Abstract
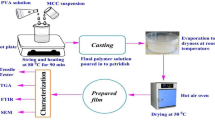
With the increasing demand for environmentally friendly and sustainable materials, research on cellulose/bio-based polyester composites has received increasing attention. However, the hydrophilicity of cellulose remains a major factor in its poor interaction with hydrophobic bio-based polyester. To prepare microcrystalline cellulose (MCC)/poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) composite monofilaments with high cellulose content to suppress the deformation of PBS, hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (KH1631) was selected for surface silylation of MCC at a mass ratio of 1:0.5 based on the principle of polarity similarity. The physical–chemical double crosslinking of KH1631 with MCC enhanced the interfacial bonding between MCC and PBS, so composite monofilaments with modified MCC (named mMCC) contents up to 35 wt% were prepared by melt spinning. After thermal stretching, mMCC/PBS composite monofilaments exhibited uniformly distributed microporous structure and double yield behaviors. Despite the continuous decrease in breaking strength (from 210 to 84 MPa) and elastic modulus (from 1380 to 590 MPa) due to the addition of mMCC, the yield strength (116 MPa) of the mMCC/PBS composite monofilaments was consistent with that of PBS when the mMCC addition reached 25 wt%, indicating no impact on usage intensity. Moreover, mMCC/PBS composite monofilaments showed excellent tensile elasticity (up to 95%), excellent fatigue resistance, and low residual strains under small deformation (15%). Notably, the addition of 15–35 wt% mMCC increased the degradability of composite monofilaments, the degradation rate following 100 days of treatment in an aqueous environment ranged from 3.8%(PBS) to 4.7% (P-mM25), and the degradation rate following 180 days of burial in soil ranged from 3.9%(PBS) to 12.3% (P-mM35). Overall, our work significantly enhanced the compatibility between MCC and PBS without the use of any high-cost modifiers or complex processing methods, and successfully developed mMCC/PBS composite monofilaments that exhibit excellent dimensional stability during use and quick degradation after disposal.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings will be shared on request.
References
Aliotta L, Seggiani M, Lazzeri A, Gigante V, Cinelli P (2022) A brief review of poly (butylene succinate) (PBS) and its main copolymers: synthesis, blends, composites, biodegradability, and applications. Polymers 14(4):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040844
Aziz T, Farid A, Haq F, Kiran M, Ullah A, Zhang K, Li C, Ghazanfar S, Sun H, Ullah R, Ali A, Muzammal M, Shah M, Akhtar N, Selim S, Hagagy N, Samy M, Jaouni SKA (2022) A review on the modification of cellulose and its applications. Polymers 14(15):3206. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153206
Barletta M, Aversa C, Ayyoob M, Gisario A, Hamad K, Mehrpouya M, Vahabi H (2022) Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS): Materials, processing, and industrial applications. Prog Polym Sci 132:101579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2022.101579
Beaumont M, Bacher M, Opietnik M, Gindl-Altmutter W, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2018) A general aqueous silanization protocol to introduce vinyl, mercapto or azido functionalities onto cellulose fibers and nanocelluloses. Molecules 23:1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061427
Cho SY, Lee ME, Kwak HW, Jin H-J (2018) Surface-modified cellulose nanocrystal-incorporated poly(butylene succinate) nanocomposites. Fiber Polym 19(7):1395–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-8138-7
Cichosz S, Masek A (2020) Superiority of cellulose non-solvent chemical modification over solvent-involving treatment: solution for green chemistry (Part I). Materials 13(11):2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112552
Fernandes SCM, Sadocco P, Alonso-Varona A, Palomares T, Eceiza A, Silvestre AJD, Mondragon I, Freire CSR (2013) Bioinspired antimicrobial and biocompatible bacterial cellulose membranes obtained by surface functionalization with aminoalkyl groups. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(8):3290–3297. https://doi.org/10.1021/am400338n
Finkenstadt VL, Millane RP (1998) Crystal structure of Valonia cellulose Iβ. Macromolecules 31(22):7776–7783. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma9804895
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gan HN, Shen YD, Guo H, Qin YX, Ren L, Zhang MY, Zhang HX (2023) Simultaneously enhancing strength and toughness for green poly (butylene succinate) composites by regulating the dispersed rice husk with the silane coupling agent. J Polym Res 30:60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03442-x
Hettegger H, Sumerskii I, Sortino S, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2016) Silane meets click chemistry: towards the functionalization of wet bacterial cellulose sheets. Chemsuschem 8:680–687. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201402991
Huang Z, Qian L, Yin Q, Yu N, Liu T, Tian D (2018) Biodegradability studies of poly(butylene succinate) composites filled with sugarcane rind fiber. Polym Test 66:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.02.003
Jiang N, Li Y, Li Y, Yu T, Li Y, Li D, Xu J, Wang C, Shi Y (2020a) Effect of short jute fibers on the hydrolytic degradation behavior of poly(lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stabil 178:109214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109214
Jiang S, Wei Y, Hu Z, Ge S, Yang H, Peng W (2020b) Potential application of bamboo powder in PBS bamboo plastic composites. J King Saud Univ Sci 32(1):1130–1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2019.10.014
Joy J, Jose C, Yu X, Matgew L, Thomas S, Pilla S (2017) The influence of nanocellulosic fiber, extracted from Helicteres isora, on thermal, wetting and viscoelastic properties of poly(butylene succinate) composites. Cellulose 24(10):4313–4323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1439-y
Karakehya N (2021) Comparison of the effects of various reinforcements on the mechanical, morphological, thermal and surface properties of poly(butylene succinate). Int J Adhes Adhes 110:102949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2021.102949
Kim HJ, Jeong JH, Choi YH, Eom Y (2021) Review on cellulose nanocrystal-reinforced polymer nanocomposites: Processing, properties, and rheology. Korea-Aust Rheol J 33(3):165–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-021-0015-z
Kramer RK, Carvalho AJF (2021) Non-freezing water sorbed on microcrystalline cellulose studied by high-resolution thermogravimetric analysis. Cellulose 28(16):10117–10125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04189-8
Mathew AP, Oksman K, Sain M (2006) The effect of morphology and chemical characteristics of cellulose reinforcements on the crystallinity of polylactic acid. J Appl Polym Sci 101(1):300–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23346
Missoum K, Belgacem MN, Bras J (2013) Nanofibrillated cellulose surface modification: a review. Materials 6(5):1745–1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6051745
Mochane MJ, Magagula SI, Sefadi JS, Mokhena TC (2021) A review on green composites based on natural fiber-reinforced polybutylene succinate (PBS). Polymers 13(8):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081200
Nam TH, Ogihara S, Tung NH, Kobayashi S (2011) Effect of alkali treatment on interfacial and mechanical properties of coir fiber reinforced poly(butylene succinate) biodegradable composites. Compos Part B-Eng 42(6):1648–1656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.04.001
Neves RM, Ornaghi JHL, Zattera AJ, Amico SC (2020) The influence of silane surface modification on microcrystalline cellulose characteristics. Carbohyd Polym 230:115595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115595
Pinheiro IF, Ferreira FV, Souza DHS, Gouveia RF, Lona LMF, Morales AR, Mei LHI (2017) Mechanical, rheological and degradation properties of PBAT nanocomposites reinforced by functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Eur Polym J 97:356–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.10.026
Platnieks O, Gaidukovs S, Barkane A, Gaidukova G, Grase L, Thakur VK, Filipova I, Fridrihsone V, Skute M, Laka M (2019) Highly loaded cellulose/poly (butylene succinate) sustainable composites for woody-like advanced materials application. Molecules 25(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010121
Platnieks O, Sereda A, Gaidukovs S, Thakur VK, Barkane A, Gaidukova G, Filipova I, Ogurcovs A, Fridrihsone V (2021) Adding value to poly (butylene succinate) and nanofibrillated cellulose-based sustainable nanocomposites by applying masterbatch process. Ind Crop Prod 169:113669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113669
Qian S, Sheng K, Yu K, Xu L, Lopez CAF (2018) Improved properties of PLA biocomposites toughened with bamboo cellulose nanowhiskers through silane modification. J Mater Sci 53(15):10920–10932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2377-2
Salon M-CB, Gerbaud G, Abdelmouleh M, Bruzzese C, Boufi S, Belgacem MN (2007) Studies of interactions between silane coupling agents and cellulose fibers with liquid and solid-state NMR. Magn Reson Chem 45(6):473–483. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.1994
Shaiju P, Dorian B-B, Senthamaraikannan R, Padamati RB (2020) Biodegradation of poly (Butylene Succinate) (PBS)/stearate modified magnesium-aluminium layered double hydroxide composites under marine conditions prepared via melt compounding. Molecules 25(23):5766. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235766
Shi K, Liu G, Sun H, Weng Y (2023) Polylactic acid/lignin composites: a review. Polymers 15(13):2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132807
Stepanova M, Korzhikova-Vlakh E (2022) Modification of cellulose micro- and nanomaterials to improve properties of aliphatic polyesters/cellulose composites: a review. Polymers 14(7):1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071477
Trache D, Hussin MH, Chuin CTH, Sabar S, Fazita MRN, Taiwo OFA, Hassan TM, Haafiz MKM (2016) Microcrystalline cellulose: isolation, characterization and bio-composites application-a review. Int J Biol Macromol 93:789–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.09.056
Utsunomia C, Ren Q, Zinn M (2020) Poly(4-Hydroxybutyrate): current state and perspectives. Front Bioeng Biotech 8:257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00257
Wu C, Zhang X, Wang X, Gan Q, Li X (2019) Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal using succinic anhydride and its effects on poly(butylene succinate) based composites. Cellulose 26(5):3167–3181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02292-5
Xu C-A, Lu M, Wu K, Shi J (2021) Functionalization of nano-cellulose by coupling agent with green strategy. Inorg Chem Commun 134:108939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108939
Yan Y, Dou Q (2020) Effect of peroxide on compatibility, microstructure, rheology, crystallization, and mechanical properties of PBS/waxy starch composites. Starch - Stärke 73:2000184. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.202000184
Yu X, Chen L, Jin Z, Jiao A (2021) Research progress of starch-based biodegradable materials: a review. J Mater Sci 56(19):11187–11208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06063-1
Yue L, Maiorana A, Khelifa F, Patel A, Raquez J-M, Bonnaud L, Gross R, Dubois P, Manas-Zloczower I (2018) Surface-modified cellulose nanocrystals for biobased epoxy nanocomposites. Polymer 134:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.11.051
Zhang X, Wang X (2018) Polybutylene succinate/cellulose nanocrystals: role of phthalic anhydride in squeeze oriented bionanocomposites. Carbohyd Polym 196:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.124
Zhang Y, Cui S, Liao H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang H (2023) Poly(butylene succinate)/cellulose composite monofilaments with microelastic response based on interfacial bonding. Carbohyd Polym 302:120387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120387
Zhou L, Ke K, Yang M-B, Yang W (2021) Recent progress on chemical modification of cellulose for high mechanical-performance Poly(lactic acid)/Cellulose composite: a review. Compos Commun 23:100548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100548
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF).
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang Zhang: Methodology, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. He Liao: Investigation. Yue Zhang: Writing—review & editing. Yumei Zhang: Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing, Resources, Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The manuscript has not been submitted to multiple publications for simultaneous consideration. The submitted work is original and has not been published elsewhere in any form or language (in part or in whole). No potential conflicts of interest existed between researchers, and informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Human and animal rights
We declare that there are no animal studies or human participant involvement in the study.
Consent for publication
The participant has agreed to submit the article manuscript to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Liao, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Simultaneously enhancing microelastic response and degradability for poly(butylene succinate) composite monofilaments by silanized microcrystalline cellulose. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05940-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05940-7