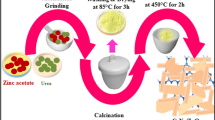
Abstract
Via a simple sol-gel approach, the high photocatalytic efficiency of Bi1-xSmxFeO3 nanoparticles were realized when x was 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15 and 0.20. Microstructural characterizations including X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometer, demonstrated a transformation from the rhombohedral structure of BiFeO3 to the orthorhombic structure of Bi0.80Sm0.20FeO3. Moreover, the experimental findings discovered that the photocatalytic efficiency of Bi0.80Sm0.20FeO3 was the highest, reaching 98.5% within 2 h based on visible light degradation. The underlying mechanisms, involved to phase transition, size effect, band energy and Fenton reaction, were discussed. The research presented in the paper is crucial in offering a fundamental strategy for utilizing BiFeO3 to address the issue of water pollutants.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
-
Bi1-xSmxFeO3 nanoparticles with varying Sm doping levels (x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, and 0.20) were successfully synthesized in this study.
-
X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy demonstrated that the transformation of the rhombohedral crystal structure (R3c space group) to the orthorhombic structure (Pnma space group) in Bi0.80Sm0.20FeO3.
-
Experimental results indicated that the photocatalytic efficiency of Bi0.80Sm0.20FeO3 reach to 98.5%, with superior chemical stability.
-
These findings offer a fundamental strategy for utilizing BiFeO3 in addressing water pollutant issues.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Zhang J, Gondal MA, Wei W, Zhang TN, Xu QY, Shen K (2012) Preparation of room temperature ferromagnetic BiFeO3 and its application as an highly efficient magnetic separable adsorbent for removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. J Alloy Compd 530:107–110
Ćirković J, Radojković A, Luković Golić D, Tasić N, Čizmić M, Branković G et al. (2021) Visible-light photocatalytic degradation of Mordant Blue 9 by single-phase BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104587
Long JJ, Ren TT, Han J, Li NJ, Chen DY, Xu QF et al. (2022) Heterostructured BiFeO3@CdS nanofibers with enhanced piezoelectric response for efficient piezocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Sep Purif Technol 290:120861
Zhang LT, Li XJ, Chen JG, Jin DR, Cheng JR (2022) Enhanced photocatalytic activity in ferroelectric BiFeO3 nanoparticles treated by a corona poling method. Ceram Int 48(11):15908–15912
Wang YX, Chen J, Wu J, Armutlulu A, Xie RZ (2023) Constructing durable BiFeO3@SrBi2B2O7 p-n heterojunction for persulfate enhanced piezo-photocatalytic water purification. Sep Purif Technol 324:124479
Gupta G, Kansal SK, Umar A, Akbar AS (2023) Visible-light driven excellent photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin antibiotic using BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 314:137611
Higuchi T, Liu YS, Yao P, Glans PA, Guo JH, Chang CL et al. (2008) Electronic structure of multiferroic BiFeO3 by resonant soft x-ray emission spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 78(8):085106
Gao T, Chen Z, Niu F, Zhou DT, Huang QL, Zhu TX et al. (2015) Shape-controlled preparation of bismuth ferrite by hydrothermal method and their visible-light degradation properties. J Alloy Compd 648:564–570
Parida S, Nanda J, Sarangi B (2023) Investigation of structural, optical, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of Eu–Mg co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Sol Gel Sci Technol https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06257-w
Bossini D, Juraschek DM, Geilhufe RM, Nagaosa N, Balatsky AV, Milanović M et al. (2023) Magnetoelectrics and multiferroics: theory, synthesis, characterisation, preliminary results and perspectives for all-optical manipulations. J Phys D Appl Phys 56:273001
Yan YJ, Wang RH, Maimaitituersun M, Sun HJ, Liu XF, Mater J (2022) Built-in electric field enhanced BiFeO3 photo-Fenton degradation Rhodamine B solution. J Mater Sci 57(13):6900–6913
Rusevova K, Köferstein R, Rosell M, Richnow HH, Kopinke FD, Georgi A (2014) LaFeO3 and BiFeO3 perovskites as nanocatalysts for contaminant degradation in heterogeneous Fenton-like reactions. Chem Eng J 239:322–331
Moreau JM, Michel C, Gerson R, James WJ (1971) Ferroelectric BiFeO3 X-ray and neutron diffraction study. Phys Chem Solids 32(6):1315–1320
Chen JR, Wang WL, Li JB, Rao GH (2008) X-ray diffraction analysis and specific heat capacity of (Bi1−xLax)FeO3 perovskites. J Alloy Compd 459(1):66–70
Ahmad T, Jindal K, Tomar M, Jha PK (2023) Theoretical insight of origin of Rashba–Dresselhaus effect in tetragonal and rhombohedral phases of BiFeO3. Phys Chem Chem Phys 25:5857–5868
Gervits NE, Tkachev AV, Zhurenko SV, Gunbin AV, Lomanova NA, Danilovich DP et al. (2023) The size effect of BiFeO3 nanocrystals on the spatial spin modulated structure. Phys Chem Chem Phys 25(37):25526–25536
Yu JD, Koshikawa N, Arai Y, Yoda S, Saitou H (2001) Containerless solidification of oxide material using an electrostatic levitation furnace in microgravity. J Cryst Growth 231(4):568–576
Wang YP, Zhou L, Zhang MF, Chen XY, Liu JM, Liu ZG (2004) Room-temperature saturated ferroelectric polarization in BiFeO3 ceramics synthesized by rapid liquid phase sintering. Appl Phys Lett 84:1731–1733
Quan ZC, Hu H, Xu S, Liu W, Fang GJ, Li MY (2008) Surface chemical bonding states and ferroelectricity of Ce-doped BiFeO3 thin films prepared by sol–gel process. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 48:261–266
Xu JH, Ke H, Jia DC, Wang W, Zhou Y (2009) Low-temperature synthesis of BiFeO3 nanopowders via a sol–gel method. J Alloy Compd 472:473–477
Mao WW, Wang XF, Han YM, Li X, Li YT, Wang YF et al. (2014) Effect of Ln (Ln = La, Pr) and Co co-doped on the magnetic and ferroelectric properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 584:520–523
Liu Y, Zuo RZ, Qi SS (2013) Controllable preparation of BiFeO3@carbon core/shell nanofibers with enhanced visible photocatalytic activity. J Mol Catal A Chem 376:1–6
Nie Y, Ma HE, Wang Z, Lan CY, Zhang Wei, Chen LM et al. (2023) New insights into the photocatalytic and magnetic activity of Co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles via competing structures. J Phys D: Appl Phys 56:234002–234015
Vanga PR, Mangalaraja RV, Ashok M (2015) Structural, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of La and alkaline co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process 40:796–802
Arya GS, Sharma RK, Negi NS (2013) Enhanced magnetic properties of Sm and Mn co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles at room temperature. Mater Lett 93:341–344
Li Q, Bao SX, Liu YL, Li YX, Jing YL, Li J (2016) Influence of lightly Sm-substitution on crystal structure, magnetic and dielectric properties of BiFeO3 ceramics. J Alloy Compd 682:672–678
Yotburut B, Thongbai P, Yamwong T, Maensiri S (2017) Synthesis and characterization of multiferroic Sm-doped BiFeO3 nanopowders and their bulk dielectric properties. J Magn Magn Mater 437:51–61
Karpinsky DV, Pakalnis A, Niaura G, Zhaludkevich DV, Zhaludkevich AL, Latushka SI (2021) Evolution of the crystal structure and magnetic properties of Sm-doped BiFeO3 ceramics across the phase boundary region. Ceram Int 47:5399–5406
Zhao HH, Lai YJ, Feng LS, Shen JD, Jia XY, Mi W (2023) Ferroelectric, ferromagnetic and magneto-capacitance properties of Sm-doped BiFeO3-BaTiO3 solid solution. Appl Phys 129:77
Kebede MT, Devi S, Dillu V, Chauhan S (2022) Effects of Sm and Cr co-doping on structural, magnetic, optical and photocatalytic properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng B-Adv 283:115859
Vishwakarma AK, Hussain M, Verma SK, Shukla V, Shaz MA, Srivastava ON (2021) Synthesis and characterizations of graphene/Sm doped BiFeO3 composites photoanode for efficient photo-electrochemical water splitting. Int J Hydrog Energy 46(29):15550–15560
Huang CF (2019) Structural and magnetic characterization of Bi1–xLaxFeO3 and BiFe1–yMnyO3 nanoparticles synthesized via a sol–gel method. Phase Transit 92(2):164–171
Huang CF, Zhang XL, Zhang H, Zhang W, Lan CY, Li MX (2020) Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic performance from size effects in pure and La-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 126(4):273
Lin TK, Chang HW, Sung YH, Wang CR, Wei DH, Tu CS et al. (2020) Multiferroic properties of Bi0.95R0.05FeO3 polycrystalline films on the glass substrates (R = La, Pr, Nd, Sm, and Ho). Mater Lett 276:128216
Singh HH, Sharma HB (2019) Enhanced electrical and magnetic properties of samarium (Sm) doped multiferroic bismuth ferrite (BFO) ceramics. Integr Ferroelectr 203(1):120–132
Supplemental material for Rietveld analysis and magnetic characteristics of the prepared nanoparticles.
Rodríguez-Carvajal J (1993) Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys B 192:55–69
Roisnel T, Rodríguez-Carvajal J (2001) WinPLOTR: A Windows Tool for Powder Diffraction Pattern Analysis. Mater Sci Forum 378:118–123
Kumar P, Kar M (2015) Mater Sci Semiconductor Process Mater Sci Semicond Process 31:262–271
Kumar P, Shankhwar N, Srinivasan A, Kar M (2015) Oxygen octahedra distortion induced structural and magnetic phase transitions in Bi1-xCaxFe1-xMnxO3 ceramics. J Appl Phys 117:194103
Kumar P, Panda C, Kar M (2015) Effect of rhombohedral to orthorhombic transition on magnetic and dielectric properties of La and Ti co-substituted BiFeO3. Smart Mater Struct 24:045028–045040
Rhaman MM, Matin MA, Hossain MN, Mozahid FA, Hakim AM, Rizvi MH et al. (2018) Bandgap tuning of Sm and Co co-doped BFO nanoparticles for photovoltaic application. J Electron Mater 47(12):6954–6958
Dutta DP, Mandal BP, Naik R, Lawes RG, Tyagi AK (2013) Magnetic, Ferroelectric, and magnetocapacitive properties of sonochemically synthesized Sc-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 117(5):2382–2389
Zhang JY, Xue W, Chen XY, Hou ZL (2020) Sm doped BiFeO3 nanofibers for improved photovoltaic devices. Chin J Phys 66:301–306
Kothari D, Reddy VR, Sathe VG, Gupta A, Banerjee A, Awasthi AM (2008) Raman scattering study of polycrystalline magnetoelectric BiFeO3. J Magn Magn Mater 320(3-4):548–552
Suresh P, Babu PD, Srinath S (2014) Effect of Ho substitution on structure and magnetic properties of BiFeO3. J Appl Phys 115:17D905
Dieguez O, Gonzalez-Vazquez OE, Wojdel JC, Iniguez J (2011) First-principles predictions of low-energy phases of multiferroic BiFeO3. Phys Rev B 83:094105
Liu HM, Wei GL, Xu Z, Liu P, Li Y (2016) Quantitative analysis of Fe and Co in Co-substituted magnetite using XPS: the application of non-linear least squares fitting (NLLSF). Appl Surf Sci 389:438–446
Gao T, Chen Z, Zhu TX, Niu F, Huang QL, Qin LS (2014) Synthesis of BiFeo3 nanoparticles for the visible-light induced photocatalytic property. Mater Res Bull 59:6–12
Jamil H, Dildar IM, Ilyas U, Hashmi JZ, Shaukat S, Sarwar MN et al. (2021) Microstructural and optical study of polycrystalline manganese oxide films using Kubelka-Munk function. Thin Solid Films 732:138796
Xun BW, Song AZ, Yu JR, Yin Y, Li JF, Zhang BP (2021) Lead-free BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ceramics with high curie temperature: fine compositional tuning across the phase boundary for high piezoelectric charge and strain coefficients. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:4192–4202
Orudzhev FF, Alikhanov NMR, Ramazanov SM, Sobola DA, Murtazali RK, Ismailov EH et al. (2022) Morphotropic Phase Boundary Enhanced Photocatalysis in Sm Doped BiFeO3. Mol 27(20):7029–7048
Hu ZJ, Chen D, Wang S, Zhang N, Qin LS, Huang YX et al. (2017) Facile synthesis of Sm-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles for enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance. Mater Sci Eng: B 220:1–12
Kumar P, Chand P (2022) Sm3+-BiFeO3 nano catalyst: A synergetic effect of Sm3+ on enhanced multiferroic properties and photocatalysis. J Alloy Compd 891:161896
Gu YH, Zhou Y, Zhang WY, Guo GY, Zhang XH, Zhao JG et al. (2021) Optical and magnetic properties of Sm-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles around the morphotropic phase boundary region. AIP Adv 11:045223
Irfan S, Shen Y, Rizwan S, Wang HC, Khan HB, Nan CW (2016) Band-Gap Engineering and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Sm and Mn. J Am Ceram Soc 100(1):31–40
Arya G, Yogiraj J, Negi NS, Shah J, Kotnala RK (2017) Observation of enhanced multiferroic, magnetoelectric and photocatalytic properties in Sm-Co codoped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 723:983–994
Mohamed WAA, Mousa HA, Abd El-Gawad HH, Handal HT, Galal HR, Ibrahim IA et al. (2023) Photophysical effects of TiO2 quantum dots on phytotoxicity, recycling for solar and photocatalytic processes of industrial effluent. Results Phys 46:106316
Kleiman A, Meichtry JM, Xaubet M, Grondona D, Litter MI, Márquez A (2023) Efficiency of cathodic arc-grown N-doped TiO2 films for the photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) under UV-Vis irradiation. J Phys D Appl Phys 56:495303
Ullah S, Shabir M, Rasheed MA, Ahmad I, Ahmed E, Ahmad M et al. (2023) Silver and yttrium co-doped ZnO nanoparticles as a potential water splitting photocatalyst for the H2 evolution reaction. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 108:756
Xu YH, Han JN, Li ZH, Zhang ZH (2023) Two-dimensional g-GeC/PtSe2 van der Waals heterostructure: a visible light-driven direct Z-scheme photocatalyst for overall water splitting. J Phys D: Appl Phys 56:365504
Yang H, Yang M, Hu TP, Guo LJ, Meng RQ, Shi Y et al. (2023) Heterostructured Mo and Co-based phosphides as high-performance bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Phys Chem Chem Phys 25:17186–17196
Meng WW, Hu RS, Yang J, Du YF, Li JJ, Wang HY (2016) Influence of lanthanum-doping on photocatalytic properties of BiFeO3 for phenol degradation. Chin J Catal 37:1283–1292
Chen Y, Liu KR (2017) Fabrication of Ce/N co-doped TiO2/diatomite granule catalyst and its improved visible-light-driven photoactivity. J Hazard Mater 324:139–150
Yuan GL, Or SW, Chan HLW, Liu ZG (2007) Reduced ferroelectric coercivity in multiferroic Bi0.825Nd0.175FeO3 thin film. J Appl Phys 101(2):024106
Wang BJ, Li XH, Zhao RQ, Cai XL, Yu WY, Li WB et al. (2018) Electronic structures and enhanced photocatalytic properties of blue phosphorene/BSe van der Waals heterostructures. J Mater Chem A 6:8923–8929
Wang GM, Cheng D, He TC, Hu YY, Deng QR, Mao YW et al. (2019) Enhanced visible-light responsive photocatalytic activity of Bi25FeO40/Bi2Fe4O9 composites and mechanism investigation. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:10923–10933
Gadhi TA, Hernandez S, Cástellino M, Chiodono A, Husak T, Barrera G et al. (2018) Single BiFeO3 and mixed BiFeO3/Fe2O3/Bi2Fe4O9 ferromagnetic photocatalysts for solar light driven water oxidation and dye pollutants degradation. J Ind Eng Chen 6:437–448
Zhang T, Shen Y, Qiu YH, Liu Y, Xiong R, Shi J et al. (2017) Facial Synthesis and Photoreaction Mechanism of BiFeO3/Bi2Fe4O9 Heterojunction Nanofibers. J Am Chem Soc 6:4630–4636
Alkan S, DemirbasÖ, Celikcapa S, Doğan M (2004) Sorption of acid red 57 from aqueous solution onto sepiolite. J Hazard Mater 116(1-2):135–145
Acknowledgements
Our research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 12004424, and the Key Academic Discipline Project of China University of Mining and Technology under Grant No. 2022WLXK07 and National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China under Grant No. M35012.
Author contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: CFH, YN, JGW; data collection: YN, RZH, XFY; analysis and interpretation of results: CFH, YN, RZH, XFY, LZ, JW, XWX; draft manuscript preparation: CFH, YN, JGW. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Nie, Y., Han, R. et al. Preparation, characterization, and mechanism for enhanced photocatalytic performance in Bi1-xSmxFeO3 nanoparticles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-024-06392-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-024-06392-y