Abstract
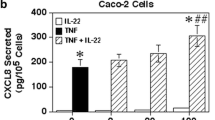
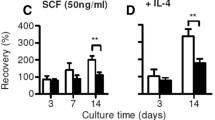
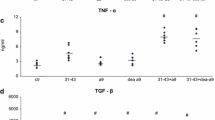
Intestinal epithelial cells are an important source of many biologically active molecules that modulate immune responses in the mucosa. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the synthesis of complement C3 component in the rat non-transformed crypt-like intestinal epithelial cell line, IEC-6. Unstimulated IEC-6 cells secreted a low level of C3 protein and showed weak expression of C3 mRNA. The addition of interleukin (IL)-1β induced a dose- and time-dependent increase in C3 production. These effects of IL-1β were observed at a concentration as low as 0.01 ng/ml and reached a plateau at a concentration of 5 ng/ml. The effects were observed at the mRNA level as early as 6 h after the beginning of incubation. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β alone had no effect. However, TGF-β at low concentrations (0.001–1 ng/ml) enhanced the effect of IL-1β in increasing C3 production; this enhancement was not observed at high concentrations (5–10 ng/ml). These effects of TGF-β were also observed at the mRNA level. The present findings indicate that intestinal epithelial cells are indeed capable of synthesizing complement C3 in response to IL-1β and TGF-β.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morgan BP. The complement system. In: Morgan BP (ed) Complement: Clinical aspects and relevance to disease. London: Academic, 1990;1–35.
Andoh A, Fujiyama Y, Kitoh K, et al. Flow cytometric assay for phagocytosis of human monocytes mediated via Fcγ-receptors and complement receptor CRI (CD35). Cytometry 1991;12:677–686.
Quaroni A, Wands J, Trelstad TL, et al. Epithelial cell cultures from rat small intestine. J Cell Biol 1979;80:245–265.
Halstensen TS, Mollnes TE, Brandtzaeg P. Persistent complement activation in submucosal blood vessels of active inflammatory bowel disease: Immunohistchemical evidence. Gastroenterology 1989;97:10–19.
Halstensen TS, Mollnes TE, Garred P, et al. Epithelial deposition of immunoglobulin GI and activated complement (C3b and terminal complement complex) in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 1990;98:1264–1271.
Ahrenstedt O, Knutson B, Nilsson-Ekdahl K, et al. Enhanced local production of complement components in the small intestines of patients with Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med 1990;322:1345–1349.
Andoh A, Fujiyama Y, Bamba T, et al. Differential cytokine regulation of complement C3, C4, and factor B synthesis in human intestinal epithelial cell line. Caco-2. J Immunol 1993;151:4239–4247.
Andoh A, Fujiyama Y, Sumiyoshi K, et al. Modulation of complement C3, C4, and factor B production in human intestinal epithelial cells: Differential effects of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-4. Pathophysiology 1995;2:251–259.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N, Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 1987;162:156–159.
Sundstrom SA, Komm BS, Ponce-de-Leon H, et al. Estrogen regulation of tissue-specific expression of complement C3. J Biol Chem 1989;264:1641–1647.
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR. DNA sequencing with chaniterminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1977;74:5463–5467.
Perlmutter DH, Dinarello CA, Punsal PI, et al. Regulation of class III major histocompatibility complex (MHC) gene products by interleukin 1. Science 1986;232:850–852.
Katz Y, Strunk RC, IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor: similaritics and differences in stimulation of expression of alternative pathway of complement and 638-1 genes in human fibroblasts. J Immunol 1989;142:3862–3867.
Brooimans RA, Van Der Ark AAJ, Buurman WA, et al. Differential regulation of complement factor H and C3 production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by IFNγ and IL-1. J Immunol 1990;144:3835–3840.
Rachmilewitz D, Simon PL, Schwartz LW, et al. Inflammatory mediators of experimental colitis in rats. Gastroenterology 1989;97:326–337.
Ligumsky M, Simon PL, Karmeli F, et al. Role of interleukin-1 in inflammatory bowel disease-enhanced production during active disease. Gut 1990;31:686–689.
Radema SA, Van Deventer SJH, Cerami A. Interleukin 1β is expressed predominantly by enterocytes in experimental colitis. Gastroenterology 1991;100:1180–1186.
Casini-Raggi V, Kam L, Chong YJT, et al. Mucosal imbalance of IL-1 and IL-1 receptor antagonist in inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol 1995;154:2434–2440.
Wahl SM. The role of transforming growth factor-beta in inflammatory processes. Immunol Res 1991;10:249–254.
Chantry D, Turner M, Abney E, et al. Modulation of cytokine production by transforming growth factor-β1. J Immunol 1989; 142:4295–4300.
Taylor AW, Ku N, Mortensen RF. Regulation of cytokine-induced human C-reactive protein production by transforming growth factor-β. J Immunol 1990;145:2507–2513.
Assoian RK, Komoriga A, Meyers CA, et al. Transforming growth factor-β in human platelets: Identification of a major storage site, purification and characterization. J Biol Chem 1983; 258:7155–7160.
Assoian RK, Fleurdelys BE, Stevenson HC, et al. Expression and secretion of type β transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987;84:6020–6024.
Kehrl JG, Roberts RB, Wakefield LM, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta is an important immuno-regulatory protein for human B-lymphocytes. J Immunol 1986;137:3855–3860.
Kehrl JH, Wakefield IM, Roberts AB, et al. Production of transforming growth factor β by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp med 1986; 163:1037–1050.
Barnard JA, Beauchamp RD, Coffey JR, et al. Regulation of intestinal epithelial cell growth by transforming growth factor β. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989;86:1578–1582.
Koyama S, Podolsky DK. Differential expression of transforming growth factors α and β in rat intestinal epithelial cell lines. J Clin Invest 1989;83:1768–1773.
Eckmann L, Jung HC, Schurer-Maly C, et al. Differential cytokine expression by human intestinal epithelial cell lines: Regulated expression of interleukin 8. Gastroenterology 1993; 105:1689–1697.
Elias JA, Lentz V, Cummings PJ. Transforming growth factor-β regulation of IL-6 production by unstimulated and IL-1 stimulated human fibroblasts. J Immunol 1991;146:3437–3443.
Lebman DA, Lee FD, Cummings PJ. Transforming growth factor-β and IL-2 enhancement of IgA expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated B cell culture. J Immunol 1990; 144:952–959.
Coffmann RL, Lebmann DA, Shrader B. Transforming growth factor β specifically enhances IgA production by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 1989;170:1039–1044.
McGee DW, Elson CO, McGhee JR. Enhancing effect of cholera toxin on IL-6 secretion by IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells: Mode of action and augmenting effect of inflammatory cytokines. Infect Immun 1993;61:4637–4644.
McGee DW, Aicher WK, Eldridge JH, et al. Transforming growth factor-β enhances secretory component and major histocompatibility complex class I antigen expression on rat IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells. Cytokine 1991;3:543–550.
Barnum SR, Jones JL. Transforming growth factor-β1 inhibits inflammatory cytokine-induced C3 gene expression in astrocytes. J Immunol 1994;152:765–773.
McGee DW, Beagley KW, Aicher WK, et al. Transforming growth factor-β and IL-1β act in synergy to enhance IL-6 secretion by the intestinal epithelial cel line, IEC-6. J Immunol 1993;151:970–978.
Dubois CM, Ruscetti FW, Palaszynski EW, et al. Transforming growth factor-β is a potent inhibitor of interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor expression: Proposed mechanism of inhibition of IL-1 action. J Ext Med 1990;172:737–741.
Mestecky J, McGhee JR. Immunoglobulin A (IgA): Molecular and cellular interactions involved in IgA biosynthesis and immune response. Adv Immunol 1987;40:153–245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andoh, A., Fujiyama, Y., Hata, K. et al. Regulation of complement C3 synthesis by interleukin-1 and transforming growth factor-β in rat non-transformed intestinal epithelial cell line, IEC-6. J Gastroenterol 31, 633–638 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347609
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347609