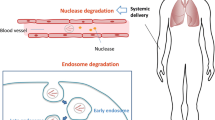
Abstract
Targeted delivery of functional nucleic acids (genes and oligonucleotides) to pulmonary endothelium may become a novel therapy for the treatment of various types of lung diseases. It may also provide a new research tool to study the functions and regulation of novel genes in pulmonary endothelium. Its success is largely dependent on the development of a vehicle that is capable of efficient pulmonary delivery with minimal toxicity. This review summarizes the recent progress that has been made in our laboratory along these research directions. Factors that affect pulmonary nucleic acids delivery are also discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Dalby, and J. Suman. Inhalation therapy: technological milestones in asthma treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 55:779–791 (2003).
G. Scheuch, M. J. Kohlhaeufl, P. Brand, and R. Siekmeier. Clinical perspectives on pulmonary systemic and macromolecular delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58:996–1008 (2006).
M. Thomas, J. J. Lu, J. Chen, and A. M. Klibanov. Non-viral siRNA delivery to the lung. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59:124–133 (2007).
A. Mori, S. J. Kennel, and L. Huang. Immunotargeting of liposomes containing lipophilic antitumor prodrugs. Pharm. Res. 10:507–514 (1993).
S. J. Kennel, T. K. Lankford, L. J. Foote, I. A. Davis, R. A. Boll, and S. Mirzadeh. Combination vascular targeted and tumor targeted radioimmunotherapy. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 14:371–379 (1999).
V. Muzykantov, M. Christofidou-Solomidou, I. Balyasnikova, D. Harshaw, L. Schultz, A. Fisher, and S. Albelda. Streptavidin facilitates internalization and pulmonary targeting of anti-endothelial antibody (PECAM-1): a strategy for intraendothelial drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96:2379–2384 (1999).
B. D. Kozower, M. Christofidou-Solomidou, T. D. Sweitzer, S. Muro, D. G. Buerk, C. C. Solomides, S. M. Albelda, G. A. Patterson, and V. R. Muzykantov. Immunotargeting of catalase to the pulmonary endothelium alleviates oxidative stress and reduces acute lung transplantation injury. Nat. Biotechnol. 21:392–398 (2003).
K. Nowak, S. Weih, R. Metzger, R. F. Albrecht II, S. Post, P. Hohenberger, M. M. Gebhard, and S. M. Danilov. Immunotargeting of catalase to lung endothelium via anti-angiotensin-converting enzyme antibodies attenuates ischemia–reperfusion injury of the lung in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 293:L162–L169 (2007).
S. Li, and Z. Ma. Non-viral gene therapy. Current Gene Therapy. 1:201–226 (2001).
M. Simionescu. Lung endothelium: structure-function correlates. In R. G. Crystal, and J. B. West (eds.), The Lung: Scientific Foundations, Raven, New York, 1991, pp. 301–331.
S. Mukherjee, R. N. Ghosh, and F. R. Maxfield. Endocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 77:759–803 (1997).
M. Simionescu, N. Simionescu, and G. E. Palade. Differentiated microdomains on the luminal surface of capillary endothelium: distribution of lectin receptors. J. Cell Biol. 94:406–413 (1982).
T. Stevens. Molecular and cellular determinants of lung endothelial cell heterogeneity. Chest. 128(6 Suppl):558S–564S (2005).
V. S. Trubeskoy, V. P. Torchilin, S. J. Kennel, and L. Huang. Use of N-terminal modified poly(l-lysin)-antibody conjugate as a carrier for targeted gene delivery in mouse lung endothelial cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 3:323–327 (1992).
S. Li, Y. Tan, E. Viroonchatapan, B. R. Pitt, and L. Huang. Targeted gene delivery to the lung by anti-PECAM antibody. Am. J. Physiol. 278:504–511 (2000).
P. Newman. The biology of PECAM-1. J. Clin. Invest. 99:3–8 (1997).
S. M. Danilov, et al. Lung uptake of antibodies to endothelial antigens: key determinants of vascular immunotargeting. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 280:1335–1347 (2001).
M. J. Eppihimer, B. Wolitzky, D. C. Anderson, M. A. Labow, and D. N. Granger. Heterogeneity of expression of E- and P-selectins in vivo. Circ. Res. 79:560–569 (1996).
M. S. Diamond, D. E. Staunton, A. R. de Fougerolles, S. A. Stacker, J. Garcia-Aguilar, M. L. Hibbs, and T. A. Springer. ICAM-1 (CD54): a counter-receptor for Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). J. Cell Biol. 111:3129–3139 (1990).
H. Kataoka, N. Kume, S. Miyamoto, M. Minami, H. Moriwaki, T. Murase, T. Sawamura, T. Masaki, N. Hashimoto, and T. Kita. Expression of lectinlike oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 in human atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation. 99:3110–3117 (1999).
J. Hao, A. W. Serohijos, G. Newton, G. Tassone, Z. Wang, D. C. Sgroi, N. V. Dokholyan, and J. P. Basilion. Identification and rational redesign of peptide ligands to CRIP1, a novel biomarker for cancers. PLoS. Comput. Biol. 4:e1000138 (2008).
R. H. Yeh, T. R. Lee, and D. S. Lawrence. From consensus sequence peptide to high affinity ligand, a “library scan” strategy. J. Biol. Chem. 276:12235–12240 (2001).
N. W. Morrell, E. N. Atochina, K. G. Morris, S. M. Danilov, and K. R. Stenmark. Angiotensin converting enzyme expression is increased in small pulmonary arteries of rats with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. J. Clin. Invest. 96:1823–1833 (1995).
J. Wong, R. A. Patel, and P. R. Kowey. The clinical use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 47:116–130 (2004).
D. R. Hwang, W. C. Eckelman, C. J. Mathias, E. W. Petrillo Jr., J. Lloyd, and M. J. Welch. Positron-labeled angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor: fluorine-18-fluorocaptopril. Probing the ACE activity in vivo by positron emission tomography. J. Nucl. Med. 32:1730–1737 (1991).
F. Qing, T. J. McCarthy, J. Markham, and D. P. Schuster. . Pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) binding and inhibition in humans. A positron emission tomography study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 161:2019–2025 (2000).
F. J. Femia, K. P. Maresca, S. M. Hillier, C. N. Zimmerman, J. L. Joyal, J. A. Barrett, O. Aras, V. V. Dilsizian, W. C. Eckelman, and J. W. Babich. Synthesis and evaluation of a series of 99mTc(CO)3+ lisinopril complexes for in vivo imaging of angiotensin-converting enzyme expression. J. Nucl. Med. 49:970–977 (2008).
F. Liu, H. Qi, L. Huang, and D. Liu. Factors controlling the efficiency of cationic lipid-mediated transfection in vivo via intravenous administration. Gene Ther. 4:517–523 (1997).
Y. Liu, L. C. Mounkes, H. D. Liggitt, C. S. Brown, I. Solodin, T. D. Heath, and R. J. Debs. Factors influencing the efficiency of cationic liposome-mediated intravenous gene delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 15:167–173 (1997).
S. Li, and L. Huang. In vivo gene transfer via intravenous administration of cationic lipid-protamine-DNA (LPD) complexes. Gene Ther. 4:891–900 (1997).
N. S. Templeton, D. D. Lasic, P. M. Frederik, H. H. Strey, D. D. Roberts, and G. N. Pavlakis. Improved DNA: liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery and gene expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 15:167–173 (1997).
J. Wang, X. Guo, Y. Xu, L. Barron, and F. C. Szoka Jr. Synthesis and characterization of long chain alkyl acyl carnitine esters. Potentially biodegradable cationic lipids for use in gene delivery. J. Med. Chem. 41:2207–2215 (1999).
S. Li, W. C. Tseng, D. B. Stolz, S. P. Wu, S. C. Watkins, and L. Huang. Dynamic changes in the characteristics of cationic lipidic vectors after exposure to mouse serum: implications for intravenous lipofection. Gene Ther. 6:585–594 (1999).
A. Y. Nikitin, M. I. Juarez-Perez, S. Li, L. Huang, and W. H Lee. RB-mediated suppression of spontaneous multiple neuroendocrine neoplasia and lung metastases in RB+/- mice. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of USA. 96:3916–3921 (1999).
S. Li, S. P Wu, M. Whitmore, L. Wang, S. Watkins, and L. Huang. Effect of immune response on gene transfer to the lung via systemic administration of cationic lipidic vectors. Am. J. Physiol. 276:796–804 (1999).
Y. Tan, S. Li, B. R. Pitt, and L. Huang. The inhibitory role of CpG immunostimulatory motifs in cationic lipid vector-mediated transgene expression in vivo. Hum. Gene Ther. 10:2153–2161 (1999).
B. D. Freimark, H. P. Blezinger, V. J. Florack, J. L. Nordstrom, S. D Long, D. S. Deshpande, S. Nochumson, and K. L. Petrak. Cationic lipids enhance cytokine and cell influx levels in the lung following administration of plasmid: cationic lipid complexes. J. Immunol. 160:4580–4586 (1998).
N. S. Yew, K. X. Wang, M. Przybylska, R. G. Bagley, M. Stedman, J. Marshall, R. K. Scheule, and S. H. Cheng. Contribution of plasmid DNA to inflammation in the lung after administration of cationic lipid:pDNA complexes. Hum. Gene Ther. 10:223–234 (1999).
S. Li, Y. Tan, E. Viroonchatapan, B. R. Pitt, and L. Huang. Targeted gene delivery to the lung by anti-PECAM antibody. Am. J. Physiol. 278:504–511 (2000).
Y. Tan, F. Liu, Z. Li, S. Li, and L. Huang. Sequential injection of cationic liposome and plasmid DNA effectively transfects the lung with minimal inflammatory toxicity. Molec. Ther. 3:673–682 (2001).
C. R. Hoffman, J. P. Dileo, Z. Li, S. Li, and L. Huang. Efficient in vivo gene transfer by PCR amplified fragment with reduced inflammatory activity. Gene Ther. 8:71–74 (2001).
Z. Ma, J. Li, Y. Mu, L. Yang, W. Xie, B. R. Pitt, and S. Li. Inhibition of LPS- and CpG DNA-induced TNF-a response by oxidized phospholipids. Am. J. Physiol.: Lung Cellular Molecular Physiol. 286:808–816 (2004).
G. Y. Wu, and C. H. Wu. Receptor-mediated in vitro gene transformation by a soluble DNA carrier system. J. Biol. Chem. 262:4429–4432 (1987).
O. Boussif, F. Lezoualc’h, M. A. Zanta, M. D. Mergny, D. Scherman, B. Demeneix, and J. P. Behr. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 92:7297–7301 (1995).
S. Li, and Z. Ma. Non-viral gene therapy. Current Gene Therapy. 1:201–226 (2001).
X. Gao, K. S. Kim, and D. Liu. Nonviral gene delivery: what we know and what is next. AAPS J. 23:92–104 (2007).
D. Goula, C. Benoist, S. Mantero, G. Merlo, G. Levi, and B. A. Demeneix. Polyethylenimine-based intravenous delivery of transgenes to mouse lung. Gene Ther. 5:1291–1295 (1998).
S. Idell, K. K. James, E. G. Levin, B. S. Schwartz, N. Manchanda, R. J. Maunder, T. R. Martin, J. McLarty, and D. S. Fair. Local abnormalities in coagulation and fibrinolytic pathways predispose to alveolar fibrin deposition in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 84:695–705 (1989).
S. Idell. Coagulation, fibrinolysis, and fibrin deposition in acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 31:213–220 (2003).
T. Ikeda, N. Hirose, H. Koto, H. Hirano, and N. Shigematsu. Fibrin deposition and fibrinolysis in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Nippon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 27:448–451 (1989).
D. A. Hart, P. Whidden, F. Green, J. Henkin, and D. E. Woods. Partial reversal of established bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by rh-urokinase in a rat model. Clin. Invest. Med. 17:69–76 (1994).
N. Hattori, T. H. Sisson, Y. Xu, and R. H. Simon. Upregulation of fibrinolysis by adenovirus-mediated transfer of urokinase-type plasminogen activator genes to lung cells in vitro and in vivo. Hum. Gene Ther. 10:215–222 (1999).
T. H. Sisson, N. Hattori, Y. Xu, and R. H. Simon. Treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by transfer of urokinase-type plasminogen activator genes. Hum. Gene Ther. 10:2315–23 (1999).
J. Zhang, A. Wilson, S. Alber, Z. Ma, E. Sato, O. Mazda, S. Watkins, L. Huang, B. Pitt, and S. Li. Prolonged gene expression in mouse lung endothelial cells following transfection with Epstein-Barr virus-based episomal plasmid. Gene Ther. 10:822–826 (2003).
X. Q. Wang, K. Bdeir, S. Yarovoi, D. B. Cines, W. Fang, and E. Abraham. Involvement of the urokinase kringle domain in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. J. Immunol. 177:5550–5557 (2006).
U. Griesenbach, D. M. Geddes, and E. W. Alton. Gene therapy progress and prospects: cystic fibrosis. Gene Ther. 13:1061–1067 (2006).
P. N. Reynolds, K. R. Zinn, V. D. Gavrilyuk, I. V. Balyasnikova, B. E. Rogers, D. J. Buchsbaum, M. H. Wang, D. J. Miletich, W. E. Grizzle, J. T. Douglas, S. M. Danilov, and D. T. Curiel. A targetable, injectable adenoviral vector for selective gene delivery to pulmonary endothelium in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2:562–578 (2000).
P. N. Reynolds, S. A. Nicklin, L. Kaliberova, B. G. Boatman, W. E. Grizzle, I. V. Balyasnikova, A. H. Baker, S. M. Danilov, and D. T. Curiel. Combined transductional and transcriptional targeting improves the specificity of transgene expression in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 19:838–842 (2001).
W. H. Miller, M. J. Brosnan, D. Graham, C. G. Nicol, I. Morecroft, K. M. Channon, S. M. Danilov, P. N. Reynolds, A. H. Baker, and A. F. Dominiczak. Targeting endothelial cells with adenovirus expressing nitric oxide synthase prevents elevation of blood pressure in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Ther. 12:321–327 (2005).
L. M. Work, H. Büning, E. Hunt, S. A. Nicklin, L. Denby, N. Britton, K. Leike, M. Odenthal, U. Drebber, M. Hallek, and A. H. Baker. Vascular bed-targeted in vivo gene delivery using tropism-modified adeno-associated viruses. Mol. Ther. 13:683–693 (2006).
Z. Ma, Z. Mi, A. Wilson, P. D. Robbins, B. Pitt, and S. Li. Redirecting adenovirus to pulmonary endothelium by cationic liposomes. Gene Ther. 9:176–182 (2002).
Y. K. Song, F. Liu, and D. Liu. Enhanced gene expression in mouse lung by prolonging the retention time of intravenously injected plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 5:1531–1537 (1998).
Z. Ma, J. Zhang, S. Alber, J. Dileo, D. Stolz, S. C. Watkins, L. Huang, B. R. Pitt, and S. Li. Lipid-mediated delivery of oligonucleotide to pulmonary endothelium. Am. J. Resir Cell Mol. Biol. 27:151–159 (2002).
T. M. Allen. Liposomal drug formulations. Rationale for development and what we can expect for the future. Drugs. 56:747–756 (1998).
M. Hussein. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, vincristine, and reduced-dose dexamethasone as first-line therapy for multiple myeloma. Clin. Lymphoma. 1:S18–S22 (2003).
R. Herbrecht, S. Natarajan-Ame, Y. Nivoix, and V. Letscher-Bru. The lipid formulations of amphotericin B. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 4:1277–1287 (2003).
D. D. Stuart, S. C. Semple, and T. M. Allen. High efficiency entrapment of antisense oligonucleotides in liposomes. Methods Enzymol. 387:171–188 (2004).
S. C. Semple, S. K. Klimuk, T. O. Harasym, N. Dos Santos, S. M. Ansell, K. F. Wong, N. Mauer, H. Stark, P. R. Cullis, M. J. Hope, and P. Scherrer. Efficient encapsulation of antisense oligonucleotides in lipid vesicles using ionizable aminolipids: formation of novel small multilamellar vesicle structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1510:152–166 (2001).
A. Wilson, W. Zhou, H. Champion, S. Alber, Z.-L. Tang, S. Kennel, S. Watkins, L. Huang, B. R. Pitt, and S. Li. Targeted delivery of oligodeoxynucleotides to mouse lung endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Molec. Ther. 12:510–518 (2005).
E. L. Schiffrin. Vascular endothelin in hypertension. Vascul Pharmacol. 43:19–29 (2005).
W. Zhou, X. Yuan, A. Wilson, L. Yang, M. Mokotoff, B. R. Pitt, and S. Li. Efficient intracellular delivery of oligonucleotides formulated in folate receptor-targeted lipid vesicles. Bioconjug. Chem. 13:1220–1225 (2002).
L. Yang, J. Li, W. Zhou, X. Yuan, and S. Li. Targeted delivery of antisense oligodeoxy-nucleotides to folate receptor-overexpressing tumor cells. J. Control. Release. 95:321–331 (2004).
W. Li, and F. C. Szoka Jr. Lipid-based nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Pharm Res. 24:438–449 (2007).
E. Rytting, J. Nguyen, X. Wang, and T. Kissel. Biodegradable polymeric nanocarriers for pulmonary drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 5:629–639 (2008).
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants HL-63080 and HL-68688 and by American Heart Association Grant 026540U.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuruba, R., Wilson, A., Gao, X. et al. Targeted Delivery of Nucleic Acid-Based Therapeutics to the Pulmonary Circulation. AAPS J 11, 23–30 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-008-9073-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-008-9073-0