Abstract
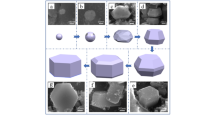
Al-TiB2 in situ composites are important class of structural materials where the TiB2 particles are grown in situ within the aluminum matrix. The true morphology of the in situ grown TiB2 particles is not clear as particles with different morphologies are reported in the literature. The present work reports the three-dimensional morphologies and habits of in situ grown TiB2 particles in aluminum-based composites by the halide slat method. TiB2 particles were grown in molten aluminum by the reaction of two fluoride salts; K2TiF6 and KBF4. The TiB2 particles exhibited truncated hexagonal pyramid morphology. It was found that the pyramidal planes are morphologically more important and the crystal is bounded by the fast-growing faces. The habit (predominant facet plane) and growth morphology of the crystals was analyzed through the kinetic-geometric model. The ratio of the relative growth rates of different forms was calculated. The pyramidal form can increase its size by growing faster than the adjacent faces, whereas the basal and prism forms decrease in size if they grow faster than the adjacent faces. We show that depending on the interfacial angle geometry, a given face may or may not enlarge, and the face needs not always constrain the crystal with the slowest growth rate. Both the theoretical analysis and the experiments demonstrate the particles to have hexagonal pyramidal morphology. Finally, the present work explains how past observations suggesting the TiB2 particles to have hexagonal, elongated hexagonal, rectangular, and cubic habits are due to the two-dimensional sections of the truncated hexagonal pyramid.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Chawla and K.K. Chawla, Metal Matrix Composites, Springer, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-9548-2
S.C. Tjong and Z.Y. Ma, Microstructural and Mechanical Characteristics of In Situ Metal Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2000, 29, p 49–113.
R.G. Munro, Materials Properties of Titanium Diboride, J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol., 2000, 105, p 709–720.
N.E. Mahallawy, M.A. Taha, A.E.W. Jarfors and H. Fredriksson, On the Reaction Between Aluminium, K2TiF6 and KBF4, J. Alloys. Comp., 1999, 292, p 221–229.
J. Fjellstedt and A.E.W. Jarfors, On the Precipitation of TiB2 in Aluminum Melts from the Reaction with KBF4 and K2TiF6, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 413–415, p 527–532.
Z. Liu, Q. Han, Z. Huang and J. Xing, A Quantitative Study of the Synthesis of TiB2 Particles via Salts-Metal Reaction at Different Temperatures, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, 47, p 916–926.
L. Lu, M.O. Lai and F.L. Chen, Al-4 wt.% Cu Composite Reinforced with In-Situ TiB2 Particles, Acta Mater., 1997, 45, p 4297–4309.
K.L. Tee, L. Lu and M.O. Lai, Synthesis of In Situ Al-TiB2 Composites Using Stir Cast Route, Compos. Struct., 1999, 47, p 589–593.
C. Wang, M. Wang, B. Yu, D. Chen, P. Qin, M. Feng and Q. Dai, The Grain Refinement Behaviour of TiB2 Particles Prepared with In Situ Technology, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 459, p 238–243.
I.G. Watson, M.F. Forster, P.D. Lee, R.J. Dashwood, R.W. Hamilton and A. Chirazi, Investigation of the Clustering Behaviour of Titanium Diboride Particles in Aluminium, Compos. A, 2005, 36, p 1177–1187.
J. Yuan, G. Yao, S. Pan, N. Murali and X. Li, Size Control of In Situ Synthesized TiB2 Particles in Molten Aluminium, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, 52, p 2657–2666.
L. Peng-Ting, L. Yun-Guo, N. Jin-Feng and L. Xiang-Fa, Influence of Forming Process on Three-Dimensional Morphology of TiB2 Particles in Al-Ti-B Alloys, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2012, 22, p 564–570.
I. Higashi and T. Atoda, Growth of Titanium Diboride Single Crystals in Molten Aluminium, J. Cryst. Growth, 1970, 7, p 251–253.
J. Sun, X. Wang, L. Guo, X. Zhang and H. Wang, Synthesis of Nanoscale Spherical TiB2 Particles in Al Matrix by Regulating Sc Contents, J. Mater. Res., 2019, 34, p 1258–1265.
C.F. Feng and L. Froyen, Microstructures of In Situ Al/TiB2 MMCs Prepared by a Casting Route, J. Mater. Sci., 2000, 35, p 837–850.
S. Ji, F. Amirkhanlu, A. Mostaed and R. Beanland, Atomic Structure and Interface Chemistry in a High-Stiffness and High-Strength Al-Si-Mg/TiB2 Nanocomposite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 763, p 138072.
Z.Y. Chen, Y.Y. Chen, Q. Shu and G.Y. An, Solidification and Interfacial Structure of In Situ Al-4.5Cu/TiB2 Composite, J. Mater. Sci., 2000, 35, p 5605–5608.
A.A. Abdel-Hamid, S. Hamar-Thibault and R. Hamar, Crystal Morphology of the Compound TiB2, J. Cryst. Growth, 1985, 71, p 744–750.
D. Yadav and R. Bauri, Friction Stir Processing of Al-TiB2 In Situ Composite: Effect on Particle Distribution, Microstructure and Properties, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 1116–1124.
M.I. Kozlovskii, Kinetics of Crystallization at Constant Temperature and Supersaturation, Kristallografiya, 1957, 2, p 760–769.
J. Prywer, Kinetic and Geometric Determination of the Growth Morphology of Bulk Crystals: Recent Developments, Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact., 2005, 50, p 1–38.
M. Szurgot and J. Prywer, Growth Velocities and Disappearance of Faces of Crystals, Cryst. Res. Technol., 1991, 26, p 147–153.
J. Prywer, Crystal Faces Existence and Morphological Stability from a Crystallographic Perspective, Cryst. Growth Des., 2003, 3, p 593–598.
J. Prywer, Morphological Importance of Crystal Faces in Connection with Growth Rates and Crystallographic Structure of Crystal, Cryst. Growth Des., 2002, 2, p 281–286.
J. Prywer, Effect of Crystal Geometry on Disappearance of Slow-Growing Faces, J. Cryst. Growth, 2001, 224, p 134–144.
K. Sugiyama, S. Iwakoshi, S. Mtojima and Y. Takahashi, Chemical Vapour Growth of Titanium Diboride by a Modified Hot Wire Method, J. Cryst. Growth, 1978, 43, p 533–536.
P. Hartman and P. Bennema, The attachment energy as a habit controlling factor: I. Theoretical considerations, J. Cryst. Growth, 1980, 49, p 145–156.
G. Liu, K. Chen, H. Zhou, J. Tian, C. Pereira and J.M.F. Ferreira, Fast Shape Evolution of TiN Microcrystals in Combustion Synthesis, Cryst. Growth Des., 2006, 6, p 2404–2411.
N. He, J. Zhang, Y. Jin, F. Han, X. Zhang and G. Chen, Preparation, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of in-situ TiB2/Al Composites by Mechanical Stirring and Subsequent Ultrasonic Treatment, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6, p 116553.
A. Bravais, Etudes Cristallographiques, Gauthier-Villard, Paris, 1913.
G. Friedel, Leçon de Cristallographie, Hermann, Paris, 1911.
J.D.H. Donnay and D. Harker, A New Law of Crystal Morphology Extending the Law of Bravais, Am Mineral, 1937, 22, p 446–467.
J. Prywer and M.J. Krasiński, Review: Growth Morphology of Crystals from Kinetic and Geometric Perspective, Cryst. Res. Technol., 2007, 42, p 1190–1201.
J. Prywer, On the Crystal Geometry Influence on the Growth of Fast-Growing Surfaces, J. Phys. Chem. Sol., 2002, 63, p 491–499.
J. Sun, X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, N. Ma and H. Wang, Effect of Alloy Elements on the Morphology Transformation of TiB2 Particles in Al matrix, Micron, 2015, 70, p 21–25.
W.K. Burton, N. Cabrera and F.C. Frank, The Growth of Crystals and the Equilibrium Structure of their Surfaces, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond., 1951, 243(866), p 299–358.
J. Prywer, Effect of Supersaturation on Evolution of Crystal Faces - Theoretical Analysis, J. Cryst. Growth, 2006, 289, p 630–638.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, C., Prywer, J. & Yadav, D. On the Three-Dimensional Morphology of In Situ Grown TiB2 Particles in Molten Aluminum. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 9396–9404 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07779-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07779-0