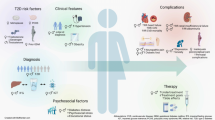
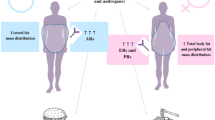
Abstract
Metabolic consequences of obesity including insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and non-alcoholic fatty liver infiltration are rapidly emerging in the pediatric population. Identifying effective strategies for identifying and treating these obesity related co-morbidities in children are crucial to the prevention of future cardiovascular disease and poor health outcomes. This review discusses the pathophysiologic connections between obesity, metabolic disease and cardiovascular risk. Current evidence and recommendations for screening and treatment for the metabolic consequences of pediatric obesity are reviewed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA. 2006;295:1549–55.
Dabelea D, Bell RA, D’Agostino RB, Imperatore G, Johansen JM, Linder B, et al. Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. JAMA. 2007;297:2716–24.
Marra F, Bertolani C. Adipokines in liver diseases. Hepatology. 2009;50:957–69.
González F, Rote NS, Minium J, Kirwan JP. Evidence of proatherogenic inflammation in polycystic ovary syndrome. Metab Clin Exp. 2009;58:954–62.
Savoia C, Schiffrin EL. Reduction of C-reactive protein and the use of anti-hypertensives. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2007;3:975–83.
Rueda-Clausen CF, López-Jaramillo P, Luengas C, del Pilar Oubiña M, Cachofeiro V, Lahera V. Inflammation but not endothelial dysfunction is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease in dyslipidemic subjects. Mediators Inflamm 2009. 2009;2009:469169.
Gozal D, Kheirandish-Gozal L. Cardiovascular morbidity in obstructive sleep apnea:oxidative stress, inflammation, and much more. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:369–75.
Rasouli N, Kern PA. Adipocytokines and the metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:S64–73.
Nemet D, Wang P, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Tanaka S, Engelman L, et al. Adipocytokines, body composition, and fitness in children. Pediatr Res. 2003;53:148–52.
Anty R, Bekri S, Luciani N, Saint-Paul M, Dahman M, Iannelli A, et al. The inflammatory C-reactive protein is increased in both liver and adipose tissue in severely obese patients independently from metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and NASH. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1824–33.
Bisoendial RJ, Birjmohun RS, Akdim F, Van ’t Veer C, Spek CA, Hartman D, et al. C-reactive protein elicits white blood cell activation in humans. Am J Med. 2009;122:582.e1-9.
Ridker PM. C-reactive protein and the prediction of cardiovascular events among those at intermediate risk:moving an inflammatory hypothesis toward consensus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:2129–38.
Venner AA, Lyon ME, Doyle-Baker PK. Leptin:a potential biomarker for childhood obesity? Clin Biochem. 2006;39:1047–56.
Ahima RS, Flier JS. Leptin. Annu Rev Physiol. 2000;62:413–37.
Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, et al. Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J. 1998;12:57–65.
Bastard J, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, et al. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:4–12.
Plaisance EP, Grandjean PW, Judd RL, Jones KW, Taylor JK. The influence of sex, body composition, and nonesterified fatty acids on serum adipokine concentrations. Metab Clin Exp. 2009; doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2009.04.038.
Böttner A, Kratzsch J, Müller G, Kapellen TM, Blüher S, Keller E, et al. Gender differences of adiponectin levels develop during the progression of puberty and are related to serum androgen levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:4053–61.
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2005;436:356–62.
Gavi S, Qurashi S, Stuart LM, Lau R, Melendez MM, Mynarcik DC, et al. Influence of age on the association of retinol-binding protein 4 with metabolic syndrome. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16:893–5.
Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K, et al. Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science. 2005;307:426–30.
Revollo JR, Körner A, Mills KF, Satoh A, Wang T, Garten A, et al. Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin regulates insulin secretion in beta cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme. Cell Metab. 2007;6:363–75.
Liu SW, Qiao SB, Yuan JS, Liu DQ. Association of plasma visfatin levels with inflammation, atherosclerosis, and acute coronary syndromes in humans. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009;71:202–7.
Badman MK, Flier JS. The adipocyte as an active participant in energy balance and metabolism. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2103–15.
Vachharajani V, Granger DN. Adipose tissue: a motor for the inflammation associated with obesity. IUBMB Life. 2009;61:424–30.
Kowalska I, Straczkowski M, Nikolajuk A, Adamska A, Karczewska-Kupczewska M, Otziomek E, et al. Insulin resistance, serum adiponectin, and proinflammatory markers in young subjects with the metabolic syndrome. Metab Clin Exp. 2008;57:1539–44.
Ford ES, Ajani UA, Mokdad AH. The metabolic syndrome and concentrations of C-reactive protein among U.S. youth. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:878–81.
Valle M, Martos R, Gascón F, Cañete R, Zafra MA, Morales R. Low-grade systemic inflammation, hypoadiponectinemia and a high concentration of leptin are present in very young obese children, and correlate with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2005;31:55–62.
Wärnberg J, Marcos A. Low-grade inflammation and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008;19:11–5.
Wärnberg J, Nova E, Romeo J, Moreno LA, Sjöström M, Marcos A. Lifestyle-related determinants of inflammation in adolescence. Br J Nutr. 2007;98(Suppl 1):S116–20.
Cizmecioglu F, Etiler N, Ergen A, Keser A, Hekim N, Hamzaoglu O, et al. Association of Adiponectin, Resistin and High Sensitive CRP Level with the Metabolic Syndrome in Childhood and Adolescence. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009; doi:10.1055/s-0028-1112151.
McGill HC, McMahan CA. Determinants of atherosclerosis in the young. Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY) Research Group. Am J Cardiol. 1998;82:30T–6.
Berenson GS, Srinivasan SR, Bao W, Newman WP, Tracy RE, Wattigney WA. Association between multiple cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in children and young adults. The Bogalusa Heart Study. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1650–6.
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP. Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:367–77.
Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000;106:473–81.
Nathan BM, Moran A. Metabolic complications of obesity in childhood and adolescence:more than just diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2008;15:21–9.
Huerta MG, Roemmich JN, Kington ML, Bovbjerg VE, Weltman AL, Holmes VF, et al. Magnesium deficiency is associated with insulin resistance in obese children. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1175–81.
Krekoukia M, Nassis GP, Psarra G, Skenderi K, Chrousos GP, Sidossis LS. Elevated total and central adiposity and low physical activity are associated with insulin resistance in children. Metab Clin Exp. 2007;56:206–13.
Schwartz B, Jacobs DR, Moran A, Steinberger J, Hong C, Sinaiko AR. Measurement of Insulin Sensitivity in Children:Comparison Between the Euglycemic Hyperinsulinemic Clamp and Surrogate Measures. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:783–8.
Eyzaguirre F, Mericq V. Insulin resistance markers in children. Horm Res. 2009;71:65–74.
Lee JM, Okumura MJ, Davis MM, Herman WH, Gurney JG. Prevalence and determinants of insulin resistance among U.S. adolescents:a population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2427–32.
Sinaiko AR, Steinberger J, Moran A, Hong C, Prineas RJ, Jacobs DR. Influence of insulin resistance and body mass index at age 13 on systolic blood pressure, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol at age 19. Hypertension. 2006;48:730–6.
Sinaiko AR, Jacobs DR, Steinberger J, Moran A, Luepker R, Rocchini AP, et al. Insulin resistance syndrome in childhood:associations of the euglycemic insulin clamp and fasting insulin with fatness and other risk factors. J Pediatr. 2001;139:700–7.
Williams DE, Cadwell BL, Cheng YJ, Cowie CC, Gregg EW, Geiss LS, et al. Prevalence of impaired fasting glucose and its relationship with cardiovascular disease risk factors in US adolescents, 1999–2000. Pediatrics. 2005;116:1122–6.
Oliveira AC, Oliveira AM, Adan LF, Oliveira NF, Silva AM, Ladeia AM. C-reactive protein and metabolic syndrome in youth:a strong relationship? Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16:1094–8.
Steinberger J, Daniels SR, Eckel RH, Hayman L, Lustig RH, McCrindle B, et al. Progress and challenges in metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents:a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young;Council on Cardiovascular Nursing;and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 2009;119:628–47.
Sinaiko AR, Steinberger J, Moran A, Prineas RJ, Vessby B, Basu S, et al. Relation of body mass index and insulin resistance to cardiovascular risk factors, inflammatory factors, and oxidative stress during adolescence. Circulation. 2005;111:1985–91.
Morrison JA, Friedman LA, Wang P, Glueck CJ. Metabolic syndrome in childhood predicts adult metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus 25 to 30 years later. J. Pediatr. 2008;152:201–6.
Sanders BH, Lubsch LM, West DS. Prevalence and treatment of metabolic syndrome in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Ann Pharmacother. 2006;40:1517–21.
Schwimmer JB, Pardee PE, Lavine JE, Blumkin AK, Cook S. Cardiovascular risk factors and the metabolic syndrome in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Circulation. 2008;118:277–83.
Ekelund U, Anderssen S, Andersen LB, Riddoch CJ, Sardinha LB, Luan J, et al. Prevalence and correlates of the metabolic syndrome in a population-based sample of European youth. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:90–6.
Kelishadi R, Razaghi EM, Gouya MM, Ardalan G, Gheiratmand R, Delavari A, et al. Association of physical activity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: CASPIAN study. Horm Res. 2007;67:46–52.
Pan Y, Pratt CA. Metabolic syndrome and its association with diet and physical activity in US adolescents. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108:276–86. discussion 286.
Cook S, Auinger P, Li C, Ford ES. Metabolic syndrome rates in United States adolescents, from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2002. J Pediatr. 2008;152:165–70.
Jago R, Baranowski T, Buse J, Edelstein S, Galassetti P, Harrell J, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among a racially/ethnically diverse group of U.S. eighth-grade adolescents and associations with fasting insulin and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance levels: Studies to Treat or Prevent Pediatric Type 2 Diabetes (STOPP-T2D) Prevention Study Group. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(10):2020–5.
Monzavi R, Dreimane D, Geffner ME, Braun S, Conrad B, Klier M, et al. Improvement in risk factors for metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in overweight youth who are treated with lifestyle intervention. Pediatrics. 2006;117:e1111–8.
Steele RM, Brage S, Corder K, Wareham NJ, Ekelund U. Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and the metabolic syndrome in youth. J Appl Physiol. 2008;105:342–51.
DuBose KD, Eisenmann JC, Donnelly JE. Aerobic fitness attenuates the metabolic syndrome score in normal-weight, at-risk-for-overweight, and overweight children. Pediatrics. 2007;120:e1262–8.
Mark AE, Janssen I. Relationship between screen time and metabolic syndrome in adolescents. J Public Health (Oxf). 2008;30:153–60.
Casazza K, Dulin-Keita A, Gower BA, Fernandez JR. Differential influence of diet and physical activity on components of metabolic syndrome in a multiethnic sample of children. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009;109:236–44.
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute scientific statement. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006;21:1–6.
Stone NJ, Saxon D. Approach to treatment of the patient with metabolic syndrome:lifestyle therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:15E–21.
Chen AK, Roberts CK, Barnard RJ. Effect of a short-term diet and exercise intervention on metabolic syndrome in overweight children. Metab Clin Exp. 2006;55:871–8.
Stevens J, Cai J, Evenson KR, Thomas R. Fitness and fatness as predictors of mortality from all causes and from cardiovascular disease in men and women in the lipid research clinics study. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:832–41.
Sacheck J. Pediatric obesity: an inflammatory condition? JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2008;32:633–7.
Kadoglou NPE, Iliadis F, Angelopoulou N, Perrea D, Ampatzidis G, Liapis CD, et al. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007;14:837–43.
Goldhammer E, Tanchilevitch A, Maor I, Beniamini Y, Rosenschein U, Sagiv M. Exercise training modulates cytokines activity in coronary heart disease patients. Int J Cardiol. 2005;100:93–9.
Carrel AL, Clark RR, Peterson SE, Nemeth BA, Sullivan J, Allen DB. Improvement of fitness, body composition, and insulin sensitivity in overweight children in a school-based exercise program: a randomized, controlled study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2005;159:963–8.
Savoye M, Shaw M, Dziura J, Tamborlane WV, Rose P, Guandalini C, et al. Effects of a weight management program on body composition and metabolic parameters in overweight children: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;297:2697–704.
Kim ES, Im J, Kim KC, Park JH, Suh S, Kang ES, et al. Improved insulin sensitivity and adiponectin level after exercise training in obese Korean youth. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15:3023–30.
Reinehr T, Stoffel-Wagner B, Roth CL. Retinol-binding protein 4 and its relation to insulin resistance in obese children before and after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2287–93.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Lerner-Geva L, Copperman N, Jacobson MS. Insulin resistance and parental obesity as predictors to response to therapeutic life style change in obese children and adolescents 10–18 years old. J Adolesc Health. 2008;43:437–43.
Rohrer TR, Rizzo VF, Cäsar JJ, Muelbredt O, Sprengart S, Gortner L, et al. Changes in hepatic risk factors, metabolic variables, body composition, and physical fitness in obese children after a one-year weight loss program. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2008;21:837–45.
Nassis GP, Papantakou K, Skenderi K, Triandafillopoulou M, Kavouras SA, Yannakoulia M, et al. Aerobic exercise training improves insulin sensitivity without changes in body weight, body fat, adiponectin, and inflammatory markers in overweight and obese girls. Metab Clin Exp. 2005;54:1472–9.
Faintuch J, Horie LM, Barbeiro HV, Barbeiro DF, Soriano FG, Ishida RK, et al. Systemic inflammation in morbidly obese subjects:response to oral supplementation with alpha-linolenic acid. Obes Surg. 2007;17:341–7.
Bloedon LT, Balikai S, Chittams J, Cunnane SC, Berlin JA, Rader DJ, et al. Flaxseed and cardiovascular risk factors:results from a double blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Am Coll Nutr. 2008;27:65–74.
Molnár D, Decsi T, Koletzko B. Reduced antioxidant status in obese children with multimetabolic syndrome. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28:1197–202.
Lütjens A, Smit JL. Effect of biguanide treatment in obese children. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1977;31:473–80.
Love-Osborne K, Sheeder J, Zeitler P. Addition of metformin to a lifestyle modification program in adolescents with insulin resistance. J Pediatr. 2008;152:817–22.
Srinivasan S, Ambler GR, Baur LA, Garnett SP, Tepsa M, Yap F, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of metformin for obesity and insulin resistance in children and adolescents:improvement in body composition and fasting insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:2074–80.
Burgert TS, Duran EJ, Goldberg-Gell R, Dziura J, Yeckel CW, Katz S, et al. Short-term metabolic and cardiovascular effects of metformin in markedly obese adolescents with normal glucose tolerance. Pediatr Diabetes. 2008;9:567–76.
Atabek ME, Pirgon O. Use of metformin in obese adolescents with hyperinsulinemia:a 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2008;21:339–48.
Freemark M, Bursey D. The effects of metformin on body mass index and glucose tolerance in obese adolescents with fasting hyperinsulinemia and a family history of type 2 diabetes. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E55.
Kay JP, Alemzadeh R, Langley G, D’Angelo L, Smith P, Holshouser S. Beneficial effects of metformin in normoglycemic morbidly obese adolescents. Metab Clin Exp. 2001;50:1457–61.
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:393–403.
Zeitler P, Epstein L, Grey M, Hirst K, Kaufman F, Tamborlane W, et al. Treatment options for type 2 diabetes in adolescents and youth:a study of the comparative efficacy of metformin alone or in combination with rosiglitazone or lifestyle intervention in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8:74–87.
Gungor N, Hannon T, Libman I, Bacha F, Arslanian S. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in youth:the complete picture to date. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2005;52:1579–609.
Shalitin S, Abrahami M, Lilos P, Phillip M. Insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance in obese children and adolescents referred to a tertiary-care center in Israel. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005;29:571–8.
Fagot-Campagna A, Saaddine JB, Flegal KM, Beckles GL. Diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and elevated HbA1c in U.S. adolescents:the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:834–7.
Wabitsch M, Hauner H, Hertrampf M, Muche R, Hay B, Mayer H, et al. Type II diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in Caucasian children and adolescents with obesity living in Germany. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28:307–13.
Sinha R, Fisch G, Teague B, Tamborlane WV, Banyas B, Allen K, et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:802–10.
Szamosi A, Czinner A, Szamosi T, Sallai A, Hatunic M, Berla Z, et al. Effect of diet and physical exercise treatment on insulin resistance syndrome of schoolchildren. J Am Coll Nutr. 2008;27:177–83.
Libman IM, Barinas-Mitchell E, Bartucci A, Robertson R, Arslanian S. Reproducibility of the oral glucose tolerance test in overweight children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4231–7.
Goran MI, Davis J, Kelly L, Shaibi G, Spruijt-Metz D, Soni SM, et al. Low prevalence of pediatric type 2 diabetes:where’s the epidemic? J Pediatr. 2008;152:753–5.
Rosenbloom AL, Joe JR, Young RS, Winter WE. Emerging epidemic of type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:345–54.
Nathan DM, Balkau B, Bonora E, Borch-Johnsen K, Buse JB, Colagiuri S, et al. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(7):1327–34.
Benavides S, Striet J, Germak J, Nahata MC. Efficacy and safety of hypoglycemic drugs in children with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacotherapy. 2005;25:803–9.
Shield JPH, Lynn R, Wan KC, Haines L, Barrett TG. Management and 1 year outcome for UK children with type 2 diabetes. Arch Dis Child. 2009;94:206–9.
Gottschalk M, Danne T, Vlajnic A, Cara JF. Glimepiride versus metformin as monotherapy in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes:a randomized, single-blind comparative study. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:790–4.
Hannon TS, Rao G, Arslanian SA. Childhood obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics. 2005;116:473–80.
Rosenbloom AL, Silverstein JH, Amemiya S, Zeitler P, Klingensmith GJ. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guideline 2006–2007. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in the child and adolescent. Pediatr Diabetes. 2008;9:512–26.
Jacobson-Dickman E, Levitsky L. Oral agents in managing diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2005;52:1689–703.
Jones KL, Arslanian S, Peterokova VA, Park J, Tomlinson MJ. Effect of metformin in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:89–94.
Yeap BB. Controversies in type 2 diabetes—An update. Aust Fam Physician. 2009;38:22–5.
Chia CW, Egan JM. Incretin-based therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:3703–16.
Fleischman A, Shoelson SE, Bernier R, Goldfine AB. Salsalate improves glycemia and inflammatory parameters in obese young adults. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:289–94.
Yuan M, Konstantopoulos N, Lee J, Hansen L, Li ZW, Karin M, et al. Reversal of obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of Ikkbeta. Science. 2001;293:1673–7.
Park E, Wong V, Guan X, Oprescu AI, Giacca A. Salicylate prevents hepatic insulin resistance caused by short-term elevation of free fatty acids in vivo. J Endocrinol. 2007;195:323–31.
Hundal RS, Petersen KF, Mayerson AB, Randhawa PS, Inzucchi S, Shoelson SE, et al. Mechanism by which high-dose aspirin improves glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:1321–6.
Koska J, Ortega E, Bunt JC, Gasser A, Impson J, Hanson RL, et al. The effect of salsalate on insulin action and glucose tolerance in obese non-diabetic patients:results of a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia. 2009;52:385–93.
McCrindle BW, Urbina EM, Dennison BA, Jacobson MS, Steinberger J, Rocchini AP, et al. Drug therapy of high-risk lipid abnormalities in children and adolescents:a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in Youth Committee, Council of Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, with the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing. Circulation. 2007;115:1948–67.
Berenson GS, Srnivasan SR. Cardiovascular risk factors in youth with implications for aging:the Bogalusa Heart Study. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:303–7.
Srinivasan SR, Frontini MG, Xu J, Berenson GS. Utility of childhood non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in predicting adult dyslipidemia and other cardiovascular risks:the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 2006;118:201–6.
Magnussen CG, Raitakari OT, Thomson R, Juonala M, Patel DA, Viikari JSA, et al. Utility of currently recommended pediatric dyslipidemia classifications in predicting dyslipidemia in adulthood:evidence from the Childhood Determinants of Adult Health (CDAH) study, Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study, and Bogalusa Heart Study. Circulation. 2008;117:32–42.
Steinberger J, Moran A, Hong CP, Jacobs DR, Sinaiko AR. Adiposity in childhood predicts obesity and insulin resistance in young adulthood. J Pediatr. 2001;138:469–73.
Daniels SR, Greer FR. Lipid screening and cardiovascular health in childhood. Pediatrics. 2008;122:198–208.
Korsten-Reck U, Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Korsten K, Baumstark MW, Dickhuth H, Berg A. Frequency of secondary dyslipidemia in obese children. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4:1089–94.
Freedman DS, Dietz WH, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. The relation of overweight to cardiovascular risk factors among children and adolescents:the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 1999;103:1175–82.
Manlhiot C, Larsson P, Gurofsky RC, Smith RW, Fillingham C, Clarizia NA, et al. Spectrum and management of hypertriglyceridemia among children in clinical practice. Pediatrics. 2009;123:458–65.
Steinberger J, Moorehead C, Katch V, Rocchini AP. Relationship between insulin resistance and abnormal lipid profile in obese adolescents. J Pediatr. 1995;126:690–5.
Wiegman A, Hutten BA, de Groot E, Rodenburg J, Bakker HD, Büller HR, et al. Efficacy and safety of statin therapy in children with familial hypercholesterolemia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;292:331–7.
Kwiterovich PO, Hartmuller G, Van Horn L, Christoffel KK, Gernhoffer N, Gidding S, et al. The Writing Group for the DISC Collaborative Research Group. Efficacy and safety of lowering dietary intake of fat and cholesterol in children with elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The Dietary Intervention Study in Children (DISC): JAMA. 1995;273(18):1429–35.
Jonkers IJAM, Smelt AHM, Princen HMG, Kuipers F, Romijn JA, Boverhof R, et al. Fish oil increases bile acid synthesis in male patients with hypertriglyceridemia. J Nutr. 2006;136:987–91.
Engler MM, Engler MB, Malloy MJ, Paul SM, Kulkarni KR, Mietus-Snyder ML. Effect of docosahexaenoic acid on lipoprotein subclasses in hyperlipidemic children (the EARLY study). Am J Cardiol. 2005;95:869–71.
Tolfrey K, Jones AM, Campbell IG. The effect of aerobic exercise training on the lipid-lipoprotein profile of children and adolescents. Sports Med. 2000;29:99–112.
McCrindle BW, O’Neill MB, Cullen-Dean G, Helden E. Acceptability and compliance with two forms of cholestyramine in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia in children:a randomized, crossover trial. J Pediatr. 1997;130:266–73.
Lauer RM, Clarke WR. Childhood risk factors for high adult blood pressure: the Muscatine Study. Pediatrics. 1989;84:633–41.
Rademacher E, Jacobs D, Moran A, Steinberger J, Prineas R, Sinaiko A. Relation of blood pressure and body mass index during childhood to cardiovascular risk factor levels in young adults. J Hypertens. 2009;27:1766–74.
Sorof JM, Lai D, Turner J, Poffenbarger T, Portman RJ. Overweight, ethnicity, and the prevalence of hypertension in school-aged children. Pediatrics. 2004;113:475–82.
Paradis G, Lambert M, O’Loughlin J, Lavallée C, Aubin J, Delvin E, et al. Blood pressure and adiposity in children and adolescents. Circulation. 2004;110:1832–8.
McNiece KL, Poffenbarger TS, Turner JL, Franco KD, Sorof JM, Portman RJ. Prevalence of hypertension and pre-hypertension among adolescents. J Pediatr. 2007;150:640–4. 644.e1.
Sinaiko AR, Donahue RP, Jacobs DR, Prineas RJ. Relation of weight and rate of increase in weight during childhood and adolescence to body size, blood pressure, fasting insulin, and lipids in young adults. The Minneapolis Children’s Blood Pressure Study. Circulation. 1999;99:1471–6.
Gidding SS, Bao W, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. Effects of secular trends in obesity on coronary risk factors in children:the Bogalusa Heart Study. J Pediatr. 1995;127:868–74.
Sorof J, Daniels S. Obesity hypertension in children: a problem of epidemic proportions. Hypertension. 2002;40:441–7.
Hansen ML, Gunn PW, Kaelber DC. Underdiagnosis of hypertension in children and adolescents. JAMA. 2007;298:874–9.
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004;114(2 Suppl 4th Report):555–76.
Rocchini AP, Katch V, Anderson J, Hinderliter J, Becque D, Martin M, et al. Blood pressure in obese adolescents:effect of weight loss. Pediatrics. 1988;82:16–23.
Reinehr T, de Sousa G, Toschke AM, Andler W. Long-term follow-up of cardiovascular disease risk factors in children after an obesity intervention. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84:490–6.
Jiang JX, Xia XL, Greiner T, Lian GL, Rosenqvist U. A two year family based behaviour treatment for obese children. Arch Dis Child. 2005;90:1235–8.
Yildiz BO, Knochenhauer ES, Azziz R. Impact of obesity on the risk for polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:162–8.
Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Consensus Workshop Group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Hum Reprod. 2004;19(1):41–7.
Franks S. Controversy in clinical endocrinology:diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome:in defense of the Rotterdam criteria. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:786–9.
Boomsma CM, Eijkemans MJC, Hughes EG, Visser GHA, Fauser BCJM, Macklon NS. A meta-analysis of pregnancy outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod Update. 2006;12:673–83.
Leibel NI, Baumann EE, Kocherginsky M, Rosenfield RL. Relationship of adolescent polycystic ovary syndrome to parental metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1275–83.
Essah PA, Wickham EP, Nestler JE. The metabolic syndrome in polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2007;50:205–25.
Meyer C, McGrath BP, Teede HJ. Overweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome have evidence of subclinical cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:5711–6.
Talbott E, Clerici A, Berga SL, Kuller L, Guzick D, Detre K, et al. Adverse lipid and coronary heart disease risk profiles in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome:results of a case-control study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1998;51:415–22.
Littlejohn EE, Weiss RE, Deplewski D, Edidin DV, Rosenfield R. Intractable early childhood obesity as the initial sign of insulin resistant hyperinsulinism and precursor of polycystic ovary syndrome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007;20:41–51.
de Zegher F, Ibáñez L. Prenatal growth restraint followed by catch-up of weight:a hyperinsulinemic pathway to polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(Suppl 1):S4–5.
Rosenfield RL. Clinical review:Identifying children at risk for polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:787–96.
Ibáñez L, Potau N, Carrascosa A. Insulin Resistance, Premature Adrenarche, and a Risk of the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1998;9:72–7.
Arslanian SA, Lewy V, Danadian K, Saad R. Metformin therapy in obese adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome and impaired glucose tolerance:amelioration of exaggerated adrenal response to adrenocorticotropin with reduction of insulinemia/insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1555–9.
Dunaif A. Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome:mechanism and implications for pathogenesis. Endocr Rev. 1997;18:774–800.
Lewy VD, Danadian K, Witchel SF, Arslanian S. Early metabolic abnormalities in adolescent girls with polycystic ovarian syndrome. J Pediatr. 2001;138:38–44.
Sawathiparnich P, Weerakulwattana L, Santiprabhob J, Likitmaskul S. Obese adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have more severe insulin resistance measured by HOMA-IR score than obese girls without PCOS. J Med Assoc Thai. 2005;88(Suppl 8):S33–7.
Ibáñez L, Ong K, Ferrer A, Amin R, Dunger D, de Zegher F. Low-dose flutamide-metformin therapy reverses insulin resistance and reduces fat mass in nonobese adolescents with ovarian hyperandrogenism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:2600–6.
Hoeger K, Davidson K, Kochman L, Cherry T, Kopin L, Guzick DS. The impact of metformin, oral contraceptives, and lifestyle modification on polycystic ovary syndrome in obese adolescent women in two randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4299–306.
Arslanian SA, Lewy VD, Danadian K. Glucose intolerance in obese adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome:roles of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction and risk of cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:66–71.
Rossi B, Sukalich S, Droz J, Griffin A, Cook S, Blumkin A, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and related characteristics in obese adolescents with and without polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4780–6.
Martin KA, Chang RJ, Ehrmann DA, Ibáñez L, Lobo RA, Rosenfield RL, et al. Evaluation and treatment of hirsutism in premenopausal women:an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1105–20.
Legro RS. Detection of insulin resistance and its treatment in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002;15(Suppl 5):1367–78.
Thomson RL, Buckley JD, Noakes M, Clifton PM, Norman RJ, Brinkworth GD. The effect of a hypocaloric diet with and without exercise training on body composition, cardiometabolic risk profile, and reproductive function in overweight and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:3373–80.
Allen HF, Mazzoni C, Heptulla RA, Murray MA, Miller N, Koenigs L, et al. Randomized controlled trial evaluating response to metformin versus standard therapy in the treatment of adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2005;18:761–8.
Mastorakos G, Lambrinoudaki I, Creatsas G. Polycystic ovary syndrome in adolescents:current and future treatment options. Paediatr Drugs. 2006;8:311–8.
Mastorakos G, Koliopoulos C, Deligeoroglou E, Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Creatsas G. Effects of two forms of combined oral contraceptives on carbohydrate metabolism in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2006;85:420–7.
Mastorakos G, Koliopoulos C, Creatsas G. Androgen and lipid profiles in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome who were treated with two forms of combined oral contraceptives. Fertil Steril. 2002;77:919–27.
Lord JM, Flight IHK, Norman RJ. Metformin in polycystic ovary syndrome:systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2003;327:951–3.
Mathur R, Alexander CJ, Yano J, Trivax B, Azziz R. Use of metformin in polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199:596–609.
Ibáñez L, Valls C, Potau N, Marcos MV, de Zegher F. Sensitization to insulin in adolescent girls to normalize hirsutism, hyperandrogenism, oligomenorrhea, dyslipidemia, and hyperinsulinism after precocious pubarche. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:3526–30.
Glueck CJ, Wang P, Fontaine R, Tracy T, Sieve-Smith L. Metformin to restore normal menses in oligo-amenorrheic teenage girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). J Adolesc Health. 2001;29:160–9.
Aroda VR, Ciaraldi TP, Burke P, Mudaliar S, Clopton P, Phillips S, et al. Metabolic and hormonal changes induced by pioglitazone in polycystic ovary syndrome:a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:469–76.
Brettenthaler N, De Geyter C, Huber PR, Keller U. Effect of the insulin sensitizer pioglitazone on insulin resistance, hyperandrogenism, and ovulatory dysfunction in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:3835–40.
Narsing Rao L, Jacob JJ, Paul TV, Rajarathinam S, Thomas N, Seshadri MS. Effects of pioglitazone on menstrual frequency, hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance in adoloscents and young adults with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2009;22:91–5.
Stout DL, Fugate SE. Thiazolidinediones for treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome. Pharmacotherapy. 2005;25:244–52.
Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2005;70(Suppl 3):52–6.
Marion AW, Baker AJ, Dhawan A. Fatty liver disease in children. Arch Dis Child. 2004;89:648–52.
Manco M, Marcellini M, Devito R, Comparcola D, Sartorelli MR, Nobili V. Metabolic syndrome and liver histology in paediatric non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008;32:381–7.
Vajro P, Mandato C, Franzese A, Ciccimarra E, Lucariello S, Savoia M, et al. Vitamin E treatment in pediatric obesity-related liver disease:a randomized study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;38:48–55.
Nobili V, Manco M, Devito R, Ciampalini P, Piemonte F, Marcellini M. Effect of vitamin E on aminotransferase levels and insulin resistance in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:1553–61.
Nobili V, Marcellini M, Devito R, Ciampalini P, Piemonte F, Comparcola D, et al. NAFLD in children:a prospective clinical-pathological study and effect of lifestyle advice. Hepatology. 2006;44:458–65.
Patton HM, Lavine JE, Van Natta ML, Schwimmer JB, Kleiner D, Molleston J. Clinical correlates of histopathology in pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1961–1971.e2.
Manco M, Bottazzo G, DeVito R, Marcellini M, Mingrone G, Nobili V. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. J Am Coll Nutr. 2008;27:667–76.
Burgert TS, Taksali SE, Dziura J, Goodman TR, Yeckel CW, Papademetris X, et al. Alanine aminotransferase levels and fatty liver in childhood obesity:associations with insulin resistance, adiponectin, and visceral fat. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:4287–94.
Fracanzani AL, Valenti L, Bugianesi E, Andreoletti M, Colli A, Vanni E, et al. Risk of severe liver disease in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with normal aminotransferase levels:a role for insulin resistance and diabetes. Hepatology. 2008;48:792–8.
Strauss RS, Barlow SE, Dietz WH. Prevalence of abnormal serum aminotransferase values in overweight and obese adolescents. J Pediatr. 2000;136:727–33.
Fraser A, Longnecker MP, Lawlor DA. Prevalence of elevated alanine aminotransferase among US adolescents and associated factors:NHANES 1999–2004. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1814–20.
Schwimmer JB, Deutsch R, Kahen T, Lavine JE, Stanley C, Behling C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006;118:1388–93.
Sagi R, Reif S, Neuman G, Webb M, Phillip M, Shalitin S. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96:1209–13.
Jankowska I, Socha P, Pawlowska J, Teisseyre M, Gliwicz D, Czubkowski P, et al. Recurrence of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis after liver transplantation in a 13-yr-old boy. Pediatr Transplant. 2007;11:796–8.
Schwimmer JB, Middleton MS, Deutsch R, Lavine JE. A phase 2 clinical trial of metformin as a treatment for non-diabetic paediatric non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;21:871–9.
Barshop NJ, Sirlin CB, Schwimmer JB, Lavine JE. Review article:epidemiology, pathogenesis and potential treatments of paediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28:13–24.
Wang C, Liang L, Fu J, Zou C, Hong F, Xue J, et al. Effect of lifestyle intervention on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese obese children. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:1598–602.
Reinehr T, Schmidt C, Toschke AM, Andler W. Lifestyle intervention in obese children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:2-year follow-up study. Arch Dis Child. 2009;94:437–42.
Nobili V, Manco M, Devito R, Di Ciommo V, Comparcola D, Sartorelli MR, et al. Lifestyle intervention and antioxidant therapy in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:a randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology. 2008;48:119–28.
Nissen SE, Wolski K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2457–71.
Singh S, Loke YK, Furberg CD. Long-term risk of cardiovascular events with rosiglitazone:a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2007;298:1189–95.
Nobili V, Manco M, Ciampalini P, Alisi A, Devito R, Bugianesi E, et al. Metformin use in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:an open-label, 24-month, observational pilot study. Clin Ther. 2008;30:1168–76.
Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB. Clinical Research Network launches TONIC trial for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006;42:129–30.
Vajro P, Franzese A, Valerio G, Iannucci MP, Aragione N. Lack of efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid for the treatment of liver abnormalities in obese children. J Pediatr. 2000;136:739–43.
Lindor KD, Kowdley KV, Heathcote EJ, Harrison ME, Jorgensen R, Angulo P, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:results of a randomized trial. Hepatology. 2004;39:770–8.
Méndez-Sánchez N, González V, Chávez-Tapia N, Ramos MH, Uribe M. Weight reduction and ursodeoxycholic acid in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Hepatol. 2004;3:108–12.
Satapathy SK, Sakhuja P, Malhotra V, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Beneficial effects of pentoxifylline on hepatic steatosis, fibrosis and necroinflammation in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:634–8.
Andersen T, Gluud C, Franzmann MB, Christoffersen P. Hepatic effects of dietary weight loss in morbidly obese subjects. J Hepatol. 1991;12:224–9.
de Ferranti S, Mozaffarian D. The perfect storm:obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic consequences. Clin Chem. 2008;54:945–55.
Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC. Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med. 2008;14:741–51.
Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose Tissue, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2005;96:939–49.
Guzik TJ, Mangalat D, Korbut R. Adipocytokines - novel link between inflammation and vascular function? J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;57:505–28.
de Ferranti SD, Gauvreau K, Ludwig DS, Neufeld EJ, Newburger JW, Rifai N. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in American adolescents:findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Circulation. 2004;110:2494–7.
Alberti G, Zimmet P, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S, et al. The IDF consensus definition of the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. In: International Diabetes Federation. 2007. http://www.idf.org/met_syndromechildren Accessed 5 Aug 2009.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2009. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:S13–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ode, K.L., Frohnert, B.I. & Nathan, B.M. Identification and treatment of metabolic complications in pediatric obesity. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 10, 167–188 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-009-9115-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-009-9115-7