Abstract
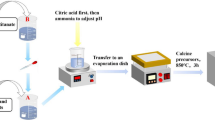
Visible-light active La-Fe-SrTiO3 (La0.01Sr0.99Fe0.01Ti0.99O3) photocatalysts were synthesized via a dynamic hydrothermal route under different NaOH concentrations (2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 M). The results showed that altering NaOH concentrations changed the physicochemical characteristics of the materials. Namely, the decrease in particle size was observed when the NaOH levels were increased. The specific surface area of the photocatalysts changed with an increased concentration of NaOH, and the maximum value was 17.10 m2/g in 5 M of NaOH. The crystal structure of all prepared samples remained unaffected when altered the NaOH concentration or when incorporated La and Fe in the lattice of SrTiO3. Namely, all samples synthesized under various NaOH concentrations crystallized and maintained in the standard cubic perovskite structure of SrTiO3. The increased NaOH concentration slightly altered the absorption wavelength towards a longer wavelength region. The La atom, replacing some Sr2+ in the structure of modified SrTiO3, was confirmed to be in the La3+ valence state. Simultaneously, Fe atoms demonstrating oxidation states of Fe3+ can also be incorporated into the SrTiO3 network. The photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotic revealed that the highest performance was approximately 75% within 9 h over the La0.01Sr0.99Fe0.01Ti0.99O3 sample prepared at 5 M of NaOH via the dynamic hydrothermal process. Meanwhile, this photocatalyst also displayed greater activity than the pristine SrTiO3, the single-doped samples (SrFe0.01Ti0.99O3 and La0.01Sr0.99TiO3), and the La0.01Sr0.99Fe0.01Ti0.99O3 sample prepared through a static hydrothermal technique under the same synthesis condition.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdi M, Mahdikhah V, Sheibani S (2020) Visible light photocatalytic performance of La-Fe co-doped SrTiO3 perovskite powder. Opt Mater 102:109803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109803
Abebe B, Murthy HCA, Amare E (2020) Enhancing the photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO: Defects, heterojunction, and optimization. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 14:100336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100336
Abedi K, Shahmoradi B, Wantala K et al (2022) Immobilized Mo:TiO2 nanoparticles for humic acid removal in an aqueous medium using solar spectrum. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:16777–16788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08542-w
Adedara IA, Godswill UAS, Mike MA et al (2021) Chronic ciprofloxacin and atrazine co-exposure aggravates locomotor and exploratory deficits in non-target detritivore speckled cockroach (Nauphoeta cinerea). Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:25680–25691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12460-5
Chakraborty T, Meneghini C, Aquilanti G, Ray S (2013) Microscopic distribution of metal dopants and anion vacancies in Fe-doped BaTiO3-δ single crystals. J Phys Condens Matter 25:236002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/25/23/236002
Chen C, Jiao X, Chen D, Zhao Y (2001) Effects of precursors on hydrothermally synthesized SrTiO3 powders. Mater Res Bull 36:2119–2126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5408(01)00694-8
Chen S, Pan B, Zeng L et al (2017) La2Sn2O7 enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction with H2O by deposition of Au co-catalyst. RSC Adv 7:14186–14191. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA00765E
Cheng CY, Yang YC, Zhong YZ et al (2017) Physical metallurgy of concentrated solid solutions from low-entropy to high-entropy alloys. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 21:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2017.09.002
Cuerda-Correa EM, Alexandre-Franco MF, Fernández-González C (2020) Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of antibiotics from water. An Overview. Water 12:102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010102
da Silva LF, Bernardi MIB, Maia LJQ et al (2009) Synthesis and thermal decomposition of SrTi1-xFexO3 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1) powders obtained by the polymeric precursor method. J Therm Anal Calorim 97:173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0241-y
de Ilurdoz MS, Sadhwani JJ, Reboso JV (2022) Antibiotic removal processes from water & wastewater for the protection of the aquatic environment: a review. J Water Process Eng 45:102474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102474
Dharma HNC, Jaafar J, Widiastuti N et al (2022) A review of titanium dioxide (TiO2)-based photocatalyst for oilfield-produced water treatment. Membranes 12:345. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030345
Faisal M, Rashed MA, Abdullah MM et al (2020) Efficient hydrazine electrochemical sensor based on PANI doped mesoporous SrTiO3 nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. J Electroanal Chem 879:114805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114805
Fakhri H, Shahi A, Ovez S, Aydin S (2021) Bioaugmentation with immobilized endophytic Penicillium restrictum to improve quorum quenching activity for biofouling control in an aerobic hollow-fiber membrane bioreactor treating antibiotic-containing wastewater. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 210:111831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111831
Fang B, Xing Z, Sun D et al (2022) Hollow semiconductor photocatalysts for solar energy conversion. Adv Powder Mater 1:100021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmate.2021.11.008
Feng Y, Hu K, Zhang M et al (2022) Engineering A-site cation deficiency into LaCoO3 thin sheets for improved microwave absorption performance. J Mater Sci 57:204–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06650-2
Fernández-Rodríguez L, Gorni G, Mather GC et al (2021) X-ray absorption spectroscopy and neutron-diffraction study of persistent luminescent Sr2MgSi2O7 glass-ceramics. Acta Mater 215:117080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117080
Fu J, Zhao Y, Yao Q et al (2022) A review on antibiotics removal: leveraging the combination of grey and green techniques. Sci Total Environ 838:156427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156427
Fuentes S, Muñoz P, Barraza N et al (2015) Structural characterisation of slightly Fe-doped SrTiO3 grown via a sol-gel hydrothermal synthesis. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 75:593–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3730-4
Ghazal H, Koumaki E, Hoslett J et al (2022) Insights into current physical, chemical and hybrid technologies used for the treatment of wastewater contaminated with pharmaceuticals. J Clean Prod 361:132079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132079
Guediri MK, Chebli D, Bouguettoucha A et al (2022) Interfacial coupling effects on adsorptive and photocatalytic performances for photoresponsive graphene-wrapped SrTiO3@Ag under UV-visible light: Experimental and DFT approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:28098–28114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17543-x
Hameed TA, Sharmoukh W, Anis B, Youssef AM (2022) Enhanced photocatalytic activity and diode performance of ZnO-GO nanocomposites via doping with aluminum. Int J Energy Res 2022:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.8563
Hu J, Men J, Liu Y et al (2015) One-pot synthesis of Ag-modified LaMnO3-graphene hybrid photocatalysts and application in the photocatalytic discoloration of an azo-dye. RSC Adv 5:54028–54036. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA09585A
Hu X, Hu X, Peng Q et al (2020) Mechanisms underlying the photocatalytic degradation pathway of ciprofloxacin with heterogeneous TiO2. Chem Eng J 380:122366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122366
Karim AV, Shriwastav A (2020) Degradation of ciprofloxacin using photo, sono, and sonophotocatalytic oxidation with visible light and low-frequency ultrasound: Degradation kinetics and pathways. Chem Eng J 392:124853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124853
Kayaalp B, Lee S, Klauke K et al (2019) Template-free mesoporous La0.3Sr0.7Ti1-xFexO3±δ for CH4 and CO oxidation catalysis. Appl Catal B Environ 245:536–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.077
Koch N, Islam NF, Sonowal S et al (2021) Environmental antibiotics and resistance genes as emerging contaminants: methods of detection and bioremediation. Curr Res Microb Sci 2:100027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100027
Kumar RD, Thangappan R, Jayavel R (2018) Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of LaMnO3 nanostructures for water purification. Res Chem Intermed 44:4323–4337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3371-7
Kumar M, Jaiswal S, Sodhi KK et al (2019) Antibiotics bioremediation: perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance. Environ Int 124:448–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.065
Larsson DGJ, Flach CF (2022) Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat Rev Microbiol 20:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00649-x
Li X, Chen Y, Tao Y et al (2022) Challenges of photocatalysis and their coping strategies. Chem Catal 2:1315–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.checat.2022.04.007
Liguori K, Keenum I, Davis BC et al (2022) Antimicrobial resistance monitoring of water environments: A framework for standardized methods and quality control. Environ Sci Technol 56:9149–9160. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c08918
Ma F, Xu S, Tang Z et al (2021) Use of antimicrobials in food animals and impact of transmission of antimicrobial resistance on humans. Biosaf Health 3:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsheal.2020.09.004
Nunocha P, Kaewpanha M, Bongkarn T et al (2021) A new route to synthesizing La-doped SrTiO3 nanoparticles using the sol-gel auto combustion method and their characterization and photocatalytic application. Mater Sci Semicond Process 134:106001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2021.106001
Park D, Ju H, Kim J (2020) Effect of SrTiO3 nanoparticles in conductive polymer on the thermoelectric performance for efficient thermoelectrics. Polymers 12:777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040777
Patel M, Kumar R, Kishor K et al (2019) Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem Rev 119:3510–3673. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00299
Peng Y, Si W, Luo J et al (2016) Surface tuning of La0.5Sr0.5CoO3 perovskite catalysts by acetic acid for NOx storage and reduction. Environ Sci Technol 50:6442–6448. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00110
Polianciuc SI, Gurzău AE, Kiss B et al (2020) Antibiotics in the environment: causes and consequences. Med Pharm Rep 93:231–240. https://doi.org/10.15386/mpr-1742
Priya AK, Gnanasekaran L, Rajendran S et al (2022) Occurrences and removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products from aquatic systems using advanced treatment: A review. Environ Res 204:112298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112298
Qin Y, Fang F, Xie Z et al (2021) La, Al-codoped SrTiO3 as a photocatalyst in overall water splitting: Significant surface engineering effects on defect engineering. ACS Catal 11:11429–11439. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c02874
Ruzimuradov O, Hojamberdiev M, Fasel C, Riedel R (2017) Fabrication of lanthanum and nitrogen-co-doped SrTiO3-TiO2 heterostructured macroporous monolithic materials for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes under visible light. J Alloys Compd 699:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.355
Sharmoukh W, Hameed TA, Yakout SM (2022) New nonmagnetic aliovalent dopants (Li+, Cu2+, In3+ and Ti4+): optical and strong intrinsic room temperature ferromagnetism of perovskite BaSnO3. J Alloys Compd 925:166702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166702
Sharwani AA, Narayanan KB, Khan ME, Han SS (2022) Photocatalytic degradation activity of goji berry extract synthesized silver-loaded mesoporous zinc oxide (Ag@ZnO) nanocomposites under simulated solar light irradiation. Sci Rep 12:10017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-14117-w
Somdee A, Osotchan T (2019) Effect of precipitating agent NaOH on the synthesis of SrTiO3/TiO2 heterostructure for dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater Chem Phys 229:210–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.03.018
Sulistiani FA, Suharyadi E, Kato T, Iwata S (2020) Effects of NaOH concentration and temperature on microstructures and magnetic properties of bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3) nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation method. Key Eng Mater 855:9–15. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.855.9
Suwannaruang T, Kidkhunthod P, Chanlek N et al (2019) High anatase purity of nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanorice particles for the photocatalytic treatment activity of pharmaceutical wastewater. Appl Surf Sci 478:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.158
Suwannaruang T, Hildebrand JP, Taffa DH et al (2020) Visible light-induced degradation of antibiotic ciprofloxacin over Fe-N-TiO2 mesoporous photocatalyst with anatase/rutile/brookite nanocrystal mixture. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 391:112371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112371
Suwannaruang T, Kidkhunthod P, Butburee T et al (2021) Facile synthesis of cooperative mesoporous-assembled CexSr1-xFexTi1-xO3 perovskite catalysts for enhancement beta-lactam antibiotic photodegradation under visible light irradiation. Surf Interfaces 23:101013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101013
Tawfik EA, Tawfik AF, Alajmi AM et al (2022) Localizing pharmaceuticals manufacturing and its impact on drug security in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharm J 30:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2021.12.002
Ullah B, Lei W, Song XQ et al (2017) Crystal structure, defect chemistry and radio frequency relaxor characteristics of Ce-doped SrTiO3 perovskite. J Alloys Compd 728:623–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.292
Vračar M, Kuzmin A, Merkle R et al (2007) Jahn-Teller distortion around Fe4+ in Sr(FexTi1-x)O3-δ from X-ray absorption spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and vibrational spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 76:174107. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.174107
Vu THT, Au HT, Tran LT et al (2014) Synthesis of titanium dioxide nanotubes via one-step dynamic hydrothermal process. J Mater Sci 49:5617–5625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8274-4
Wahba MA, Sharmoukh W, Yakout SM, Khalil MSh (2022) Fast and full spectrum sunlight photocatalysts: Fe/Co or Ni implanted multiferroic LaMnO3. Opt Mater 124:111973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.111973
Wang F, Yu X, Ge M, Wu S (2020) One-step synthesis of TiO /γ-Fe O /GO nanocomposites for visible light-driven degradation of ciprofloxacin. Chem Eng J 384:123381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123381
Wang J, Yin S, Komatsu M, Sato T (2005) Lanthanum and nitrogen co-doped SrTiO3 powders as visible light sensitive photocatalyst. J Eur Ceram Soc 25:3207–3212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2004.07.027
Wang L, Gui M, Jin HB et al (2018) Temperature dependent conductivity of Bi4Ti3O12 ceramics induced by Sr dopants. J Adv Ceram 7:256–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-018-0277-1
Wang Z, Lin Z, Shen S et al (2021) Advances in designing heterojunction photocatalytic materials. Chin J Catal 42:710–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63698-1
Xiao F, Xu J, Cao L et al (2020) In situ hydrothermal fabrication of visible light-driven g-C3N4/SrTiO3 composite for photocatalytic degradation of TC. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:5788–5796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07060-3
Xie Y, Ye M, Xiong B et al (2021) Enhanced reactive-oxygen-species generation and photocatalytic efficiency with internal imide structures of different ratio in metal-free perylene-g-C3N4 semiconductors. Appl Surf Sci 546:149138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149138
Xue Y, Geng C, Guo Y (2020) Two-dimensional (001) LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures with adjustable band gap and magnetic properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:3134–3139. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b17140
Yakout SM, Youssef AM, Wahba MA et al (2022) Superior ferromagnetic and electrical properties: High purity multiferroic Bi0.98M0.02FeO3 (M = La, Pr, Gd) compositions. J Magn Magn Mater 561:169751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169751
Yang D, Zou X, Sun Y et al (2018) Fabrication of three-dimensional porous La-doped SrTiO3 microspheres with enhanced visible light catalytic activity for Cr(VI) reduction. Front Chem Sci Eng 12:440–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-018-1700-4
Yasasve M, Manjusha M, Manojj D et al (2022) Unravelling the emerging carcinogenic contaminants from industrial waste water for prospective remediation by electrocoagulation - a review. Chemosphere 307:136017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136017
Ying Z, Chen S, Peng T et al (2019) Fabrication of an Fe-doped SrTiO3 photocatalyst with enhanced dinitrogen photofixation performance. Eur J Inorg Chem 2019:2182–2192. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201900098
Zhang J, Zhang L, Wang W, Yu J (2022) In situ irradiated X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy investigation on electron transfer mechanism in S-scheme photocatalyst. J Phys Chem Lett 13:8462–8469. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c02125
Zhong X, Cai Y, Bai H et al (2020) Visible light driven spherical CuBi2O4 with surface oxygen vacancy enhanced photocatalytic activity: catalyst fabrication, performance, and reaction mechanism. Catalysts 10:945. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080945
Zhu L, Gu W, Zou W et al (2020) Enhancing the sonolysis efficiency of SrTiO3 particles with Cr-doping. Catal Lett 150:562–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-03008-x
Acknowledgements
This work has received a scholarship under the Post-Doctoral Training Program from Khon Kaen University, Thailand (Grant No. PD2565-21). Additionally, the authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Research Center for Environmental and Hazardous Substance Management (EHSM), Khon Kaen University, Thailand. Furthermore, the authors would also like to express their appreciation to the Synchrotron Light Research Institute (Public Organization), Thailand, for beamtime on XAS and XPS measurements as well as the expertise in data analysis of the scientists.
Funding
This work has been funded by the Post-Doctoral Training Program (Grant No. PD2565-21), Khon Kaen University, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Totsaporn Suwannaruang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Visualization, Writing—review & editing, Validation. Acapol Pratyanuwat: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation. Putichot Sinthujariwat: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation. Kitirote Wantala: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing—review & editing, Validation. Prae Chirawatkul: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation. Narong Junlek: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation. Supinya Nijpanich: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation. Behzad Shahmoradi: Writing—review & editing, Validation. Harikaranahalli Puttaiah Shivaraju: Writing—review & editing, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Suwannaruang, T., Pratyanuwat, A., Sinthujariwat, P. et al. Dynamically driven perovskite La-Fe-modified SrTiO3 nanocubes and their improved photoresponsive activity under visible light: influence of alkaline environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 90298–90317 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23977-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23977-8