Abstract
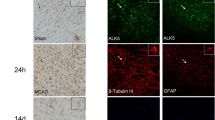
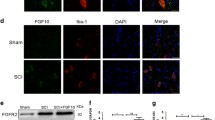
Transforming growth factor-β 1 (TGFβ1) has a diverse role in astrogliosis and neuronal survival, but the underlying mechanism remains to be elucidated, especially in traumatic brain injury (TBI). Here, we show that the expression of TGFβ1 was increased in the pericontusional region, accompanied with astrogliosis and neuronal loss in TBI rats. Moreover, TGFβ1 knockdown not only reduced the number of neurons and inhibited astrogliosis but also resulted in a significant neurological dysfunction in rats with TBI. Subsequently, Smad3, a key downstream signal of TGFβ1, was involved in pericontusional region after TBI. These findings therefore indicate that TGFβ1 is involved in neuroprotection and astrogliosis, via activation of down stream Smad3 signal in the brain after injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harbeck-Seu A, Brunk I, Platz T, Vajkoczy P, Endres M, Spies C et al (2011) A speedy recovery: amphetamines and other therapeutics that might impact the recovery from brain injury. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 24(2):144–153
Chen H, Epstein J, Stern E (2010) Neural plasticity after acquired brain injury: evidence from functional neuroimaging. PMR 2(12 Suppl 2):S306–S312
Bashir S, Mizrahi I, Weaver K, Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A (2010) Assessment and modulation of neural plasticity in rehabilitation with transcranial magnetic stimulation. PMR 2(12 Suppl 2):S253–S268
Warraich Z, Kleim JA (2010) Neural plasticity: the biological substrate for neurorehabilitation. PMR 2(12 Suppl 2):S208–S219
Joyce ME, Roberts AB, Sporn MB, Bolander ME (1990) Transforming growth factor-beta and the initiation of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in the rat femur. J Cell Biol 110(6):2195–2207
Nathan C, Sporn M (1991) Cytokines in context. J Cell Biol 113:981–986
Alexandrow MG, Moses HL (1995) Transforming growth factor-β and cell cycle regulation. Cancer Res 55:1452–1457
Martinou JC, Le Van Thai A, Valette A, Weber MJ (1990) Transforming growth factor β1 is a potent survival factor for rat embryo motoneurons in culture. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 52:175–181
Chalazonitis A, Kalberg J, Twardzik DR, Morrison RS, Kessler JA (1992) Transforming growth factor-β has neurotrophic actions on sensory neurons in vitro and is synergistic with nerve growth factor. Dev Biol 152:121–132
Prewitt CM, Niesman IR, Kane CJ, Houle JD (1997) Activated macrophage/microglial cells can promote the regeneration of sensory axons into the injured spinal cord. Exp Neurol 148:433–443
Chin J, Angers A, Cleary LJ, Eskin A, Byrne JH (2002) Transforming growth factor-β1 alters synapsin distribution and modulates synaptic depression in Aplysia. J Neurosci 22:RC220
Flanders KC, LuÈdecke G, Engels S, Cissel DS, Roberts AB, Kondaiah P et al (1991) Immunhistochemical localization of transforming growth factor-βs in the nervous system of the mouse embryo. Development 113:183–191
Unsicker K, Flanders KC, Cissel DS, Lafyatis R, Sporn MB (1991) Transforming growth factor-β isoforms in the adult rat central and peripheral nervous system. Neuroscience 44:613–625
Massagué J (2000) How cells read TGF-β signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:169–178
Logan TT, Villapol S, Symes AJ (2013) TGF -β superfamily gene expression and induction of the Runx1 transcription factor in adult neurogenic regions after brain injury. PLoS ONE 8(3):e59250
Zhou HL, Zhang LS, Kang Y, Zhang W, Wang TH (2008) Effects of electro-acupuncture on CNTF expression in spared dorsal root ganglion and the associated spinal lamina II and nucleus dorsalis following adjacent dorsal root ganglionectomies in cats. Neuropeptides 42:95–106
Zhang RJ, You C, Cai BW, He M, Yang YB, Liu Z et al (2006) Changes in P-selectin expression after brain injury in rats. J South Med Univ 26(3):348–351 (Chinese)
Anesti AM, Peeters PJ, Royaux I, Coffin RS (2008) Efficient delivery of RNA Interference to peripheral neurons in vivo using herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res 36(14):1–12
Zhou X, Yang JW, Zhang W, Ou KQ, Zhou HL, Ma YQ et al (2009) Role of NGF in spared DRG following partial dorsal rhizotomy in cats. Neuropeptides 43:363–369
Liu J, Zhang Z, Li JT, Zhu YH, Zhou HL, Liu S et al (2009) Effects of NT-4 gene modified fibroblasts transplanted into AD rats. Neurosci Lett 466:1–5
Qin DX, Zou XL, Luo W, Zhang W, Zhang HT, Li XL et al (2006) Expression of some neurotrophins in the spinal motoneurons after cord hemisection in adult rats. Neurosci Lett 410(3):222–227
Zhang HT, Li LY, Zou XL, Song XB, Hu YL, Feng ZT et al (2007) The immunohistochemical distribution of NGF, BDNF, NT-3, NT-4 in the brains of adult rhesus monkeys. J Histochem Cytochem 55(1):1–19
Wang XY, Li XL, Hong SQ, Xi-Yang YB, Wang TH (2009) Electroacupuncture induced spinal plasticity is linked to multiple gene expressions in dorsal root deafferented rats. J Mol Neurosci 37(2):97–110
Liu F, Sun WW, Wang Y, Hu LQ, Dai P, Tian CF et al (2009) Effects of electro-acupuncture on NT-4 expression in spinal dorsal root ganglion and associated segments of the spinal dorsal horn in cats subjected to adjacent dorsal root ganglionectomy. Neurosci Lett 450(2):158–162
Ip NY, Wiegand SJ, Morse J, Rudge JS (1993) Injury-induced regulation of ciliary neurotrophic factor mRNA in the adult rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 5:25–33
Rudge JS, Morrissey D, Lindsay RM, Pasnikowski EM (1994) Regulation of ciliary neurotrophic factor in cultured rat hippocampal astrocytes. Eur J Neurosci 6:218–229
Kirsch M, Schneider T, Lee MY, Hofmann HD (1998) Lesion-induced changes in the expression of ciliary neurotrophic factor and its receptor in rat optic nerve. Glia 23:239–248
Zhou J, Lei P, Zhang X (2008) Resveratrol on brain injury after traumatic brain tissue in neural cell apoptosis. Trauma Surg 9(1):106–109
Hu R, Zhou J, Luo C, Lin J, Wang X, Li X et al (2010) Glial scar and neuroregeneration: histological, functional, and magnetic resonance imaging analysis in chronic spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Spine 13(2):169–180
Kopp MA, Brommer B, Gatzemeier N, Schwab JM, Prüss H (2010) Spinal cord injury induces differential expression of the profibrotic semaphorin 7A in the developing and mature glial scar. Glia 58(14):1748–1756
Gao X, Chen J (2011) Mild traumatic brain injury results in extensive neuronal degeneration in the cerebral cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70(3):183–191
Hagen EM, Eide GE, Rekand T, Gilhus NE, Gronning M (2010) Traumatic spinal cord injury and concomitant brain injury: a cohort study. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 190:51–57
Wang TH, Meng QS, Qi JG, Zhang WM, Chen J, Wu LF (2008) NT-3 expression in spared DRG and the associated spinal laminae as well as its anterograde transport in sensory neurons following removal of adjacent DRG in cats. Neurochem Res 33(1):1–7
Li XL, Zhang W, Zhou X, Wang TH (2007) Temporal changes in the expression of some neurotrophins in spinal cord transected adult rats. Neuropeptides 41(3):135–143
Chen J, Qi JG, Zhang W, Zhou X, Meng QS, Zhang WM et al (2007) Electro-acupuncture induced NGF, BDNF and NT-3 expression in spared L6 dorsal root ganglion in cats subjected to removal of adjacent ganglia. Neurosci Res 59:399–405
Zhang W, Li Y, Wang ZJ, Zhou X, Ou KQ, Zhou HL et al (2010) Functional roles of intrinsic neurotrophin-3 in spinal neuroplasticity of cats following partial ganglionectomy. Growth Factors 28(5):351–358
Huang RQ, Cheng HL, Zhao XD, Dai W, Zhuang Z, Wu Y, Liu Y, Shi JX (2010) Preliminary study on the effect of trauma-induced secondary cellular hypoxia in brain injury. Neurosci Lett 473(1):22–27
Sillesen M, Johansson PI, Rasmussen LS, Jin G, Jepsen CH, Imam AM, Hwabejire J, Lu J, Duggan M, Velmahos G, deMoya M, Alam HB (2013) Platelet activation and dysfunction in a large-animal model of traumatic brain injury and hemorrhage. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 74(5):1252–1259
Chin J, Angers A, Cleary LJ, Eskin A, Byrne JH (2002) Transforming growth factor-β1 alters synapsin distribution and modulates synaptic depression in Aplysia. J Neurosci 22:RC220
Welser JV, Li L, Milner R (2010) Microglial activation state exerts a biphasic influence on brain endothelial cell proliferation by regulating the balance of TNF and TGFβ1. J Neuroinflammation 7:89
Bain JM, Ziegler A, Yang Z, Levison SW, Sen E (2010) TGF beta1 stimulates the over-production of white matter astrocytes from precursors of the “brain marrow” in a rodent model of neonatal encephalopathy. PLoS ONE 5(3):e9567
Kaiser O, Paasche G, Stöver T, Ernst S, Lenarz T, Kral A, Warnecke A (2013) TGF-beta superfamily member activin A acts with BDNF and erythropoietin to improvesurvivalof spiral ganglion neurons invitro. Neuropharmacology 75:416–425
Khodosevich K, Lazarini F, von Engelhardt J, Kaneko H, Lledo PM, Monyer H (2013) Connective tissue growth factor regulates interneuron survival and information processing in the olfactory bulb. Neuron 79(6):1136–1151
Kandasamy M, Lehner B, Kraus S, Sander PR, Marschallinger J, Rivera FJ, Trümbach D, Ueberham U, Reitsamer HA, Strauss O, Bogdahn U, Couillard-Despres S, Aigner L (2014) TGF-beta signalling in the adult neurogenic niche promotes stem cell quiescence as well as generation of new neurons. J Cell Mol Med 18(7):1444–1459
Liu Y, Liu H, Meyer C, Li J, Nadalin S, Königsrainer A, Weng H, Dooley S, ten Dijke P (2013) Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-mediated connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) expression in hepatic stellate cells requires Stat3 signaling activation. J Biol Chem 288(42):30708–30719
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by natural science foundation of Yunnan province (No. 2013FB119), and natural science foundation of Zhejiang province (No. Y2090864).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xu-Yang Wang, Ying-Chun Ba, Fang Wang, Heng-Li Tian and Jin-Tao Li have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XY., Ba, YC., Xiong, LL. et al. Endogenous TGFβ1 Plays a Crucial Role in Functional Recovery After Traumatic Brain Injury Associated with Smad3 Signal in Rats. Neurochem Res 40, 1671–1680 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1634-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1634-x