Abstract
Purpose
Signaling by cancer stem cells (CSCs) is known to occur at least in part through conserved developmental pathways. Here, the role of one of these pathways, i.e., the hedgehog pathway, was evaluated in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC).
Methods and results
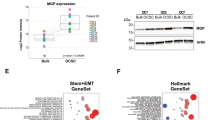
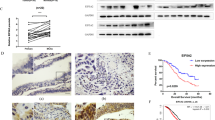
We found that in HGSOC, hedgehog inhibitors (HHIs) GANT61, LDE225 and GDC0449 reduced or inhibited the formation of spheroids enriched in CSCs. Primary malignant cells (PMCs) in ascites from HGSOC patients cultured in the presence of HHIs showed significant reduction in CSCs. Sonic hedgehog (SHH) significantly increased the expression of ALDH1A1, which was inhibited by GANT61. In the presence of a SHH neutralizing antibody (5E1), a significant reduction in the number of spheroids was observed in HGSOC-derived cell lines. Further, the motility, migration and clonogenic growth of the cells were significantly reduced by HHIs. In the presence of GANT61, a reduction of cells from PMCs in the G0 phase of the cell cycle was observed. The magnitude of difference in expression of Gli1 in tumors from the same HGSOC patients at presentation and at interval debulking surgery was greater in patients who had a recurrence on follow up. GANT61 also significantly inhibited the growth of CSCs in nude mice. Finally, RNA sequencing of HGSOC cells treated with GANT61 showed a significantly reduced expression of CSC markers.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that the hedgehog pathway plays an important role in maintaining the integrity of CSCs in HGSOC and could be a potential therapeutic target.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary files]. The RNA-Seq data generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA): Bio Project ID PRJNA477252 and PRJNA488919 (https://submit.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/subs/sra/SUB4484897/overview) (https://submit.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/subs/sra/SUB4486097/overview).
References
A. Desai, Y. Yan, S.L. Gerson, Concise reviews: cancer stem cell targeted therapies: toward clinical success. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 8, 75–81 (2019)
R.P. Nagare, S. Sneha, S.K. Priya, T.S. Ganesan, Cancer stem cells - are surface markers alone sufficient? Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12, 37–44 (2017)
N. Perrimon, C. Pitsouli, B.Z. Shilo, Signaling mechanisms controlling cell fate and embryonic patterning. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4, a005975 (2012)
S. Schmid, M. Bieber, F. Zhang, M. Zhang, B. He, D. Jablons, N.N. Teng, Wnt and hedgehog gene pathway expression in serous ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 21, 975–980 (2011)
X. Liao, M.K. Siu, C.W. Au, E.S. Wong, H.Y. Chan, P.P. Ip, H.Y. Ngan, A.N. Cheung, Aberrant activation of hedgehog signaling pathway in ovarian cancers: effect on prognosis, cell invasion and differentiation. Carcinogenesis 30, 131–140 (2009)
A.D. Steg, A.A. Katre, K.S. Bevis, A. Ziebarth, Z.C. Dobbin, M.M. Shah, R.D. Alvarez, C.N. Landen, Smoothened antagonists reverse taxane resistance in ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 11, 1587–1597 (2012)
F.D. Ibrahim, Preliminary studies on the physiological and pharmacological actions of the extract of Orobanche crenata. J. Egypt. Med. Assoc. 51, 939–948 (1968)
D. Abetov, Z. Mustapova, T. Saliev, D. Bulanin, K. Batyrbekov, C.P. Gilman, Novel small molecule inhibitors of cancer stem cell signaling pathways. Stem Cell Rev. 11, 909–918 (2015)
T. Ishiguro, H. Ohata, A. Sato, K. Yamawaki, T. Enomoto, K. Okamoto, Tumor-derived spheroids: relevance to cancer stem cells and clinical applications. Cancer Sci. 108, 283–289 (2017)
P.A. Bignone, K.Y. Lee, Y. Liu, G. Emilion, J. Finch, A.E. Soosay, F.M. Charnock, S. Beck, I. Dunham, A.J. Mungall, T.S. Ganesan, RPS6KA2, a putative tumour suppressor gene at 6q27 in sporadic epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncogene 26, 683–700 (2007)
R.C. Dregalla, J. Zhou, R.R. Idate, C.L. Battaglia, H.L. Liber, S.M. Bailey, Regulatory roles of tankyrase 1 at telomeres and in DNA repair: suppression of T-SCE and stabilization of DNA-PKcs. Aging (Albany N. Y.) 2, 691–708 (2010)
S.J. Scales, F.J. de Sauvage, Mechanisms of Hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 30, 303–312 (2009)
N. Gopalakrishnan, N.D. Sivasithamparam, H. Devaraj, Synergistic association of Notch and NFkappaB signaling and role of Notch signaling in modulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Biochimie 107 Pt B, 310–318 (2014)
M. Lauth, A. Bergstrom, T. Shimokawa, R. Toftgard, Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 8455–8460 (2007)
S. Pan, X. Wu, J. Jiang, W. Gao, Y. Wan, D. Cheng, D. Han, J. Liu, N.P. Englund, Y. Wang, S. Peukert, K. Miller-Moslin, J. Yuan, R. Guo, M. Matsumoto, A. Vattay, Y. Jiang, J. Tsao, F. Sun, A.C. Pferdekamper, S. Dodd, Tuntland T, W. Maniara, J.F. Kelleher, Y.M. Yao, M. Warmuth, J. Williams, M. Dorsch, Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective smoothened antagonist. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 1, 130–134 (2010)
P.B. Gupta, T.T. Onder, G. Jiang, K. Tao, C. Kuperwasser, R.A. Weinberg, E.S. Lander, Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 138, 645–659 (2009)
B.A. Kaipparettu, I. Kuiatse, B. Tak-Yee Chan, M. Benny Kaipparettu, A.V. Lee, S. Oesterreich, Novel egg white-based 3-D cell culture system. Biotechniques 45, 165–168 (2008) 170 – 161
Z. Darzynkiewicz, G. Juan, E. Bedner, Determining cell cycle stages by flow cytometry. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 1, 8.4.1–8.4.18 (1999)
R.P. Nagare, S. Sneha, S. Ramesh, T.S. Ganesan, Analysis of hematopoietic stem cells using a composite approach. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 109, 82–89 (2019)
Y.C. Wang, Y.T. Yo, H.Y. Lee, Y.P. Liao, T.K. Chao, P.H. Su, H.C. Lai, ALDH1-bright epithelial ovarian cancer cells are associated with CD44 expression, drug resistance, and poor clinical outcome. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 1159–1169 (2012)
S. Krishna Priya, K. Kumar, K.R. Hiran, M.R. Bindhu, R.P. Nagare, D.K. Vijaykumar, T.S. Ganesan, Expression of a novel endothelial marker, C-type lectin 14A, in epithelial ovarian cancer and its prognostic significance. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 22, 107–117 (2017)
S. Condello, C.A. Morgan, S. Nagdas, L. Cao, J. Turek, T.D. Hurley, and D. Matei, beta-Catenin-regulated ALDH1A1 is a target in ovarian cancer spheroids. Oncogene 34, 2297–2308 (2015)
S. Sneha, R.P. Nagare, P. Manasa, S. Vasudevan, A. Shabna, T.S. Ganesan, Analysis of human stem cell transcription factors. Cell. Reprogram. 21, 171–180 (2019)
H.G. Lee, S.J. Shin, H.W. Chung, S.H. Kwon, S.D. Cha, J.E. Lee, C.H. Cho, Salinomycin reduces stemness and induces apoptosis on human ovarian cancer stem cell. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 28, e14 (2017)
H.R. Maun, X. Wen, A. Lingel, F.J. de Sauvage, R.A. Lazarus, S.J. Scales, S.G. Hymowitz, Hedgehog pathway antagonist 5E1 binds hedgehog at the pseudo-active site. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 26570–26580 (2010)
O.H. Yilmaz, R. Valdez, B.K. Theisen, W. Guo, D.O. Ferguson, H. Wu, S.J. Morrison, Pten dependence distinguishes haematopoietic stem cells from leukaemia-initiating cells. Nature 441, 475–482 (2006)
M.C. Boelens, T.J. Wu, B.Y. Nabet, B. Xu, Y. Qiu, T. Yoon, D.J. Azzam, C. Twyman-Saint, B.Z. Victor, H. Wiemann, P.J. Ishwaran, J. Ter Brugge, J. Jonkers, Slingerland, A.J. Minn, Exosome transfer from stromal to breast cancer cells regulates therapy resistance pathways. Cell 159, 499–513 (2014)
L. Hernandez, M.K. Kim, L.T. Lyle, K.P. Bunch, C.D. House, F. Ning, A.M. Noonan, C.M. Annunziata, Characterization of ovarian cancer cell lines as in vivo models for preclinical studies. Gynecol. Oncol. 142, 332–340 (2016)
A.K. Mitra, D.A. Davis, S. Tomar, L. Roy, H. Gurler, J. Xie, D.D. Lantvit, H. Cardenas, F. Fang, Y. Liu, E. Loughran, J. Yang, M. Sharon Stack, R.E. Emerson, K.D. Cowden, V.B. Dahl, K.P. M, D. Nephew, Matei, J.E. Burdette, In vivo tumor growth of high-grade serous ovarian cancer cell lines. Gynecol. Oncol. 138, 372–377 (2015)
C.R. Cochrane, A. Szczepny, D.N. Watkins, J.E. Cain, Hedgehog signaling in the maintenance of cancer stem cells. Cancers (Basel) 7, 1554–1585 (2015)
V.J. Guen, T.E. Chavarria, C. Kroger, X. Ye, R.A. Weinberg, J.A. Lees, EMT programs promote basal mammary stem cell and tumor-initiating cell stemness by inducing primary ciliogenesis and Hedgehog signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114, E10532-E10539 (2017)
A. Ray, E. Meng, E. Reed, L.A. Shevde, R.P. Rocconi, Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates the growth of ovarian cancer spheroid forming cells. Int. J. Oncol. 39, 797–804 (2011)
P. Ozretic, D. Trnski, V. Musani, I. Maurac, D. Kalafatic, S. Oreskovic, S. Levanat, M. Sabol, Non-canonical Hedgehog signaling activation in ovarian borderline tumors and ovarian carcinomas. Int. J. Oncol. 51, 1869–1877 (2017)
A. Ciucci, I. De Stefano, V.G. Vellone, L. Lisi, C. Bottoni, G. Scambia, G.F. Zannoni, D. Gallo, Expression of the glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 (gli1) in advanced serous ovarian cancer is associated with unfavorable overall survival. PLoS One 8, e60145 (2013)
X. Li, W. Deng, S.M. Lobo-Ruppert, J.M. Ruppert, Gli1 acts through Snail and E-cadherin to promote nuclear signaling by beta-catenin. Oncogene 26, 4489–4498 (2007)
J. Li, J. Cai, S. Zhao, K. Yao, Y. Sun, Y. Li, L. Chen, R. Li, X. Zhai, J. Zhang, C. Jiang, GANT61, a GLI inhibitor, sensitizes glioma cells to the temozolomide treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 35, 184 (2016)
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 474, 609–615 (2011)
J. Zhang, Z.Y. Li, X.J. Duan, X.M. Fan, W.N. Liu, Y.H. Li, [Clinical significance of FOXM1 and Gli-1 protein expression in high-grade ovarian serous carcinoma]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 38, 904–908 (2016)
Q. Li, R.K. Lex, H. Chung, S.M. Giovanetti, Z. Ji, H. Ji, M.D. Person, J. Kim, S.A. Vokes, The pluripotency factor NANOG binds to GLI proteins and represses hedgehog-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 7171–7182 (2016)
M. Ding, X. Wang, Antagonism between Hedgehog and Wnt signaling pathways regulates tumorigenicity. Oncol. Lett. 14, 6327–6333 (2017)
J. Reda, J. Vachtenheim, K. Vlckova, P. Horak, J. Vachtenheim Jr., L. Ondrusova, Widespread expression of hedgehog pathway components in a large panel of human tumor cells and inhibition of tumor growth by GANT61: implications for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, (2018)
A. Po, M. Silvano, E. Miele, C. Capalbo, A. Eramo, V. Salvati, M. Todaro, Z.M. Besharat, G. Catanzaro, D. Cucchi, S. Coni, L. Di Marcotullio, G. Canettieri, A. Vacca, G. Stassi, E. De Smaele, M. Tartaglia, I. Screpanti, R. De Maria, E. Ferretti, Noncanonical GLI1 signaling promotes stemness features and in vivo growth in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 36, 4641–4652 (2017)
N. Li, S. Truong, M. Nouri, J. Moore, N. Al Nakouzi, A.A. Lubik, R. Buttyan, Non-canonical activation of hedgehog in prostate cancer cells mediated by the interaction of transcriptionally active androgen receptor proteins with Gli3. Oncogene 37, 2313–2325 (2018)
A. Sanchez-Danes, J.C. Larsimont, M. Liagre, E. Munoz-Couselo, G. Lapouge, A. Brisebarre, C. Dubois, M. Suppa, V. Sukumaran, V. Del Marmol, J. Tabernero, C. Blanpain, A slow-cycling LGR5 tumour population mediates basal cell carcinoma relapse after therapy. Nature 562, 434–438 (2018)
J. Rodriguez-Blanco, L. Pednekar, C. Penas, B. Li, V. Martin, J. Long, E. Lee, W.A. Weiss, C. Rodriguez, N. Mehrdad, D.M. Nguyen, N.G. Ayad, P. Rai, A.J. Capobianco, D.J. Robbins, Inhibition of WNT signaling attenuates self-renewal of SHH-subgroup medulloblastoma. Oncogene 36, 6306–6314 (2017)
J. Gao, S. Graves, U. Koch, S. Liu, V. Jankovic, S. Buonamici, A. El Andaloussi, S.D. Nimer, B.L. Kee, R. Taichman, F. Radtke, I. Aifantis, Hedgehog signaling is dispensable for adult hematopoietic stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell 4, 548–558 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and a research fellowship for Ms. S. Sneha was provided by the University Grants Commission (UGC). We would like to extend our gratitude to Dr. V. Sridevi and Dr. Ujwala for identifying the patients and for the tissues used in the experiments, and the staff and nurses for collecting malignant ascites samples from patients under aseptic conditions. We acknowledge Dr. Priya, Dr. Hascitha and Dr. Hemavathi, Department of Molecular Oncology, for the flow cytometry experiments and the Department of Pathology, Epidemiology and Statistics for their help and support. We also thank Dr. Srividhya and Ms. Kayalvizhi, flow cytometry core facility, IIT-Madras, for the cell sorting experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors provided critical feedback and helped in shaping the research, results and analyses, and commented on the manuscript. SS contributed substantially to the concept and design, performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted data and drafted the manuscript. RPN optimized flow cytometry analysis, collected clinical data of patients for immunohistochemistry experiments and helped in critical analysis of the data and interpretation of the results. CS and MG contributed in designing the biochemical studies and provided experimental suggestions. SK helped in optimizing the immunohistochemistry experiments and in SPSS analyses, while RB performed the xenograft study. KM and SS contributed in procuring tissue sections and scoring the slides of the immunohistochemistry experiments. TSG conceived the original idea, critically reviewed and edited all versions of the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.50 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sneha, S., Nagare, R.P., Sidhanth, C. et al. The hedgehog pathway regulates cancer stem cells in serous adenocarcinoma of the ovary. Cell Oncol. 43, 601–616 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00504-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00504-w