Abstract
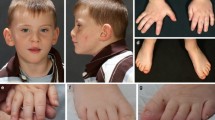
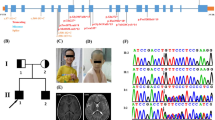
The glutamate pyruvate transaminase 2 (GPT2) gene produces a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the reversible transfer of an amino group from glutamate to pyruvate, generating alanine and alpha-ketoglutarate. Recessive mutations in GPT2 have been recently identified in a new syndrome involving intellectual and developmental disability (IDD), postnatal microcephaly, and spastic paraplegia. We have identified additional families with recessive GPT2 mutations and expanded the phenotype to include small stature. GPT2 loss-of-function mutations were identified in four families, nine patients total, including: a homozygous mutation in one child [c.775T>C (p.C259R)]; compound heterozygous mutations in two siblings [c.812A>C (p.N271T)/c.1432_1433delGT (p.V478Rfs*73)]; a novel homozygous, putative splicing mutation [c.1035C>T (p.G345=)]; and finally, a recurrent mutation, previously identified in a distinct family [c.1210C>T (p.R404*)]. All patients were diagnosed with IDD. A majority of patients had remarkably small stature throughout development, many < 1st percentile for height and weight. Given the potential biological function of GPT2 in cellular growth, this phenotype is strongly suggestive of a newly identified clinical susceptibility. Further, homozygous GPT2 mutations manifested in at least 2 of 176 families with IDD (approximately 1.1%) in a Pakistani cohort, thereby representing a relatively common cause of recessive IDD in this population, with recurrence of the p.R404* mutation in this population. Based on variants in the ExAC database, we estimated that approximately 1 in 248 individuals are carriers of moderately or severely deleterious variants in GPT2.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
All data generated or analyzed as part of this study are included herein or are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Berman HM et al (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242
Cao Y, Lin SH, Wang Y, Chin YE, Kang L, Mi J (2017) Glutamic pyruvate transaminase GPT2 promotes tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells by activating sonic hedgehog signaling. Theranostics 7:3021–3033. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.18992
Celis K, Shuldiner S, Haverfield EV, Cappell J, Yang R, Gong DW, Chung WK (2015) Loss of function mutation in glutamic pyruvate transaminase 2 (GPT2) causes developmental encephalopathy. J Inherit Metab Dis 38:941–948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-015-9824-x
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2004) Economic costs associated with mental retardation, cerebral palsy, hearing loss, and vision impairment–United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 53:57–59
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013) Intellectual Disability Among Children. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/developmentaldisabilities/documents/IntellectualDisabilities.pdf. Accessed on 10 Oct 2018
Chaudhury S, Lyskov S, Gray JJ (2010) PyRosetta: a script-based interface for implementing molecular modeling algorithms using Rosetta. Bioinformatics 26:689–691. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq007
DeLuca S, Khar K, Meiler J (2015) Fully flexible docking of medium sized ligand libraries with RosettaLigand. PLoS One 10:e0132508. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132508
Feng X, Hao Y, Wang Z (2016) Targeting glutamine metabolism in PIK3CA mutant colorectal cancers. Genes Dis 3:241–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2016.09.001
Hao Y et al (2016) Oncogenic PIK3CA mutations reprogram glutamine metabolism in colorectal cancer. Nat Commun 7:11971. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11971
Harripaul R et al (2018) Mapping autosomal recessive intellectual disability: combined microarray and exome sequencing identifies 26 novel candidate genes in 192 consanguineous families. Mol Psychiatry 23:973–984. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.60
Hengel H et al (2018) GPT2 mutations cause developmental encephalopathy with microcephaly and features of complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia. Clin Genet 94:356–361. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13390
Iglesias A et al (2014) The usefulness of whole-exome sequencing in routine clinical practice. Genet Med 16:922–931. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2014.58
Itkonen HM et al (2016) Inhibition of O-GlcNAc transferase activity reprograms prostate cancer cell metabolism. Oncotarget 7:12464–12476. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7039
Jamra R (2018) Genetics of autosomal recessive intellectual disability. Med Genet 30:323–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11825-018-0209-z
Kaymakcalan H, Yarman Y, Goc N, Toy F, Meral C, Ercan-Sencicek AG, Gunel M (2018) Novel compound heterozygous mutations in GPT2 linked to microcephaly, and intellectual developmental disability with or without spastic paraplegia. Am J Med Genet A 176:421–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.38558
Kim M, Gwak J, Hwang S, Yang S, Jeong SM (2019) Mitochondrial GPT2 plays a pivotal role in metabolic adaptation to the perturbation of mitochondrial glutamine metabolism. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0751-4
Lee H et al (2014) Clinical exome sequencing for genetic identification of rare Mendelian disorders. JAMA 312:1880–1887. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.14604
Lek M et al (2016) Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 536:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19057
Lobo-Prada T, Sticht H, Bogantes-Ledezma S, Ekici A, Uebe S, Reis A, Leal A (2017) A homozygous mutation in GPT2 associated with nonsyndromic intellectual disability in a consanguineous family from Costa Rica. JIMD Rep 36:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2016_40
Lyskov S et al (2013) Serverification of molecular modeling applications: the Rosetta Online Server that Includes Everyone (ROSIE). PLoS One 8:e63906. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063906
Marchler-Bauer A et al (2017) CDD/SPARCLE: functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D200–D203. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1129
Moretti R, Lyskov S, Das R, Meiler J, Gray JJ (2018) Web-accessible molecular modeling with Rosetta: the Rosetta Online Server that Includes Everyone (ROSIE). Protein Sci 27:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3313
Nambot S et al (2018) Clinical whole-exome sequencing for the diagnosis of rare disorders with congenital anomalies and/or intellectual disability: substantial interest of prospective annual reanalysis. Genet Med 20:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.162
Ouyang Q et al (2016) Mutations in mitochondrial enzyme GPT2 cause metabolic dysfunction and neurological disease with developmental and progressive features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E5598–E5607. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1609221113
Owen OE, Kalhan SC, Hanson RW (2002) The key role of anaplerosis and cataplerosis for citric acid cycle function. J Biol Chem 277:30409–30412. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R200006200
Rebhan M, Chalifa-Caspi V, Prilusky J, Lancet D (1997) GeneCards: integrating information about genes, proteins and diseases. Trends Genet 13:163
Rose NC, Wick M (2016) Current recommendations: screening for Mendelian disorders. Semin Perinatol 40:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semperi.2015.11.004
Rump P et al (2016) Whole-exome sequencing is a powerful approach for establishing the etiological diagnosis in patients with intellectual disability and microcephaly. BMC Med Genom 9:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-016-0167-8
Sayers EW et al (2011) Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D38–D51. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq1172
Smith B, Schafer XL, Ambeskovic A, Spencer CM, Land H, Munger J (2016) Addiction to coupling of the Warburg effect with glutamine catabolism in cancer cells. Cell Rep 17:821–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.09.045
Thevenon J et al (2016) Diagnostic odyssey in severe neurodevelopmental disorders: toward clinical whole-exome sequencing as a first-line diagnostic test. Clin Genet 89:700–707. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12732
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2010) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38:e164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq603
Xu P et al (2016) LRH-1-dependent programming of mitochondrial glutamine processing drives liver cancer. Genes Dev 30:1255–1260. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.277483.116
Yang RZ, Blaileanu G, Hansen BC, Shuldiner AR, Gong DW (2002) cDNA cloning, genomic structure, chromosomal mapping, and functional expression of a novel human alanine aminotransferase. Genomics 79:445–450. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.2002.6722
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the families for their participation in the current study.
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported in part by the following: National Institute of Mental Health grant numbers R01MH102418 and R01MH105442 and the Hassenfeld Child Health Innovation Institute at Brown University (EMM); Canadian Institutes of Health Research grant numbers MOP-102758 and PJT-156402 (JBV); and a Carney Institute for Brain Science and Suna Kıraç Fellowship Graduate Award in Brain Science (OB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, Q., Kavanaugh, B.C., Joesch-Cohen, L. et al. GPT2 mutations in autosomal recessive developmental disability: extending the clinical phenotype and population prevalence estimates. Hum Genet 138, 1183–1200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02057-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02057-x