Abstract
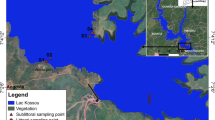
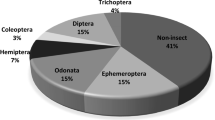
Dachigam-Dara catchment feeding the world-famous Dal Lake was assessed and evaluated for water quality and anthropogenic impacts using physico-chemical and biological data from 2016 to 2018. Seven sites belonging to Dachigam (DACZ) and Dara zone (DARZ) catchment, three sites from the confluence zone (WANZ), and two sites at the downstream end (TELZ) were selected characterized by varying degrees of anthropogenic pressures. Biological Monitoring Working Program, and Average Score Per Taxon at the upstream zones (DACZ, DARZ, and WANZ) recorded significantly higher scores with water quality indices falling within the good category than the downstream zone (TELZ). Taxa richness, and diversity indices of benthic macroinvertebrates recorded higher values at the upstream zones (DACZ, and DARZ), and confluence zone (WANZ), compared to the downstream zone (TELZ). Results revealed that phylum Arthropoda was most dominant contributing 37 invertebrate families (constituting 90% of the total macroinvertebrate community, including Crustacea and Arachnida) while phylum Mollusca and Annelida constitute 5% each. Macroinvertebrate families Baetidae, Erpobdellidae, Gammaridae, Chironomidae, and Heptagenidae contributed significantly to the similarity and dissimilarity between the sampling zones. The best subset of environmental variables (BIOENV) test revealed that the distribution of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblage in the Dachigam-Dara catchment is driven by pH, electrical conductivity, dissolved oxygen, and phosphate phosphorous. The upstream zones (DACZ, and DARZ) and confluence zone (WANZ), compared to the downstream zone (TELZ) suggest progressive shift of pollution sensitive macroinvertebrate taxa to pollution tolerant taxa in response to anthropogenic activities in the stream ecosystem over time.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used/or analyzed that support the findings of this study are available in the main manuscript file and from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abhijna, U. G., Ratheesh, R., & Kumar, B. A. (2013). Distribution and diversity of aquatic insects of Vellayani lake in Kerala. Journal of Environmental Biology, 34(3), 605–611.
Alig, R. J., Kline, J. D., & Lichtenstein, M. (2004). Urbanization on the US landscape: Looking ahead the 21st century. Landscape and Urban Planning, 69, 219–234.
Allan, J D. (2004). Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.35.120202.110122
Amin A., Romshoo S.A. (2007) Assessing the hydrologic characteristics of Dal Lake catchment using GIS. In: Proceedings of TAAL 2007: the 12th World Lake Conference (pp 659–667).
APHA. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (22nd ed.). American Public Health Association.
AQEM Consortium. (2002). Manual for the application of the aqem system. A comprehensive method to assess european streams using benthic macroinvertebrates, developed for the purpose of the water framework directive. Version 1.0., 202 pp.
Arimoro, F. O. (2009). Impact of rubber effluent discharges on the water quality and macroinvertebrate community assemblages in a forest stream in the Niger Delta. Chemosphere, 77, 440–449.
Armitage, P. D., Moss, D., Wright, J. F., & Furse, M. T. (1983). The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running water sites. Water Research, 17, 333–347.
Azrina, M. Z., Yap, C. K., Rahim, I. A., & Tan, S. G. (2006). Anthropogenic impacts on the distribution and biodiversity of benthic macroinvertebrates and water quality of the Langat River. Peninsular Malaysia. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf., 64(3), 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.04.003
Badar, B., & Romshoo, S. A. (2007). Modelling the non-point source pollution load in an urban watershed using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of Dal Lake. Journal of Himalayan Ecology & Sustainable Development, 2(1), 21–30.
Bagla, P. (2014). India plans the grandest of canal networks. Science, 345, 128. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.345.6193.128
Barbour, M. T., Gerritsen, J., Snyder, B. D., & Stribling, J. B. (1999). Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and Wadeable rivers: Periphyton, benthic macroinvertebrates and fish (Vol. 339). US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water.
Batzer, D. P., Palik, B. J., & Buech, R. (2004). Relationships between environmental characteristics and macroinvertebrate communities in seasonal woodland ponds of Minnesota. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 23, 50–68.
Begon, M., Harper, J. L., & Townsend, C. R. (1996). Ecology: Individuals, populations, and communities (3rd ed.). Blackwell Science Ltd.
Bertaso, T. R. N., Spies, M. R., Kotzian, C. B., & Flores, M. L. T. (2015). Effects of forest conversion on the assemblages’ structure of aquatic insects in subtropical regions. Revista Brasileira De Entomologia, 59, 43–49.
Bhagat R.C. (2013). Aquatic Beetles (Coleoptera: Insecta) of Jammu, Kashmir & Ladakh Region (North-West Himalaya): Inventory and biodiversity. Journal of Global Biosciences 2(4): 90–97. https://www.mutagens.co.in/jgb/vol.02/4/04.pdf
Bhat, S. U., Islam, S. T., Sabha, I., & Khanday, S. A. (2021b). Understanding the spatiotemporal pollution dynamics of highly fragile montane watersheds of Kashmir Himalaya, India. Environmental Pollution, 286, 117335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117335
Bhat, S.U., Bhat, A.A. Jehangir, A, Hamid, A., Sabha,I., Qayoo, U. (2021a). Water quality characterization of marusudar river in chenab sub-basin of north-western Himalaya using multivariate statistical methods. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05394-8
Borror, D. J., Triplehorn, C. A., & Johnson, N. F. (1989). An introduction to the study of insects (Ed. 6th ). Saunders college publishing.
Bouchard, R. W., & Ferrington, L. C. (2011). The effects of subsampling and sampling frequency on the use of surface-floating pupal exuviae to measure Chironomidae (Diptera) communities in Wadeable temperate streams. Environment Monit. Assess., 181(1–4), 205–223.
Bouchard Jr, R. W. (2004). Guide to aquatic invertebrates of the Upper Midwest: Identification manual for students, Citizen Scientist ‘s and Professionals. University of Minnesota. https://dep.wv.gov/WWE/getinvolved/sos/Pages/UMW.aspx
Brito, M. F. G., & Magalhães, A. L. B. (2017). Brazil’s development turns river into sea. Science, 358(6360), 179,1-179. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aap9525
Brittain, J. E., & Milner, A. M. (2001). Ecology of glacier-fed rivers: Current status and concepts. Freshwater Biology, 46(12), 1571–1578. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.2001.00845.x
Camargo, J. A. (1992). Temporal and spatial variations in dominance, diversity and biotic indices along a limestone stream receiving a trout farm effluent. Water Air Soil Pollution, 63, 343–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00475501
Clarke, K. R., & Ainsworth, M. (1993). A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 92, 205–219.
Clarke, K.R., Gorley, R.N. (2006) PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial (Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research). PRIMER-E, Plymouth.
Clarke K.R., Warwick R.M. (2001) Change in marine communities: An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E Ltd Plymouth Marine
Cuffney T. F., Gurtz, M. E. , & Meador, M. R. (1993) Methods for collecting benthic invertebrate samples as part of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey OpenFile Report 93-406. US Geological Survey.
Cuffney, T. F., Meador, M. R., Porter, S. D., & Gurtz, M. E. (2000). Responses of physical, chemical, and biological indicators of water quality to a gradient of agricultural land use in the Yakima River Basin, Washington. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 64, 259–270.
Dar G.H., Bhagat R.C., Khan M.A. (2002). Biodiversity of the Kashmir Himalaya. Valley Book House, Srinagar. 399 pp.
Dodds, W. K., Jones, J. R., & Welch, E. B. (1998). Suggested classification of stream trophic state: Distributions of temperate stream types by chlorophyll, total nitrogen, and phosphorus. Water Research, 32, 1455–1462.
Duan, X., Wang, Z., & Tian, S. (2008). Effect of streambed substrate on macroinvertebrate biodiversity. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering China, 2(1), 122–128.
Edegbene, A. O., Odume, O. N., & Arimoro, F. O. (2021). Identifying and classifying macroinvertebrate indicator signature traits and ecological preferences along urban pollution gradient in the Niger Delta. Environmental Pollution, 281, 117076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117076
Edema, C. U., Ayeni, J. O., & Aruoture, A. (2002). Some observations on the zooplankton and macrobenthos of the Okhuo River, Nigeria. Journal of Aquatic Sciences, 17(2), 145–149.
Edmondson, W.T. (1959). Fresh-Water Biology 2nd Ed. New York (NY) John Wiley and Sons, INC. pp. 1050–1056.
Engblom, E., & Lingdell, P. E. (1999). Analyses of benthic invertebrates. In L. Nyman (Ed.), River Jhelum, Kashmir Valley- Impacts on the aquatic environment (pp. 39–75). SWEDMAR.
Fazal, S., & Amin, A. (2011). Impact of urban land transformation on water bodies in Srinagar City. India Journal of Environmental Protection, 2, 142–153. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2011.22016
Ferreira, V., Elosegi, A., Tiegs, S.D., von Schiller, D. & Young, R. (2020). Organic matter decomposition and ecosystem metabolism as tools to assess the functional integrity of streams and rivers—a systematic review. Water 12, 3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123523
Hamid, A., Dar, N. A., Bhat, S. U., & Pandit, A. K. (2016). Water quality index: A case study of Vishav stream, Kulgam, Kashmir. International Journal of Environment and Bioenergy., 5(2), 1–15.
Hamid, A., Bhat, S.U., Jehangir, A. (2021). Assessment of ecological characteristics of macroinvertebrate communities and their relationship with environmental factors in a stream ecosystem. Chemistry and Ecology, 1–21 https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2021.1987419
Harding, J. S., Young, R. G., Hayes, J. W., Shearer, K. A., & Stark, J. D. (1999). Changes in agricultural intensity and river health along arriver continuum. Freshwater Biology, 42, 345–357.
Hering, D., Feld, C. K., Moog, O., & Ofenbock, T. (2006). Cook book for the development of a Multimetric-Index for biological condition of aquatic ecosystems: Experiences from the European AQEM and STAR projects and related initiatives. Hydrobiologia, 566, 311–324.
Hoang, H.T.T., Duong, T.T., Nguyen, K.T., Le, Q.T.P., Luu, M.T.N., Trinh, D.A., Le, A.H., Ho C.T., Dang K.D., Némery J., Orange D., Klein J. (2018). Impact of anthropogenic activities on water quality and plankton communities in the Day River (Red River Delta, Vietnam). Environment Monitoring Assessment, 190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6435-z
Ikomi, R. B., Arimoro, F. O., & Odihirin, O. K. (2005). Composition, distribution, and abundance of macroinvertebrates of the upper reaches of River Ethiope, Delta State, Nigeria. The Zoologist, 3, 68–81.
Ilmonen, J., & Paasivirta, L. (2005). Benthic macro crustacean and insect assemblages in relation to spring habitat characteristics: Patterns in abundance and diversity. Hydrobiologia, 533(1–3), 99–113.
Ivol-Rigaut, J. M., Guinand, B., Richoux, P., & Tachet, H. (1997). Longitudinal changes in Trichoptera and Coleoptera assemblages and environmental conditions in the Loire River (France). Archiv für Hydrobiology, 138, 525–557.
Jacobsen, D., & Marín, R. (2008). Bolivian Altiplano streams with low richness of macroinvertebrates and large diel fluctuations in temperature and dissolved oxygen. Aquatic Ecology, 42, 643–656.
Jun, Y. C., Kim, N. Y., Kim, S. H., Park, Y. S., Kong, D. S., & Hwang, S. J. (2016a). Spatial distribution of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in relation to environmental variables in Korean nationwide streams. Water (switzerland), 8(1), 1–20.
Jun, Y.-C., Kim, N.-Y., Kim, S.-H., Park, Y.-S., Kong, D.-S., & Hwang, S.-J. (2016b). Spatial distribution of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in relation to environmental variables in Korean nationwide streams. Water, 8, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010027
Kaboré, I., Moog, O., Alp, M., et al. (2016). Using macroinvertebrates for ecosystem health assessment in semi-arid streams of Burkina Faso. Hydrobiologia, 766, 57–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2443-6
Kaufmann P. R., Levine P., Peck D. V., Robison E. G., Seeliger C. (1999). Quantifying physical habitat in Wadeable streams (p. 149). USEPA (National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory, Western Ecology Division). https://archive.epa.gov/emap/archive-emap/web/html/phyhab.html
Khan, M. A. (1993a). Occurrence of a rare euglenoid causing red-bloom in Dal Lake waters of the Kashmir Himalaya. Archiv Für Hydrobiologie, 127, 101–103.
Khan, M. A. (1993b). Euglenoid red bloom contributing the environmental pollution of Dal Lake, Kashmir Himalaya. Environment Conservation, 20, 352–356.
Khanday, S. A., Bhat, S. U., Islam, T. S., & Sabha, I. (2020). Identifying lithogenic and anthropogenic factors responsible for spatio-seasonal patterns and quality evaluation of snow melt waters of the River Jhelum Basin in Kashmir Himalaya. CATENA, 196, 104853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104853
Landrigan, P. J., Fuller, R., Fisher, S., Suk, W. A., Sly, P., Chiles, T. C., et al. (2018). Pollution and children’s health. Science of Total Environment, 650(Pt 2), 2389–2394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.375
Langdon, P. G., Ruiz, Z., Brodersen, K. P., & Foster, I. D. L. (2006). Assessing lake eutrophication using chironomids: Understanding the nature of community response in different lake types. Freshwater Biology, 51, 562–577.
Ligeiro, R., Hughes, R. M., Kaufmann, P. R., Heino, J., Melo, A. S., & Callisto, M. (2020). Choice of field and laboratory methods affects the detection of anthropogenic disturbances using stream macroinvertebrate assemblages. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106382.
Ludwig, J. A., & Reynolds, J. F. (1988). Statistical Ecology. John Wiley.
Magurran, A. E. (2003). Measuring biological diversity. Oxford: Blackwell Science. 1–264. http://eu.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-0632056339.html. Accessed on 04-6-2020.
Malmqvist, B., & Hoffsten, P. O. (2000). Macroinvertebrate taxonomic richness, community structure and nestedness in Swedish streams. Archiv Für Hydrobiologie, 150(1), 29–54. https://doi.org/10.1127/archiv-hydrobiol/150/2000/29
Maneechan, W., & Prommi, T. O. (2015). Diversity and distribution of aquatic insects in stream of the Mae Klong watershed, western Thailand. Psyche: A Journal of Entomology, 2015(2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/912451
Mason, C. F. (2002). Biology of freshwater pollution (4th ed.). Prentice Hall.
McAllister D. E., Hamilton A. L., & Harvey B. (1997). Global freshwater biodiversity: Striving for the integrity of freshwater ecosystems. Sea Wind, 11(3), 1 142. http://hdl.handle.net/10625/14024
McCafferty, W. P., & Provonsha, A. V. (1998). Aquatic entomology: The fishermen’s and Ecologists’ illustrated guide to insects and their relatives (p. 448). Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Medupin, C. (2019). Distribution of benthic macroinvertebrate communities and assessment of water quality in a small UK river catchment. SN Applied Science, 1, 544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0464-x
Merritt, R. W., & Cummins, K. W. (2006). Trophic relationships. In Methods in stream ecology (2nd ed., pp 585–610). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416558-8.00020-2
Miyake, Y., & Nakano, S. (2002). Effects of substratum stability on diversity of stream invertebrates during baseflow at two spatial scales. Freshwater Biology, 47(2), 219–230. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.00798.x
Moore J. C. (2013). Diversity, taxonomic versus functional. In Levin, S. A. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of biodiversity (2nd Ed., pp 648–656). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384719-5.00036-8
Mourier L., Bauer A., Newell C. (2019). Benthic macroinvertebrate and water quality characterization of the Yampa–Green Rivers. Ecogeomorphology, GEL 136 Final Paper. https://watershed.ucdavis.edu/education/classes/files/content/page/Ecogeo%20Bug%20Paper%20CN_AB_LM%20Final.pdf
Musonge, P. L. S., Boets, P., Lock, K., Ambarita, M. N. D., Forio, M. A. E., & Goethals, P. L. M. (2020). Rwenzori Score (RS): A benthic macroinvertebrate index for biomonitoring rivers and streams in the Rwenzori Region. Uganda. Sustainability, 12, 10473. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410473
Negi, P., & Singh, D. (2021). Benthic macroinvertebrates diversity and quality of water in first-order streams of Badiyar Gad, lesser Himalaya, Uttarakhand. India. International Journal of Environmental Studies. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2021.1992119
Newall, P., & Walsh, C. J. (2005). Response of epilithic diatom assemblages to urbanization influences. Hydrobiologia, 532, 53–67.
Nicacio, G., Cunha, E. J., Hamada, N., et al. (2020). How habitat filtering can affect taxonomic and functional composition of aquatic insect communities in small Amazonian streams. Neotropical Entomology, 49, 652–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-020-00780-z
Oliveira, V. A., de Mello, C. R., Viola, M. R., & Srinivasan, R. (2017). Assessment of climate change impacts on streamflow and hydropower potential in the headwater region of the Grande river basin, Southeastern Brazil. International Journal of Climatology, 37(15), 5005–5023. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5138
Pandiarajan, S., Thambiratnam, S., Rajasekaran, I., & Sivaruban, B. (2019). Bio-monitoring and detection of water quality using Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera (EPT) complex in Karanthamalai Stream of Eastern Ghats. Indian. Journal of Ecology, 46(4), 818–822.
Pandit A.K. (1999) Trophic structure of plankton community in some typical wetlands of Kashmir, India. In: Mishra SR (ed) Limnological research in India. Daya Publishing House, Delhi-110035 p 190–224
Paul, M. J., & Meyer, J. L. (2001). Streams in the urban landscape. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 333–365.
de Paula, F. R., Gerhard, P., Ferraz, SFd. B., & Wenger, S. J. (2018). Multi-scale assessment of forest cover in an agricultural landscape of Southeastern Brazil: Implications for management and conservation of stream habitat and water quality. Ecological Indicators, 85, 1181–1191.
De Pauw, N., Gabriels, W., & Goethals, P. (2006). River monitoring and assessment methods based on macroinvertebrates. In Ziglio, G., Siligardi, M., & Flaim G. (Eds.), Biological monitoring of rivers: Applications and perspectives (pp 113–134). John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/0470863781.ch7
Pennak, R. W. (1978). Freshwater invertebrates of United States. John Wiley and Sons.
Pitt R. (2002). Receiving water impacts associated with urban runoff. Pages 1–30 in D. Hoffman, B. Rattner. G.A. Burton, Jr. and J. Cairns Jr. Handbook of Ecotoxicology, 2 nd Edition. CRC - Lewis. Boca Raton Fl.
Rashid, I., & Romshoo, S. A. (2013). Impact of anthropogenic activities on water quality of Lidder River in Kashmir Himalayas. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(6), 4705–4719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2898-0
Rosenzweig, M. L. (1995). Species diversity in space and time. Cambridge University Press.
Sabha, I., Bhat, S. U., Hamid, A., & Rather, J. A. (2019). Monitoring stream water quality of Dagwan Stream, an important tributary of Dal Lake. Kashmir Himalaya. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 12, 273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4
Sabha, I., Khanday, S. A., Islam, S. T., & S.T., Bhat S.U. (2020). Longitudinal and temporal assemblage patterns of benthic macroinvertebrates in snow melt stream waters of the Jhelum River Basin of Kashmir Himalaya (India). Ecohydrology, 13(7), e2236.
Santos, J. M., & Ferreira, M. T. (2020). Use of aquatic biota to detect ecological changes in freshwater: Current status and future directions. Water, 12, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061611
Serpa, D., Keizer, J. J., Cassidy, J., & Cuco, A. (2014). Assessment of river water quality using an integrated physicochemical, biological and ecotoxicological approach. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 16, 1434–1444. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00488K
Shah, A. H., Teli, P. A., & Bhat, M. S. (2014). Dynamics of land use/land cover change in Dal Lake watershed of Kashmir valley—a remote sensing and GIS approach. International Journal of Advanced Information Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.15693/ijaist/2014.v3i12.1-9a
Shannon, C. E., & Weiner, W. (1949). The mathematical theory of communication (p. 144). University of Illinois Press, Urbana.
Sharma, R. C., Bhanot, G., & Singh, D. (2004). Aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity in Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve. India. Environmentalist, 24(4), 211–221.
Simpson, E. H. (1949). Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163, 688.
Sofi, M. S., Bhat, S. U., Rashid, I., & Kuniyal, J. C. (2020). The natural flow regime: A master variable for maintaining river ecosystem health. Ecohydrology, 13(8). https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.2247
Sofi, M. S., Hamid, A., Bhat, S. U., Rashid, I., & Kuniyal, J. C. (2022). Biotic alteration of benthic macroinvertebrate communities based on multispatial-scale environmental variables in a regulated river system of Kashmir Himalaya. Ecological Engineering, 177, 106560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2022.106560
Stanford, J. A., Lorang, M. S., & Hauer, F. R. (2005). The shifting habitat mosaic of river ecosystems. SIL Proceedings, 29, 123–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/03680770.2005.11901979
Subramanian K. A., & Sivaramakrishnan K. G. (2007). Aquatic insects for biomonitoring freshwater ecosystems-A methodology manual. Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and Environment (ATREE), Bangalore, India. http://wgbis.ces.iisc.ernet.in/energy/water/paper/cistup_TR1/Indian_aqua_Insects.pdf. Accessed on 02-05-2018.
Tampo, L., Kaboré, I., Alhassan, E. H., Ouéda, A., Bawa, L. M., & Djaneye-Boundjou, G. (2021). Benthic macroinvertebrates as ecological indicators: Their sensitivity to the water quality and human disturbances in a tropical river. Frontiers in Water, 3, 662765. https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2021.662765
Tan, K. W., & Beh, W. C. (2016). Evaluation of water quality and benthic macroinvertebrates fauna relationship using principal component analysis (PCA): A case study of Cameron Highlands Malaysia. Environmental Management and Sustainable Development, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.5296/emsd.v5i1.9399
Taylor, S. L., Robert, S. C., Walsh, C. J., & Hatt, B. E. (2004). Catchment urbanization and increased benthic algal biomass in streams: Linking mechanisms to management. Freshwater Biology, 49, 835–851.
Vander Laan, J. J., Hawkins, C. P., Olson, J. R., & Hill, R. A. (2013). Linking land use, in-stream stressors, and biological condition to infer causes of regional ecological impairment in streams. Freshwater Science, 32(3), 801–820. https://doi.org/10.1899/12-186.1
Walsh, C., Gooderham, J. P., Grace, M. R., Sdraulig, S., Rosyidi, M. I., & Lelono, A. (2002). The relative influence of diffuse and point-source disturbances on a small upland stream in East Java Indonesia: A preliminary investigation. Hydrobiologia, 487, 183–192.
Walsh, G., & Wepner, V. (2009). The influence of land use on water quality and diatom community structures in urban and agriculturally stressed rivers. Water SA, 35(5), 579–594. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v35i5.49184
Walsh, J.C., Fletcher, T.D., Ladson, A.R. (2005). Stream restoration in urban catchments through redesigning storm water systems: Looking to the catchment to save the stream source: Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 24(3), 690–705. https://doi.org/10.1899/04-020.1. http://www.bioone.org/doi/full/10.1899/04-020.1
Ward, J. V. (1992). Aquatic insect ecology (p. 438). John Wiley.
Wenger, S. J., Roy, A., Jackson, C. R., & Walsh, J. C. (2009). Twenty-six key research questions in urban stream ecology: An assessment of the state of the science. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 28(4), 1080–1098. https://doi.org/10.1899/08-186.1
WFD UKTAG. (2013) Water Framework Directive – United Kingdom Advisory Group (WFD-UKTAG). Environmental Standards River Basin Management 2015–2021. Wfd_Uktag, 2013
Zhang, J., Shang, Y., Liu, J., Fu, J., Wei, S. & Tong, L. (2020). Causes of variations in sediment yield in the Jinghe River Basin China. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 18054. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-74980-3
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful to the Head, Department of Environmental Sciences, and the University of Kashmir for providing lab facilities and facilitating research work. Wildlife department, J&K, and Dachigam National Park officials are thanked for the permission to work in the Dachigam National Park.
Funding
This research work is funded and supported by SERB-DST having grant no. EMR/2016/000324 dated 24/03/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Inam Sabha: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, visualization, roles/writing—original draft. Aadil Hamid: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software; writing—original draft. Sami Ullah Bhat: conceptualization, supervision, validation, visualization, roles/writing—original draft, funding acquisition, project administration. Sheikh Tajamul Islam: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sabha, I., Hamid, A., Bhat, S.U. et al. Water Quality and Anthropogenic Impact Assessment Using Macroinvertebrates as Bioindicators in a Stream Ecosystem. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05839-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05839-8