Abstract
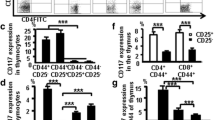
The aim of this paper is to explore the effects of transfection of Foxp3 gene on the phenotype and function of naive CD4+ T cells. The pMSCV-Foxp3 retroviral vector encoding Foxp3 gene was transduced into the PT67 packaging cell line. Virus-containing supernatant was applied to differentiate CD4+CD25− T cells. The resulting cells were sorted with flow cytometry. The expressions of CD25, CD127, CTLA-4 and the proliferation of transfected T cells were examined. The effect of transfected CD4+ T cells on the proliferation and cytokine production of CD4+CD25− T cells was examined. Foxp3-gene transfected CD4+ T cells could express Foxp3 and transfection of Foxp3 gene up-regulated the expressions of CD25 and CTLA-4, but down-regulated CD127 expression. After transfection, the proliferation of CD4+ T cells was eliminated. Transfected T cells inhibited the proliferation of CD4+CD25− T cells. CD4+CD25− T cells acquired a regulatory phenotype and function after it was transduced with the Foxp3 gene. This suggested a key role of Foxp3 in the generation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Von Boehmer H. Mechanisms of suppression by suppressor T cells. Nat Immunol, 2005, 6(4): 338–344
Gavin M A, Rasmussen J P, Fontenot J D, Vasta V, Manganiello V C, Beavo J A, Rudensky A Y. Foxp3-dependent programme of regulatory T-cell differentiation. Nature, 2007, 445(7129): 771–775
Tang Q, Bluestone J A. The Foxp3+ regulatory T cell: a jack of all trades, master of regulation. Nat Immunol, 2008, 9(3): 239–244
Kajsa W, Shimon S. Regulatory T cells as potential immunotherapy in allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2006, 6(6): 482–488
Williams L M, Rudensky A Y. Maintenance of the Foxp3-dependent developmental program in mature regulatory T cells requires continued expression of Foxp3. Nat Immunol, 2007, 8(3): 277–284
Wan Y Y, Flavell R A. Regulatory T-cell functions are subverted and converted owing to attenuated Foxp3 expression. Nature, 2007, 445(7129): 766–770
Pillai V, Ortega S B, Wang C K, Karandikar N J. Transient regulatory T-cells: A state attained by all activated human Tcells. Clin Immunol, 2007, 123(1): 18–29
Wang J, Ioan-Facsinay A, van der Voort E I, Huizinga T W, Toes R E. Transient expression of FOXP3 in human activated nonregulatory CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol, 2007, 37(1): 129–138
Bruder D, Probst-Kepper M, Westendorf A M, Geffers R, Beissert S, Loser K, Von Boehmer H, Buer J, Hansen W. Frontline: Neuropilin-1: a surface marker of regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol, 2004, 34(3): 623–630
Zheng Y, Josefowicz S Z, Kas A, Chu T T, Gavin M A, Rudensky A Y. Genome-wide analysis of Foxp3 target genes in developing and mature regulatory T cells. Nature, 2007, 445(7130): 936–940
Fontenot J D, Gavin M A, Rudensky A Y. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol, 2003, 4(4): 330–336
Zheng Y, Rudensky A Y. Foxp3 in control of regulatory T cell lineage. Nat Immunol, 2007, 8(5): 457–462
Vignali D A, Collison L W, Workman C J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol, 2008, 8(8): 523–532
Barnes P J. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol, 2008, 8(3): 183–192
Campbell D J, Ziegler S F. FOXP3 modifies the phenotypic and functional properties of regulatory T cells. Nat Rev Immunol, 2007, 7(4): 305–310
Xystrakis E, Boswell S E, Hawrylowicz C M. T regulatory T cells and the control of allergic disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2006, 6(2): 121–133
Lin Y L, Shieh C C, Wang J Y. The functional insufficiency of human CD4+CD25high T-regulatory cells in allergic asthma is subjected to TNF-α modulation. Allergy, 2008, 63(1): 67–74
Hartl D, Koller B, Mehlhorn A T, Reinhardt D, Nicolai T, Schendel D J, Griese M, Krauss-Etschmann S. Quantitative and functional impairment of pulmonary CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cells in pediatric asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2007, 119(5): 1258–1266
Leech M D, Benson R A, De Vries A, Fitch P M, Howie S E. Resolution of Der p1-induced allergic airway inflammation is dependent on CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory cells. J Immunol, 2007, 179(10): 7050–7058
Holgate S T, Polosa R. Treatment strategies for allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol, 2008, 8(3): 218–230
Sun K, Lin K, Wu K, Wang C. Effects and mechanism of CD4+ CD25+ T cells on the airway inflammation of asthmatic mice. Zhonghua Jiehe He Huxi Zazhi, 2006, 29(2): 109–112 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Acta Academiae Medicinae Militaris Tertiae, 2008, 30(3): 186–188 [译自: 第三军医大学学报]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Bi, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Changes of phenotype and function of human CD4+ CD25− T cells induced by transfection of Foxp3. Front. Med. China 2, 366–369 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0070-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0070-6