Abstract
Background
It is known that there are insufficient prognostic factors for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It was reported that PD-L1 was a prognostic factor for NSCLC,and c-Myc regulated the expression of PD-L1. Herein, we investigated c-Myc and PD-L1 expression and their association with overall survival (OS) in NSCLC.
Methods
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens were obtained from 128 patients with surgically resected primary NSCLC. Immunohistochemistry was used to assess the expression of PD-L1 and c-Myc in this study. Pearson’s Chi squared test or Fisher’s exact test was used to analyze the correlation of the expression of PD-L1 and c-Myc with clinicopathologic features. The relationship between OS and the expression of PD-L1 and c-Myc was evaluated by the Kaplan–Meier method and Cox proportional hazards model, respectively.
Results
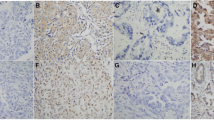
Positive expression of PD-L1 was detected in 59 patients (46.1%). Patients with negative expression of PD-L1 had remarkably longer OS than those with positive expression of PD-L1. The positive expression rate of c-Myc in NSCLC accounted for 58.6% (75/128) and its expression was significantly more frequent in males (p = 0.002) and patients with lymph node metastasis (p = 0.029). PD-L1 expression was positively correlated with c-Myc expression (r = 0.459, p < 0.001). The PD-L1 and c-Myc double-positive group had a worse prognosis than other subgroups (p < 0.05), and the PD-L1 and c-Myc double-negative group had a better OS than other subgroups (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Conjoint analysis of the expression of PD-L1 and c-Myc was a better prognostic approach for NSCLC patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbay EA, Koyama S, Carretero J, Altabef A, Tchaicha JH, Christensen CL et al (2013) Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov 3(12):1355–1363. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-13-0310
Atsaves V, Tsesmetzis N, Chioureas D, Kis L, Leventaki V, Drakos E et al (2017) PD-L1 is commonly expressed and transcriptionally regulated by STAT3 and MYC in ALK-negative anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 31(7):1633–1637. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.103
Casey SC, Tong L, Li Y, Do R, Walz S, Fitzgerald KN et al (2016) MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and PD-L1. Science 352(6282):227–231. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac9935
Chae YK, Pan A, Davis AA, Raparia K, Mohindra NA, Matsangou M et al (2016) Biomarkers for PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: is PD-L1 expression a good marker for patient selection? Clin Lung Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2016.03.011
Choueiri TK, Fay AP, Gray KP, Callea M, Ho TH, Albiges L et al (2014) PD-L1 expression in nonclear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 25(11):2178–2184. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu445
Cooper WA, Tran T, Vilain RE, Madore J, Selinger CI, Kohonen-Corish M et al (2015) PD-L1 expression is a favorable prognostic factor in early stage non-small cell carcinoma. Lung Cancer 89(2):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.05.007
Dang CV (1999) c-Myc target genes involved in cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol 19(1):1–11
Dang CV, O’Donnell KA, Zeller KI, Nguyen T, Osthus RC, Li F (2006) The c-Myc target gene network. Semin Cancer Biol 16(4):253–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.07.014
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M et al (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Guo R, Li Y, Wang Z, Bai H, Duan J, Wang S et al (2019) HIF-1alpha and NF-kappaB play important roles in regulating PD-L1 expression by EGFR mutants in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13989
Henriksson M, Luscher B (1996) Proteins of the Myc network: essential regulators of cell growth and differentiation. Adv Cancer Res 68:109–182
Hino R, Kabashima K, Kato Y, Yagi H, Nakamura M, Honjo T et al (2010) Tumor cell expression of programmed cell death-1 ligand 1 is a prognostic factor for malignant melanoma. Cancer 116(7):1757–1766. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24899
Ilie M, Hofman V, Dietel M, Soria JC, Hofman P (2016) Assessment of the PD-L1 status by immunohistochemistry: challenges and perspectives for therapeutic strategies in lung cancer patients. Virchows Arch 468(5):511–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-016-1910-4
Iwakawa R, Kohno T, Kato M, Shiraishi K, Tsuta K, Noguchi M et al (2011) MYC amplification as a prognostic marker of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma identified by whole genome copy number analysis. Clin Cancer Res 17(6):1481–1489. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2484
Kim YH, Girard L, Giacomini CP, Wang P, Hernandez-Boussard T, Tibshirani R et al (2006) Combined microarray analysis of small cell lung cancer reveals altered apoptotic balance and distinct expression signatures of MYC family gene amplification. Oncogene 25(1):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208997
Kim EY, Kim A, Kim SK, Chang YS (2017) MYC expression correlates with PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 110:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.06.006
Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Azuma M, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita H, Nishimura M (2004) B7-H1 expression on non-small cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clinical Cancer Res 10(15):5094–5100. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-04-0428
Lin CY, Loven J, Rahl PB, Paranal RM, Burge CB, Bradner JE et al (2012) Transcriptional amplification in tumor cells with elevated c-Myc. Cell 151(1):56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.026
Melaiu O, Mina M, Chierici M, Boldrini R, Jurman G, Romania P et al (2017) PD-L1 is a therapeutic target of the bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 and combined with HLA class I, a promising prognostic biomarker in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 23(15):4462–4472. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-16-2601
Merelli B, Massi D, Cattaneo L, Mandala M (2014) Targeting the PD1/PD-L1 axis in melanoma: biological rationale, clinical challenges and opportunities. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 89(1):140–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.08.002
Mu CY, Huang JA, Chen Y, Chen C, Zhang XG (2011) High expression of PD-L1 in lung cancer may contribute to poor prognosis and tumor cells immune escape through suppressing tumor infiltrating dendritic cells maturation. Med Oncol 28(3):682–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9515-2
Nakashima N, Liu D, Huang CL, Ueno M, Zhang X, Yokomise H (2012a) Wnt3 gene expression promotes tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 76(2):228–234
Nakashima N, Liu D, Huang CL, Ueno M, Zhang X, Yokomise H (2012b) Wnt3 gene expression promotes tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 76(2):228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.10.007
Nesbit CE, Tersak JM, Prochownik EV (1999) MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene 18(19):3004–3016. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202746
Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, Hamada K, Kubo A, Kanehiro H et al (2007) Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the programmed death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(7):2151–2157. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2746
Pan ZK, Ye F, Wu X, An HX, Wu JX (2015) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of programmed cell death ligand1 (PD-L1) expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis 7(3):462–470. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.02.13
Rapp UR, Korn C, Ceteci F, Karreman C, Luetkenhaus K, Serafin V et al (2009) MYC is a metastasis gene for non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One 4(6):e6029. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006029
Sabo A, Kress TR, Pelizzola M, de Pretis S, Gorski MM, Tesi A et al (2014) Selective transcriptional regulation by Myc in cellular growth control and lymphomagenesis. Nature 511(7510):488–492. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13537
Schlosser I, Holzel M, Hoffmann R, Burtscher H, Kohlhuber F, Schuhmacher M et al (2005) Dissection of transcriptional programmes in response to serum and c-Myc in a human B-cell line. Oncogene 24(3):520–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208198
Schmidt LH, Kummel A, Gorlich D, Mohr M, Brockling S, Mikesch JH et al (2015) PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in NSCLC indicate a favorable prognosis in defined subgroups. PLoS One 10(8):e0136023. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136023
Seo AN, Yang JM, Kim H, Jheon S, Kim K, Lee CT et al (2014) Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of c-MYC copy number gain in lung adenocarcinomas. Br J Cancer 110(11):2688–2699. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.218
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62(1):10–29. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20138
Thompson RH, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Dong H, Lohse CM, Webster WS et al (2006) Tumor B7-H1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res 66(7):3381–3385. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4303
Velcheti V, Schalper KA, Carvajal DE, Anagnostou VK, Syrigos KN, Sznol M et al (2014) Programmed death ligand-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lab Invest 94(1):107–116. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2013.130
Wang A, Wang HY, Liu Y, Zhao MC, Zhang HJ, Lu ZY et al (2015) The prognostic value of PD-L1 expression for non-small cell lung cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 41(4):450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2015.01.020
Wu C, Zhu Y, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhang XG, Xu N (2006) Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1 ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Acta Histochem 108(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2006.01.003
Wu CT, Chen WC, Chang YH, Lin WY, Chen MF (2016) The role of PD-L1 in the radiation response and clinical outcome for bladder cancer. Sci Rep 6:19740. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19740
Zhou C, Tang J, Sun H, Zheng X, Li Z, Sun T et al (2017) PD-L1 expression as poor prognostic factor in patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 8(35):58457–58468. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17022
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81872308, 81500030), the National Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2017A030313573, 2016A030313272, 2016A030313277), project of the Suzhou industrial technology innovation (applied basic research of the people’s Livelihood technology and applied health care) (SYSD2016062), and Youth Project of Health and Family Planning Bureau of Suzhou High-tech Zone (2017Q005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Che, G., Zheng, X. et al. Expression and clinical significance of PD-L1 and c-Myc in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145, 2663–2674 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-03025-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-03025-8