Abstract
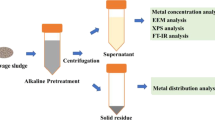
The design of this study was to investigate the solid-aqueous migration and chemical speciation transformation of heavy metals (HMs) in the sewage sludge during the combined process of thermal hydrolysis, anaerobic digestion and heat-drying. The results showed that most of the HMs were still accumulated in the solid phase of various sludge samples after treatment. After thermal hydrolysis, the concentrations of Cr, Cu and Cd increased slightly. All the HMs measured after anaerobic digestion were concentrated obviously. While the concentrations of all HMs decreased slightly after heat-drying. The stability of HMs in the sludge samples was enhanced after treatment. The environmental risks of various HMs were also relieved in the final dried sludge samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cabrera DV, Labatut RA (2021) Outlook and challenges for recovering energy and water from complex organic waste using hydrothermal liquefaction. Sustainable Energy Fuels 5:2201–2227. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0se01857k
Chang S, Filer J (2020) Thermal hydrolysis to enhance anaerobic digestion performance of wastewater sludge. Curr Pollut Rep 6:452–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-020-00163-3
Cheng Y, Chon K, Ren XH, Li ML, Kou YY, Hwang MH, Chae KJ (2021) Modified bentonite as a conditioning agent for stabilising heavy metals and retaining nutrients in sewage sludge for agricultural uses. Water Sci Technol 84:2252–2264. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.450
Dabrowska L, Rosinska A (2016) Changes of heavy metal forms and chlorinated biphenyls during digestion of pre-hydrolyzed sewage sludge. Desalin Water Treat 57:1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.989636
Dong B, Liu XG, Dai LL, Dai XH (2013) Changes of heavy metal speciation during high-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 131:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.112
DuBois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
Frolund B, Griebe T, Nielsen PH (1995) Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164784
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Huang HJ, Yuan XZ, Zeng GM, Zhu HN, Li H, Liu ZF, Jiang HW, Leng LJ, Bi WK (2011) Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals’ pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:10346–10351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.117
Husek M, Mosko J, Pohorely M (2022) Sewage sludge treatment methods and P-recovery possibilities: Current state-of-the-art. J Environ Manage 315:115090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115090
Jin JW, Li YN, Zhang JY, Wu SC, Cao YC, Liang P, Zhang J, Wong MH, Wang MY, Shan SD, Christie P (2016) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on properties and environmental safety of heavy metals in biochars derived from municipal sewage sludge. J Hazard Mater 320:417–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.050
Kowalik R, Gawdzik J, Bak-Patyna P, Ramiaczek P, Jurisevi N (2022) Risk analysis of heavy metals migration from sewage sludge of wastewater treatment plants. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:11829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811829
Larina OM, Zaichenko VM (2020) Influence of pyrolysis on evaporation and solubility of heavy metals in sewage sludge. J Phys Conf Ser 1556:012017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1556/1/012017. (IOP Publishing)
Li C, Zhang SN, Yang JK, Shi YF, Yu WB, Liang S, Song J, Xu Q, Chen Y, Hu JP, Li Y, Yang CZ (2015) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in two different sludge composite conditioning and deep dewatering processes. RSC Adv 5:102332–102339. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra20220e
Li JP, Gan JH, Hu YJ (2016) Characteristics of heavy metal species transformation of Pb, Cu, Zn from municipal sewage sludge by thermal drying. Procedia Environ Sci 31:961–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.03.001
Liu XX, Wang YM, Gui CM, Li P, Zhang JY, Zhong H, Wei YS (2016) Chemical forms and risk assessment of heavy metals in sludge-biochar produced by microwave-induced low temperature pyrolysis. RSC Adv 6:101960–101967. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra22511j
Liu XS, Wang J, Liu EH, Yang TH, Li RD, Sun YF (2020) Municipal sludge dewatering properties and heavy metal distribution: Effects of surfactant and hydrothermal treatment. Sci Total Environ 710:136346
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, National Development and Reform Commission (2011) Guideline on sludge treatment and disposal from municipal sewage treatment plant
Molaey R, Yesil H, Calli B, Tugtas AE (2021) Enhanced heavy metal leaching from sewage sludge through anaerobic fermentation and air-assisted ultrasonication. Chemosphere 279:130548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130548
Pagliaccia B, Carretti E, Severi M, Berti D, Lubello C, Lotti T (2022) Heavy metal biosorption by Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) recovered from anammox granular sludge. J Hazard Mater 424:126661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126661
Qiu CS, Zheng JX, Wang CC, Wang BB, Liu NN, Wang D, Wang SP (2021) Migration and transformation of heavy metals during the microwave-assisted thermal hydrolysis of sewage sludge. Water Sci Technol 84:917–930. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.272
Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monitor 1:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/A807854H
Rice EW, Baird RB, Eaton AD, Clesceri LS (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American public health association, Washington
Rudd T, Sterritt RM, Lester JN (1984) Complexation of heavy metals by extracellular polymers in the activated sludge process. J Water Pollution Control Fed 56:1260–1268 (http://www.jstor.org/stable/25042494). Accessed 3 Nov 2022
Udayanga WDC, Veksha A, Giannis A, Liang YN, Lisak G, Hu X, Lim TT (2019) Insights into the speciation of heavy metals during pyrolysis of industrial sludge. Sci Total Environ 691:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.095
Wang W, Lee DJ (2021) Direct interspecies electron transfer mechanism in enhanced methanogenesis: A mini-review. Bioresour Technol 330:124980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124980
Wei LL, Li JJ, Xue M, Wang S, Li QY, Qin KN, Jiang JQ, Ding J, Zhao QL (2019) Adsorption behaviors of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ onto proteins, humic acid, and polysaccharides extracted from sludge EPS: Sorption properties and mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 291:121868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121868
Wu HM, Li M, Zhang L, Sheng C (2016) Research on the stability of heavy metals (Cu, Zn) in excess sludge with the pretreatment of thermal hydrolysis. Water Sci Technol 73:890–898. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.537
Wu BR, Dai XH, Chai XL (2020) Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: Influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Res 180:115912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115912
Zhang Q, Zhang L, Sang WJ, Li M, Cheng WH (2016) Chemical speciation of heavy metals in excess sludge treatment by thermal hydrolysis and anaerobic digestion process. Desalin Water Treat 57:12770–12776. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1055518
Zhang J, Tian Y, Zhang J, Li N, Kong LC, Yu M, Zuo W (2017) Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sewage sludge after ozonation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5118–5125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6313-1
Zhang C, Yang X, Tan XJ, Wan CL, Liu X (2022) Sewage sludge treatment technology under the requirement of carbon neutrality: Recent progress and perspectives. Bioresour Technol 362:127853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127853
Zhao JQ, Qiu CS, Fan XD, Zheng JX, Liu NN, Wang CC, Wang D, Wang SP (2021) Chemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in biochars derived from sewage sludge and anaerobically digested sludge. Water Sci Technol 84:1079–1089. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.305
Zhen GY, Lu XQ, Kato H, Zhao YC, Li YY (2017) Overview of pretreatment strategies for enhancing sewage sludge disintegration and subsequent anaerobic digestion: Current advances, full-scale application and future perspectives. Renew Sust Energ Rev 69:559–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.187
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51908398), and the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (2017ZX07106001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Chunsheng Qiu, Jiakang Li, Chenchen Wang and Nannan Liu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Chunsheng Qiu and Jiakang Li, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This is an original article that did not use other information that requires ethical approval.
Consent to participate
All the authors participated in this article.
Consent for publication
All the authors have given consent to the publication of this article.
Competing interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, C., Li, J., Wang, C. et al. Transformation and environmental risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge during the combined thermal hydrolysis, anaerobic digestion and heat drying treatment process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 54234–54241 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26200-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26200-4