Abstract
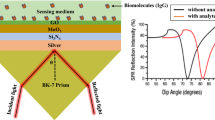
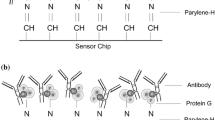
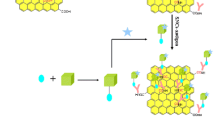
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) has gained attention as a promising method for effective label-free biosensing. Immunoglobulin (IgG) detection is very important to understand the past infection and immunity of any individual. Thus, this study aims to develop a SPR sensor with better sensitivity for detecting IgG. It emphasizes the utilization of a high-performance planar waveguide-based SPR sensor to detect IgG by analyzing a suitable sensor topology. The sensor configuration consists of five distinct layers: silver (Ag), silicon nitride (\({{\text{Si}}}_{3}{{\text{N}}}_{4}\)), black phosphorus (BP), an enzyme, and a sensing medium. Silver (Ag) stimulates surface plasmons, while Si3N4 and BP are utilized to enhance absorption capabilities and serve as the bio-molecular recognition element, respectively. The proposed sensor simulation employs the transfer matrix method and an angular interrogation scheme. To assess this proposed sensor’s impact, the sensing region is assessed while considering three layers: Ag, Ag-BP, and Ag–Si3N4. Initially, the thickness of the Ag layer is optimized by recording its transmittance and achieving a minimum transmittance of 0.0027 at a thickness of 50 nm. Subsequently, the performance parameters are assessed using four different structures with slight variations in the IgG samples. The results depict the maximum achieved sensitivities as follows: 192 \(^\circ /{\text{RIU}}\) for conventional SPR, 203 \(^\circ /{\text{RIU}}\) for BP-based SPR, 287 \(^\circ /{\text{RIU}}\) for Si3N4-based SPR, and 352 \(^\circ /{\text{RIU}}\) for the proposed structure. This comparative study demonstrates that the proposed SPR configuration significantly enhances sensitivity, quality factor, and detection accuracy performance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not Applicable.
References
Agnarsson, B., Halldorsson, J., Arnfinnsdottir, N., Ingthorsson, S., Gudjonsson, T., Leosson, K.: Fabrication of planar polymer waveguides for evanescent-wave sensing in aqueous environments. Microelectron. Eng. 87, 56–61 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2009.05.016
Akib, T.B.A., Rana, M.M., Mehedi, I.M.: Multi-layer SPR biosensor for in-situ amplified monitoring of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) variant. Biosens. Bioelectron.: X 16, 1–13 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosx.2023.100434
Amirjani, A., Haghshenas, D.F.: Ag nanostructures as the surface plasmon resonance (SPR)˗ based sensors: a mechanistic study with an emphasis on heavy metallic ions detection. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 273, 1768–1779 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.089
Bahabady, A.M., Olyaee, S.: Two-curve-shaped biosensor for detecting glucose concentration and salinity of seawater based on photonic crystal nano-ring resonator. Sens. Lett. 13(9), 774–777 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2015.3517
Bahri, H., Hocini, A., Bensalah, H., Mouetsi, S., Ingebrandt, S., Pachauri, V., Hamani, M.: A high-sensitivity biosensor based on a metal–insulator–metal diamond resonator and application for biochemical and environment detections. Optik 271, 1–9 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.170083
Beck, F., Loessl, M., Baeumner, A.J.: Signaling strategies of silver nanoparticles in optical and electrochemical biosensors: considering their potential for the point-of-care. Microchim. Acta 190, 1–19 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05666-6
Ben Salah, H., Hocini, A., Temmar, M., Khedrouche, D.: Design and analysis of mid-infrared high sensitive metal-insulator-metal plasmonic sensor. Chin. J. Phys. 61, 86–97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.07.006
Bensalah, H., Hocini, A., Bahri, H.: Design and analysis of a mid-infrared ultra-high sensitive sensor based on metal-insulator-metal structure and its application for temperature and detection of glucose. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2022(112), 81–91 (2022a). https://doi.org/10.2528/PIERM22032604
Salah, H.B., Bahri, H., Hocini, A., Zegaar, I., Ingebrandt, S., Pachauri, V.: Design of a plasmonic sensor based on a nanosized structure for biochemical application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2240, 1–5 (2022b). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2240/1/012024
Blázquez, O., López-Vidrier, J., Hernández, S., Montserrat, J., Garrido, B.: Electro-optical properties of non-stoichiometric silicon nitride films for photovoltaic applications. Energy Procedia. 44, 145–150 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2013.12.021
Chao, C.T., Chau, Y.F., Chiang, H.P.: Multiple Fano resonance modes in an ultra-compact plasmonic waveguide-cavity system for sensing applications. Res. Phys. 27, 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104527
Cherouana, A., Benaissa, S., Bencheikh, A., et al.: Optimization of waveguide parameters for minimization of the sensitivity temperature dependence for the SiO2:TiO2 planar waveguide optical sensor. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 1–21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05360-0
Diéguez, L., Darwish, N., Mir, M., Martínez, E., Moreno, M., Samitier, J.: Effect of the refractive index of buffer solutions in evanescent optical biosensors. Sens. Lett. 7, 851–855 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2009.1161
Duveneck, G.L., Pawlak, M., Neuschäfer, D., Bär, E., Budach, W., Pieles, U., Ehrat, M.: Novel bioaffinity sensors for trace analysis based on luminescence excitation by planar waveguides. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 38, 88–95 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(97)80176-1
Ebadi, S.M., Örtegren, J., Bayati, M.S., Ram, S.B.: A multipurpose and highly-compact plasmonic filter based on metal-insulator-metal waveguides. IEEE Photonics J. 12(3), 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2020.2974959
Gahlaut, S.K., Pathak, A., Gupta, B.D., Singh, J.P.: Portable fiber-optic SPR platform for the detection of NS1-antigen for dengue diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 196, 1–8 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113720
Gowdhami, D., Balaji, V.R., Murugan, M., et al.: Photonic crystal based biosensors: an overview. ISSS J. Micro. Smart Syst. 11, 147–167 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41683-022-00092-x
Han, L., Ding, H., Landry, N.N., Hua, M., Huang, T.: Highly sensitive SPR sensor based on Ag-ITO-BlueP/TMDCs-graphene heterostructure. Plasmonics 15, 1489–1498 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01165-z
Hanson, E.K., Whelan, R.J.: Application of the nicoya openSPR to studies of biomolecular binding: a review of the literature from 2016 to 2022. Sensors 23(10), 1–22 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104831
Homola, J., Yee, S.S., Gauglitz, G.: Surface plasmon resonance sensors: review. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 54, 3–15 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(98)00321-9
Hossain, B., Kabir, A., Rahman, M., Roy, S., Abdulrazak, L.F., Hossain, S., Mondol, N., Rahman, M.H., Islam, K.Z., Pathan, M.I.: Hybrid structure based high performance SPR sensor: a numerical approach of structure optimization for DNA hybridization. Opt. Quant. Electron. 53, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02650-9
Islam, M.A., et al.: Design and analysis of GO coated high sensitive tunable SPR sensor for OATR spectroscopic biosensing applications. IEEE Access 10, 103496–103508 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3211099
Janith, G.I., Herath, H.S., Hendeniya, N., Attygalle, D., Amarasinghe, D.A.S., Logeeshan, V., Wickramasinghe, P.M.T.B., Wijayasinghe, Y.S.: Advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensors for medical diagnostics: an overview of recent developments and techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. Open 2, 1–12 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpbao.2023.100019
Jha, R., Sharma, A.K.: Chalcogenide glass prism based SPR sensor with Ag–Au bimetallic nanoparticle alloy in infrared wavelength region. J. Opt. A-Pure Appl. Opt. 11, 1–7 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1464-4258/11/4/045502
Karki, B., Jha, A., Pal, A., et al.: Sensitivity enhancement of refractive index-based surface plasmon resonance sensor for glucose detection. Opt. Quant. Electron. 54, 1–13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04004-z
Kashyap, R., Nemova, G.: Surface plasmon resonance-based fiber and planar waveguide sensors. J. Sens. 2009, 1–9 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/645162
Kim, K.-J., Lu, P., Culp, J.T., Ohodnicki, P.R.: Metal-organic framework thin film coated optical fiber sensors: a novel waveguide-based chemical sensing platform. ACS Sensors 3, 386–394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00808
Kushwaha, A.S., Kumar, A., Kumar, R., Srivastava, M., Srivastava, S.: Zinc oxide, gold and graphene-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for detection of pseudomonas like bacteria: a comparative study. Optik 172, 697–707 (2018a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.07.066
Kushwaha, A., Hans, N., Kumar, S., Rani, R.: A critical review on speciation, mobilization and toxicity of lead in soil-microbe-plant system and bioremediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 147, 1035–1045 (2018b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.049
Lavers, C.R., Itoh, K., Wu, S.C., Murabayashi, M., Mauchline, I., Stewart, G., Stout, T.: Planar optical waveguides for sensing applications. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 69, 85–95 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(00)00412-3
Lee, K.L., Lee, C.W., Wang, W.S., Wei, P.K.: Sensitive biosensor array using surface plasmon resonance on metallic nanoslits. J Biomed. Opt. 12, 1–5 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.2772296
Loan, P.T.K., Zhang, W., Lin, C.T., Wei, K.H., Li, L.J., Chen, C.H.: Graphene/MoS2 heterostructures for ultrasensitive detection of DNA hybridization. Adv. Mater. 26, 4838–4844 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201401084
Mao, J., Zhai, X., Wang, L., Li, H.: Numerical analysis of near-infrared plasmonic filter with high figure of merit based on Fano resonance. Appl. Phys. Express 10(8), 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.7567/APEX.10.082201
Mitsushio, M., Miyashita, K., Higo, M.: Sensor properties and surface characterization of the metal-deposited SPR optical fiber sensors with Au, Ag, Cu, and Al. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 125, 296–303 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2005.08.019
Mondal, H.S., Ahmed, K.A., Birbilis, N., et al.: Machine learning for detecting DNA attachment on SPR biosensor. Sci. Rep. 13, 1–10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-29395-1
Moznuzzaman, M., Islam, M.R., Khan, I.: Effect of layer thickness variation on sensitivity: an SPR based sensor for formalin detection. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 32, 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2021.100419
Mudgal, N., Yupapin, P., Ali, J., Singh, G.: BaTiO3-Graphene-affinity layer-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for pseudomonas bacterial detection. Plasmonics 15, 1221–1229 (2020a). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01146-2
Mudgal, N., Saharia, A., Choure, K.K., Agarwal, A., Singh, G.: Sensitivity enhancement with anti-reflection coating of silicon nitride (Si3N4) layer in silver-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor for sensing of DNA hybridization. Appl. Phys. A 126, 1–8 (2020b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04126-9
Mudgal, N., Choure, K.K., Falaswal, M.K., et al.: Impact of Taguchi optimization in fiber surface plasmon resonance sensors based on Si3N4 layer. Braz. J. Phys. 52, 1–10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-022-01088-6
Mudgal, N., Sahara, A., Agarwal, A., Singh, G.: ZnO and Bi-metallic (Ag–Au) layers based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor with BaTiO3 and graphene for biosensing applications. IETE J. Res. 69, 932–939 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2020.1844074
Mukundan, H., Kubicek, J.Z., Holt, A., Shively, J.E., Martinez, J.S., Grace, K., Grace, W.K., Swanson, B.I.: Planar optical waveguide-based biosensor for the quantitative detection of tumor markers. Sens. Actuat., B Chem. 138, 453–460 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.01.073
Muthumanicam, M., Vibisha, A., Lordwin Prabhakar, M.C., Suresh, P., Rajesh, K.B., Jaroszewicz, Z., Jha, R.: Numerical investigation on high-performance Cu-based surface plasmon resonance sensor for biosensing application. Sensors 23(17), 1–15 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177495
Najafgholinezhad, S., Olyaee, S.: A photonic crystal biosensor with temperature dependency investigation of micro-cavity resonator. Optik 125, 6562–6565 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.043
Nangare, S., Patil, P.: Black phosphorus nanostructure based highly sensitive and selective surface plasmon resonance sensor for biological and chemical sensing: a review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 53, 1–26 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2021.1927669
Olyaee, S., Bahabady, A.M.: Design and optimization of diamond-shaped biosensor using photonic crystal nano-ring resonator. Optik 126(20), 2560–2564 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.06.037
Pal, S., Verma, A., Raikwar, S., Prajapati, Y.K., Saini, J.P.: Detection of DNA hybridization using graphene-coated black phosphorus surface plasmon resonance sensor. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 124, 394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1804-1
Parandin, F., Heidari, F., Rahimi, Z., Olyaee, S.: Two-dimensional photonic crystal biosensors: a review. Opt. Laser Technol. 144, 1–45 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107397
Qu, G., Xia, T., Zhou, W., Zhang, X., Zhang, H., Hu, L., Shi, J., Yu, X.-F., Jiang, G.: Property–activity relationship of black phosphorus at the nano–bio interface: from molecules to organisms. Chem. Rev. 120, 2288–2346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00445
Rahman, M.S., Anower, M.S., Hasan, M.R., Rikta, K.A.: Design and analysis of graphene coated planar waveguide based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Sens. Lett. 15, 485–491 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2017.3843
Raikwar, S., Prajapati, Y.K., Srivastava, D.K., Saini, J.P.: Graphene oxide based SPR sensor for sensing of sea water concentration. Res. Opt. 1, 1–5 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rio.2020.100011
Ravindran, N., Kumar, S., Yashini, M., Rajeshwari, S., Mamathi, C.A., Thirunavookarasu, S.N., Sunil, C.K.: Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors for food analysis: a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63, 1055–1077 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1958745
Rumi, R.B., Paul, A.K., Alyami, S.A., Moni, M.A.: Multi-disease detection using a prism-based surface plasmon resonance sensor: a TMM and FEM approach. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 23, 51–62 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2023.3286269
Sheng, X., Liu, J., Yang, H., Chen, L., Li, J., Liu, H.: Optimization of tunable symmetric SPR sensor based on Ag-graphene. Optik 184, 339–347 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.04.076
Singh, M.K., Pal, S., Prajapati, Y.K., Saini, P.: Sensitivity improvement of surface plasmon resonance sensor on using BlueP/MoS2 heterostructure and antimonene. IEEE Sens. Lett. 4, 1–4 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rio.2020.100011
Syms, R.R.A., Solymar, L.: Loss and thermal noise in plasmonic waveguides. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 1–12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4880663
Uniyal, A., Srivastava, G., Pal, A., et al.: Recent advances in optical biosensors for sensing applications: a review. Plasmonics 18, 735–750 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01803-2
Wu, Q., Song, D., Zhang, D., Sun, Y.: An enhanced SPR immunosensing platform for human IgG based on the use of silver nanocubes and carboxy-functionalized graphene oxide. Microchim. Acta 183, 2177–2184 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1853-0
Yang, Y., Xiang, Y., Qi, X.: Design of photonic crystal biosensors for cancer cell detection. Micromachines. 1–11 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi1407147
Yun, C., Shun, M., Jackson, K., Newiduom, L., Browndi, I.: The use of bilayers consisting of graphene and noble metals has been explored for biosensors that employ inverted surface plasmon resonance. Int J Sci Inf Syst 12, 441–449 (2022)
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LS conceptualized the whole idea and wrote the main manuscript, PP wrote the main manuscript and assisted LS; RK and VA prepared figures and abstract; NKM and AB prepared a literature review along with references.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, L., Pareek, P., Kumar, R. et al. Investigation of SPR sensor for immunoglobulin detection by using Ag–\({{\text{Si}}}_{3}{{\text{N}}}_{4}\)-BP on the sensing layer. Opt Quant Electron 56, 771 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06665-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06665-4