Abstract
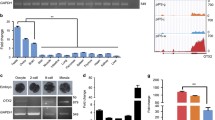
The pigs have similarities of organ size, immunology and physiology with humans. Porcine-induced pluripotent stem cells (piPSCs) have great potential application in regenerative medicine. Here, we established piPSCs induced from porcine fetal fibroblasts by the retroviral overexpression of Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc. The piPSCs not only express pluripotent markers but also have the capacity for differentiation in vivo and in vitro, including EB and teratoma formation. We supplemented microRNAs during the induction process because miR-302a, miR-302b, and miR-200c have been reported to be highly expressed in human and mouse embryonic stem cells and in iPSCs. In this study, we found that the overexpression of miR-302a, miR-302b, and miR-200c effectively improved the reprogramming efficiency and reduced the induction time for piPSCs in the OSKM and OSK induction systems. Due to the similar induction efficiency of 4F-induced piPSCs or of three factors combined with miR-302a, miR-302b, and miR-200c (3F-miRNA-induced piPSCs), we recommend the addition of miRNAs instead of c-Myc to reduce the tumorigenicity of piPSCs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall V (2008) Porcine embryonic stem cells: a possible source for cell replacement therapy. Stem Cell Rev 4:275–282. doi:10.1007/s12015-008-9040-2
Strojek RM, Reed MA, Hoover JL, Wagner TE (1990) A method for cultivating morphologically undifferentiated embryonic stem cells from porcine blastocysts. Theriogenology 33:901–913
Li M, Zhang D, Hou Y, Jiao L, Zheng X, Wang WH (2003) Isolation and culture of embryonic stem cells from porcine blastocysts. Mol Reprod Dev 65:429–434. doi:10.1002/mrd.10301
Blomberg LA, Schreier LL, Talbot NC (2008) Expression analysis of pluripotency factors in the undifferentiated porcine inner cell mass and epiblast during in vitro culture. Mol Reprod Dev 75:450–463. doi:10.1002/mrd.20780
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131:861–872. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019
Okita K, Ichisaka T, Yamanaka S (2007) Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 448:313–317. doi:10.1038/nature05934
Liu H, Zhu F, Yong J, Zhang P, Hou P, Li H, Jiang W, Cai J, Liu M, Cui K, Qu X, Xiang T, Lu D, Chi X, Gao G, Ji W, Ding M, Deng H (2008) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from adult rhesus monkey fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 3:587–590. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2008.10.014
Li W, Wei W, Zhu S, Zhu J, Shi Y, Lin T, Hao E, Hayek A, Deng H, Ding S (2009) Generation of rat and human induced pluripotent stem cells by combining genetic reprogramming and chemical inhibitors. Cell Stem Cell 4:16–19. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2008.11.014
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355. doi:10.1038/nature02871
Ezashi T, Telugu BP, Alexenko AP, Sachdev S, Sinha S, Roberts RM (2009) Derivation of induced pluripotent stem cells from pig somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:10993–10998. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905284106
Wu Z, Chen J, Ren J, Bao L, Liao J, Cui C, Rao L, Li H, Gu Y, Dai H, Zhu H, Teng X, Cheng L, Xiao L (2009) Generation of pig induced pluripotent stem cells with a drug-inducible system. J Mol Cell Biol 1:46–54. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjp003
Banito A, Gil J (2010) Induced pluripotent stem cells and senescence: learning the biology to improve the technology. EMBO Rep 11:353–359. doi:10.1038/embor.2010.47
Suh MR, Lee Y, Kim JY, Kim SK, Moon SH, Lee JY, Cha KY, Chung HM, Yoon HS, Moon SY, Kim VN, Kim KS (2004) Human embryonic stem cells express a unique set of microRNAs. Dev Biol 270:488–498. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.02.019
Zovoilis A, Nolte J, Drusenheimer N, Zechner U, Hada H, Guan K, Hasenfuss G, Nayernia K, Engel W (2008) Multipotent adult germline stem cells and embryonic stem cells have similar microRNA profiles. Mol Hum Reprod 14:521–529. doi:10.1093/molehr/gan044
Ciaudo C, Servant N, Cognat V, Sarazin A, Kieffer E, Viville S, Colot V, Barillot E, Heard E, Voinnet O (2009) Highly dynamic and sex-specific expression of microRNAs during early ES cell differentiation. PLoS Genet 5:e1000620. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000620
Wilson KD, Venkatasubrahmanyam S, Jia F, Sun N, Butte AJ, Wu JC (2009) MicroRNA profiling of human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 18:749–758. doi:10.1089/scd.2008.0247
Bar M, Wyman SK, Fritz BR, Qi J, Garg KS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Bendoraite A, Mitchell PS, Nelson AM, Ruzzo WL, Ware C, Radich JP, Gentleman R, Ruohola-Baker H, Tewari M (2008) MicroRNA discovery and profiling in human embryonic stem cells by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries. Stem Cells 26:2496–2505. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2008-0356
Rosa A, Brivanlou AH (2011) A regulatory circuitry comprised of miR-302 and the transcription factors OCT4 and NR2F2 regulates human embryonic stem cell differentiation. EMBO J 30:237–248. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.319
Card DA, Hebbar PB, Li L, Trotter KW, Komatsu Y, Mishina Y, Archer TK (2008) Oct4/Sox2-regulated miR-302 targets cyclin D1 in human embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 28:6426–6438. doi:10.1128/MCB.00359-08
Li R, Liang J, Ni S, Zhou T, Qing X, Li H, He W, Chen J, Li F, Zhuang Q, Qin B, Xu J, Li W, Yang J, Gan Y, Qin D, Feng S, Song H, Yang D, Zhang B, Zeng L, Lai L, Esteban MA, Pei D (2010) A mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition initiates and is required for the nuclear reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 7:51–63. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.04.014
Subramanyam D, Lamouille S, Judson RL, Liu JY, Bucay N, Derynck R, Blelloch R (2011) Multiple targets of miR-302 and miR-372 promote reprogramming of human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 29:443–448. doi:10.1038/nbt.1862
Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Golipour A, David L, Sung HK, Beyer TA, Datti A, Woltjen K, Nagy A, Wrana JL (2010) Functional genomics reveals a BMP-driven mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in the initiation of somatic cell reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 7:64–77. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.04.015
Liu X, Sun H, Qi J, Wang L, He S, Liu J, Feng C, Chen C, Li W, Guo Y, Qin D, Pan G, Chen J, Pei D, Zheng H (2013) Sequential introduction of reprogramming factors reveals a time-sensitive requirement for individual factors and a sequential EMT–MET mechanism for optimal reprogramming. Nat Cell Biol 15:829–838. doi:10.1038/ncb2765
Wang G, Guo X, Hong W, Liu Q, Wei T, Lu C, Gao L, Ye D, Zhou Y, Chen J, Wang J, Wu M, Liu H, Kang J (2013) Critical regulation of miR-200/ZEB2 pathway in Oct4/Sox2-induced mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and induced pluripotent stem cell generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:2858–2863. doi:10.1073/pnas.1212769110
Roberts RM, Telugu BP, Ezashi T (2009) Induced pluripotent stem cells from swine (Sus scrofa): why they may prove to be important. Cell Cycle 8:3078–3081
Telugu BP, Ezashi T, Roberts RM (2010) Porcine induced pluripotent stem cells analogous to naive and primed embryonic stem cells of the mouse. Int J Dev Biol 54:1703–1711. doi:10.1387/ijdb.103200bt00bt
Esteban MA, Xu J, Yang J, Peng M, Qin D, Li W, Jiang Z, Chen J, Deng K, Zhong M, Cai J, Lai L, Pei D (2009) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cell lines from Tibetan miniature pig. J Biol Chem 284:17634–17640. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.008938
Esteban MA, Bao X, Zhuang Q, Zhou T, Qin B, Pei D (2012) The mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in somatic cell reprogramming. Curr Opin Genet Dev 22:423–428. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2012.09.004
Bao X, Zhu X, Liao B, Benda C, Zhuang Q, Pei D, Qin B, Esteban MA (2013) MicroRNAs in somatic cell reprogramming. Curr Opin Cell Biol 25:208–214. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2012.12.004
Lin SL, Chang DC, Lin CH, Ying SY, Leu D, Wu DT (2011) Regulation of somatic cell reprogramming through inducible mir-302 expression. Nucleic Acids Res 39:1054–1065. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq850
Miyoshi N, Ishii H, Nagano H, Haraguchi N, Dewi DL, Kano Y, Nishikawa S, Tanemura M, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Saito T, Nishimura J, Takemasa I, Mizushima T, Ikeda M, Yamamoto H, Sekimoto M, Doki Y, Mori M (2011) Reprogramming of mouse and human cells to pluripotency using mature microRNAs. Cell Stem Cell 8:633–638. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2011.05.001
Dominguez-Sola D, Ying CY, Grandori C, Ruggiero L, Chen B, Li M, Galloway DA, Gu W, Gautier J, Dalla-Favera R (2007) Non-transcriptional control of DNA replication by c-Myc. Nature 448:445–451. doi:10.1038/nature05953
Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K, Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Okita K, Mochiduki Y, Takizawa N, Yamanaka S (2008) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol 26:101–106. doi:10.1038/nbt1374
Judson RL, Babiarz JE, Venere M, Blelloch R (2009) Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs promote induced pluripotency. Nat Biotechnol 27:459–461. doi:10.1038/nbt.1535
Marson A, Levine SS, Cole MF, Frampton GM, Brambrink T, Johnstone S, Guenther MG, Johnston WK, Wernig M, Newman J, Calabrese JM, Dennis LM, Volkert TL, Gupta S, Love J, Hannett N, Sharp PA, Bartel DP, Jaenisch R, Young RA (2008) Connecting microRNA genes to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells. Cell 134:521–533. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.020
Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega VB, Wong E, Orlov YL, Zhang W, Jiang J, Loh YH, Yeo HC, Yeo ZX, Narang V, Govindarajan KR, Leong B, Shahab A, Ruan Y, Bourque G, Sung WK, Clarke ND, Wei CL, Ng HH (2008) Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell 133:1106–1117. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.043
Wang Y, Baskerville S, Shenoy A, Babiarz JE, Baehner L, Blelloch R (2008) Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs regulate the G1-S transition and promote rapid proliferation. Nat Genet 40:1478–1483. doi:10.1038/ng.250
Melton C, Judson RL, Blelloch R (2010) Opposing microRNA families regulate self-renewal in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature 463:621–626. doi:10.1038/nature08725
Li Z, Yang CS, Nakashima K, Rana TM (2011) Small RNA-mediated regulation of iPS cell generation. EMBO J 30:823–834. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.2
Liao B, Bao X, Liu L, Feng S, Zovoilis A, Liu W, Xue Y, Cai J, Guo X, Qin B, Zhang R, Wu J, Lai L, Teng M, Niu L, Zhang B, Esteban MA, Pei D (2011) MicroRNA cluster 302–367 enhances somatic cell reprogramming by accelerating a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. J Biol Chem 286:17359–17364. doi:10.1074/jbc.C111.235960
Gustavsson I (1988) Standard karyotype of the domestic pig. Committee for the Standardized Karyotype of the Domestic Pig. Hereditas 109:151–157
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 31271591), the National Basic Research Program (No. 2011CBA01003) and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT1248) in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Kuiying Ma and Guangqi Song have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, K., Song, G., An, X. et al. miRNAs promote generation of porcine-induced pluripotent stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem 389, 209–218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1942-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1942-x