slow cooling) were used to generate single-pass thermal cycles with peak temperatures in the range of 750 °C to 1400 °C. The prior-austenite grain size is found to grow rapidly beyond 1100 °C in both the steels, primarily with the dissolution of niobium carbonitride (Nb(CN)) precipitates. Dilatation studies on HSLA-80 steel indicate transformation start temperatures (T s ) of 550 °C to 560 °C while cooling from a peak temperature (T p ) of 1000 °C. Transmission electron microscopy studies show here the presence of accicular ferrite in the HAZ. The T s value is lowered to 470 °C and below when cooled from a peak temperature of 1200 °C and beyond, with almost complete transformation to lath martensite. In HSLA-100 steel, the T s value for accicular ferrite is found to be 470 °C to 490 °C when cooled from a peak temperature of 1000 °C, but is lowered below 450 °C when cooled from 1200 °C and beyond, with correspondingly higher austenite grain sizes. The transformation kinetics appears to be relatively faster in the fine-grained austenite than in the coarse-grained austenite, where the niobium is in complete solid solution. A mixed microstructure consisting of accicular ferrite and lath martensite is observed for practically all HAZ treatments. The coarse-grained HAZ (CGHAZ) of HSLA-80 steel shows a higher volume fraction of lath martensite in the final microstructure and is harder than the CGHAZ of HSLA-100 steel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O.R. Myhr and O. Grong: Acta Metall. Mater., 1990, vol. 38, pp. 449–60.
L.E. Svensson: Control of Microstructures and Properties in Steel Arc Welds, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1994, pp. 101–06.
R.E. Dolby: Weld. J., 1979, vol. 58, pp. 225s-238s.
D. Radaj: Heat Effects of Welding, Springer-Verlag Publications, Heidelberg, 1992, pp. 100–03.
J.C. Ion, K.E. Easterling, and M.F. Ashby: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 1949–62.
M.R. Krishnadev, L.T. Bowker, J.T. McGrath, V.K. Vasudevan, and K.D. Challenger: Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Trends in Welding Research, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1989, pp. 799–803.
M.R. Krishnadev, W.L. Zhang, and J.T. Bowker: Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. on Welding Research, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1992, pp. 599–603.
A.D. Wilson, J. Met., 1987, vol. 29, pp. 39–48.
S.D. Bhole and A.G. Fox: Can. Metall. Q., 1996, vol. 35, pp. 151–57.
R.W. Fonda, G. Spanos, and R.A. Vandermeer: Proc. 4th Int. Conf. on Trends in Welding Research, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1995, pp. 277–82.
S.W. Thompson: 40th MWSP Conf. Proc., ISS, Warrendale, PA, 1998, pp. 663–73.
G. Spanos, R.W. Fonda, R.A. Vandermeer, and A. Matuszeski: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 3277–93.
O. Grong: Metallurgical Modelling of Welding, The Institute of Materials, London, 1997, pp. 409–11.
C.E. Cross, O. Grong, S. Liu, and J.F. Capes: in Applied Metallography, G.F. Vander Voort, ed., Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, NY, 1986, pp. 197–210.
P.L. Harrison and R.A. Farrar: Int. Mater. Rev., 1989, vol. 34, pp. 35–51.
A.D. Wilson, E.G. Hamburg, D.J. Colvin, S.W. Thompson, and G. Krauss: Proc. Int. Conf. on Microalloyed HSLA Steel, Microalloying '88, ASM INTERNATIONAL Metals Park, OH, 1988, pp. 259–75.
S.W. Thompson, D.J. Colvin, and G. Krauss: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1493–1507.
S.W. Thompson, D.J. Colvin, and G. Krauss: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 1557–71.
N.N. Rykalin: Berechnung der Wärmevorgänge beim Schweissen, VEB Verlag Technik, Berlin, 1957.
S.W. Thompson and G. Krauss: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 1573–88.
G.R. Speich and T.M. Scoonover: in Processing, Microstructure and Properties of HSLA Steels, A.J. DeArdo, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988, pp. 263–86.
A.G. Fox, S. Mikalac, and M.G. Vassilaros: proc. G.R. Speich Symp., ISS, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 155–61.
M. Mujahid, A.K. Lis, C.I. Garcia, and A.J. DeArdo: Key Eng. Mater., Trans Tech Publication, Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 1993, vols. 84–85, pp. 209–36.
M. Mujahid, A.K. Lis, C.I. Garcia, and A.J. DeArdo: J. Mater. Eng. Performance, 1998, vol. 7, pp. 247–57.
S.K. Dhua, D. Mukerjee, and D.S. Sarma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32, pp. 2259–70.
D. Wenpu, F. Zuabao, and Y. Lang: Mater. Characterization, 1996, vol. 37, pp. 169–75.
O. Grong: Metallurgical Modelling of Welding, The Institute of Materials, London, 1997, pp. 303–20.
K.W. Andrews: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, vol. 203, pp. 721–27.
S. Suzuki and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994, vol. A186, pp. 157–62.
R.W.K. Honeycombe and H.K.D.H. Bhadesia: Steels—Microstructure and Properties, Edward Arnold, London, 1995, p. 103
T. Gladman and F.B. Pickering: J. Iron Steel. Inst., 1967, vol. 205, pp. 653–64.
L.J. Cuddy and L.C. Raley: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1989–95.
E.J. Palmiere, C.I. Garcia, and A.J. DeArdo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 277–86.
P.A. Manohar, D.P. Dunne, T. Chandra, and C.R. Killmore: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. 194–200.
M.F. Ashby and K.E. Easterling: Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 1969–78.
I. Anderson and O. Grong: Acta Metall. 1995, vol. 43, pp. 2673–88.
M. Shome, D.S. Sarma, O.P. Gupta, and O.N. Mohanty: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1431–37.
T.A. Kop, P.G.W. Remijn, J. Sietsma, and S. Van der Zwaag: Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publication. Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 1998, vols. 284–286, pp. 193–200.
G.I. Rees, J. Perdrix, T. Maurickx, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, vol. 194, pp. 179–86.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. on Welding Research, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1992, pp. 213–22.
P.A. Manohar, T. Chandra, and C.R. Killmore: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int. 1996, vol. 36, pp. 1486–93.
T. Abe, K. Tsukada, and J. Kozasu: Proc. Int. Conf. on HSLA Steels'85, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Material Park, OH, 1986, pp. 103–11.
G. Krauss and A.R. Marder: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2343–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shome, M., Gupta, O.P. & Mohanty, O.N. Effect of simulated thermal cycles on the microstructure of the heat-affected zone in HSLA-80 and HSLA-100 steel plates. Metall Mater Trans A 35, 985–996 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-1002-y
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-1002-y