Abstract
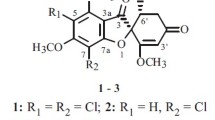
Griseofulvin (C17H17O6Cl) was first isolated from Penicillium griseofulvum Dieck by Oxford, Raistrick, and Simonart (1939), In 1946 Brian, Curtis and Hemming isolated a “curling factor” from cultures of P. janczewskii ZAL., which caused abnormal development of fungal hyphae. The chemical and physical properties of the antibiotic were reported by Mcgowan (1946). The identity of “curling factor” with griseofulvin was determined chemically by GROVE and MCGOWAN (1947), and biologically by Brian et al. (1949). Subsequent studies have demonstrated that P. patulum and P. raistrickii also produce the antibiotic (Brian et al., 1949, 1955). The griseofulvin analogs, bromogriseofulvin and dechlorogriseofulvin have also been isolated from fungi (Macmillan, 1951, 1954).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, M. T. J., and J. F. Grove: Uptake and translocation of organic compounds by fungi. II. Griseofulvin. Exptl. Cell Research 17, 105 (1959).
Aytoun, R. S. C.: The effects of griseofulvin on certain phytopathogenic fungi. Ann. Botany (London) 20, 297 (1956).
Aytoun, R. S. C., A. H. Campbell, E. J. Napier, and D. A. L. Seiler: Mycological aspects of the action of griseofulvin against dermatophytes. A.M.A. Arch. Dermatol. 81, 650 (1960).
Banbury, G. H.: Physiological studies in the mucorales. Part II. Some observations on growth regulation in the sporongiophore of Phycomyces. J. Exptl. Botany 3, 86 (1952).
Barich, L. L., T. Nakai, J. Schwarz, and D. J. Barich: Tumour promoting effect of excessively large doses of oral griseofulvin on tumours induced in mice by methylcholanthrene. Nature 187, 335 (1960).
Barnes, M. J., and B. Boothroyd: The metabolism of griseofulvin in mammals. Biochem. J. 78, 41 (1961).
Blank, H., and F. J. Roth: Systemic control of cutaneous fungus infections. Am. J. Med. Sci. 240, 104/466 (1960b).
Blank, H., D. Taplin, and F. J. Roth: Electron microscopic observations of the effects of griseofulvin on dermatophytes. A.M.A. Arch. Dermatol. 81, 667 (1960).
Boothroyd, B., E. J. Napier, and G. A. Somerfield: The demethylation of griseofulvin by fungi. Biochem. J. 80, 34 (1961).
Brian, P. W.: Studies on the biological activity of griseofulvin. Ann. Botany (London) 13, 59 (1949).
Brian, P. W.: Griseofulvin. Trans. Brit. Myco. Soc. 43, 1 (1960).
Brian, P. W., P. J. Curtis, and H. G. Hemming: A substance causing abnormal development of fungal hyphae produced by Penicillium janczewskii ZAL. I. Biological assay, production, and isolation of “curling factor”. Trans. Brit. Myco. Soc. 29, 173 (1946).
Brian, P. W., P. J. Curtis, and H. G. Hemming: A substance causing abnormal development of fungal hyphae produced by Penicillium janczewskii ZAL. III. Identity of “curling factor” with griseofulvin. Trans. Brit. Myco. Soc. 32, 20 (1949)
Brian, P. W., P. J. Curtis, and H. G. Hemming: Production of griseofulvin by Penicillium raistrichii. Trans. Brit. Myco. Soc. 38, 305 (1955).
Brian, P. W., J. M. Wright, J. Stubbs, and A. M. Way: Uptake of antibiotic metabolites of soil microorganisms by plants. Nature 167, 347 (1951).
Burgoon, C. F., J. H. Graham, R. J. Keiper, F. Urbach, J. S. Burgoon, and E. B. Helwig: Histopathologic evaluation of griseofulvin in Microsporum andovini infections. A.M.A. Arch. Dermatol. 81, 724 (1960).
Crosse, R., R. Mcwilliam, and A. Rhodes: Some relations between chemical structure and antifungal effects of griseofulvin analogues. J. Gen. Microbiol. 34, 51 (1964).
Crowdy, S. H., D. Gardner, J. F. Grove, and D. Pramer: The translocation of antibiotics in higher plants. I. Isolation of griseofulvin and chloramphenicol from plant tissue. J. Exptl. Botany 6, 371 (1955).
Crowdy, S. H., A. P. Green, J. F. Grove, P. Mccloskey, and A. Morrison: The translocation of antibiotics in higher plants. 3. The estimation of griseofulvin relatives in plant tissue. Biochem. J. 72, 230 (1959a).
Crowdy, S. H., J. F. Grove, H. G. Hemming, and K. C. Robinson: The translocation of antibiotics in higher plants. II. The movement of griseofulvin in broad bean and tomato. J. Exptl. Botany 7, 42 (1956).
Crowdy, S. H., J. F. Grove, and P. Mccloskey: The translocation of antibiotics in higher plants. 4. Systemic fungicidal activity and chemical structure in griseofulvin relatives. Biochem. J. 72, 241 (1959b).
Dennis, D. J., M. J. Davis, and J. C. Campbell: The effects of griseofulvin on epithelial cells in tissue culture. J. Invest. Dermatol. 34, 99 (1960).
Deyson, G.: Antimitotic properties of griseofulvin. Ann. pharm, franc. 22, 17 (1964a).
Deyson, G.: The influence of griseofulvin on the antimitotic properties of colchicine. Ann. pharm, franc. 22, 89 (1964b).
El-Nakeeb, M. A., and J. O. Lampen: Formation of complexes of griseofulvin and nucleic acids of fungi and its relation to griseofulvin sensitivity. Biochem. J. 92, 59p (1964a).
El-Nakeeb, M. A., and J. O. Lampen: Binding of tritiated-griseofulvin by ribosomes and RNA of Microsporum gypseum. Bacteriol. Proc. 1964, P60 (1964b).
El-Nakeeb, M. A., and J. O. Lampen: Uptake of griseofulvin by the sensitive dermatophyte, Microsporum gypseum. J. Bacteriol. 89, 564 (1965a).
El-Nakeeb, M. A., and J. O. Lampen: Distribution of griseofulvin taken up by Microsporum gypseum: Complexes of the antibiotic with cell constituents. J. Bacteriol. 89, 1075 (1965b).
El-Nakeeb, M. A., W. L. Mclellan, and J. O. Lampen: Antibiotic action of griseofulvin on dermatophytes. J. Bacteriol. 89, 557 (1965c).
El-Nakeeb, M. A., and J. O. Lampen: Uptake of H3-griseofulvin by microorganisms and its correlation with sensitivity to griseofulvin. J. Gen. Microbiol. 39, 285 (1965d).
Evans, G.: The antibiotic activity of Cylindrocarpon radicicola. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Sydney 1964.
Eveligh, D. E., and S. G. Knight: The effect of griseofulvin on the cell wall composition of Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Bacteriol. Proc. 1965, G 82, p. 27 (1965).
Foley, E. J., and G. A. Greco: Studies on the mode of action of griseofulvin. Antibiotics Ann. 1959/60, 670 (1960).
Freedman, M. H., R. M. Baxter, and G. C. Walker: In vitro sorption of griseofulvin by keratin substrates. J. Invest. Dermatol. 38, 199 (1962).
Goldman, L., A. Beyer, and J. Schwarz: Absence of local cytotoxic change in man from griseofulvin. Nature 187, 335 (1960).
Grove, J. F.: Griseofulvin. Quart. Revs. (London) 17, 1 (1963).
Grove, J. F., J. Macmillan, T. P. C. Mulholland, and M. A. T. Rogers: Griseofulvin. Part IV. Structure. J. Chem. Soc. 1952, 3977 (1952).
Grove, J. F., and J. C. Mcgowan: Identity of griseofulvin and “curling factor”. Nature 160, 574 (1947).
Huber, F. M., and D. Gottlieb: The mode of action of the antifungal antibiotic griseofulvin (1966). (In Preparation.)
Larpent, J. P.: Comparative action of griseofulvin and colchicine on growth and branching of the young thallus of Saprolegnia monoica. Compt. rend. 157, 2219 (Chem. Abstr. 61, 2407f) (1963).
Larsen, W. G., and D. J. Demis: Metabolic studies of the effect of griseofulvin and candicidin on fungi. J. Invest. Dermatol. 41, 335 (1963).
Macmillan, J.: Griseofulvin. Part 9. Isolation of the bromoanalogue from Penicillium griseofulvum and Penicillium nigricans. J. Chem. Soc. 2585 (1954).
Macmillan, J.: Dechlorogriseofulvin — a metabolic product of Penicillium griseofulvum DIERCKX and Penicillium janczewskii ZAL. Chem. & Ind. (London) 179 (1951).
Mcgowan, J. C.: A substance causing abnormal development of fungal hyphae produced by Penicillium janczewskii ZAL. II. Preliminary notes on the chemical and physical properties of “curling factor”. Trans. Brit. Myco. Soc. 29, 188 (1946).
Mcnall, E. G.: Biochemical studies on the metabolism of griseofulvin. A.M.A. Arch. Dermatol. 81, 657 (1960a).
Mcnall, E. G.: Metabolic studies on griseofulvin and its mechanism of action. Antibiotics Ann. 1959/60, 674 (1960b).
Muntoni, S., and B. Loddo: Griseofulvin — induced budding in cell cultures. Arch. intern, pharmacodynamic 151, 365 (Chem. Abstr. 62, 5755g) (1964).
Napier, E. J., D. I. Turner, and A. Rhodes: The in vitro action of griseofulvin against pathogenic fungi of plants. Ann. Botany (London) 20, 461 (1956).
Oxford, A. E., H. Raistrick, and P. Simonart: Studies on the biochemistry of microorganisms. 60. Griseofulvin, C17H17O6Cl, a metabolic product of Penicillium griseofulvum DIECK. Biochem. J. 33, 240 (1939).
Paget, G. E., and S. J. Alcock: Griseofulvin and colchicine: lack of carcinogenic action. Nature 188, 867 (1960).
Paget, G. E., and A. L. Walpole: Some cytological effects of griseofulvin. Nature 182, 1320 (1958).
Paget, G. E., and A. L. Walpole: The experimental toxicology of griseofulvin. A.M.A. Arch. Dermatol. 81, 750 (1960).
Reiss, F., L. Kornblee, and B. Gordon: Griseofulvin (fulvicin) in the treatment of fungus infections of the hair, skin, and nails with special reference to mycologic changes produced during therapy. J. Invest. Dermatol. 34, 263 (1960).
Roth, F. J.: Griseofulvin. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 89, 81, 750 (1960).
Roth, F. J., B. Sallman, and H. Blank: In vitro studies of the antifungal antibiotic griseofulvin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 33, 403 (1959b).
Schwarz, J., and J. K. Loutzenhiser: Laboratory experiences with griseofulvin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 34, 295 (1960).
Shockman, G. D., and J. O. Lampen: Inhibition by antibiotics of the growth of bacterial and yeast protoplasts. J. Bacteriol. 84, 508 (1962).
Srivastava, O. P., and V. C. Vora: Effect of griseofulvin on dermatophytes including locally isolated strains of Trichophyton rubrum and on Microsporum canis grown in keratin. J. Sci. Ind. Research (India) 20C, 163 (1961).
Stokes, A.: Uptake and translocation of griseofulvin by wheat seedlings. Plant and Soil 5, 132 (1954).
Thyagarajan, T. R., O. P. Srivastava, and V. V. Vora: Some cytological observations on the effect of griseofulvin on dermatophytes. Naturwissenschaften 50, 524 (1963).
Wright, J. M.: Phytotoxic effects of some antibiotics. Ann. Botany (London) 15, 493 (1951).
Ziegler, H.: Effect of griseofulvin on Microsporum canis. IV. Z. allgem. Mikrobiol. 3, 211 (1963).
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1967 Springer-Verlag Berlin · Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Huber, F.M. (1967). Griseofulvin. In: Gottlieb, D., Shaw, P.D. (eds) Mechanism of Action. Antibiotics, vol 1. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-46051-7_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-46051-7_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-46053-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-46051-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive