Abstract
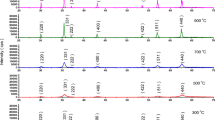
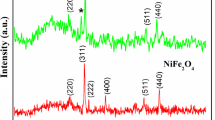
The effect of sodium chloride (NaCl) on the magnetism of nanopowders of the spinel ferrite (MgFe2O4) produced using a salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis was investigated. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was conducted to evaluate crystalline structure and phase composition of the synthesized materials. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to evaluate the particle size and morphology. Magnetic behavior was analyzed by measuring and analyzing the respective hysteresis loops using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The characterization showed that the presence of NaCl affects the phase composition, size, and dispersion of the nanoparticles, as well as their magnetic behavior. The theoretical size of the nanoparticles was calculated using the Scherrer equation, obtaining sizes of about 21.07 nm for the nanoparticles without salt, 5.90 nm for the sample salt content of 1.7 mol and 6.48 nm—for 3.4 mol. The synthesized nanoparticles showed a drastic decrease in coercivity field, remanence, and saturation with increasing salt content. Therefore, the salt content is a crucial parameter in controlling the morphology and magnetic properties of the nanoparticles obtained by the solution combustion route.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sikalidis, C., Advances in Ceramics: Synthesis and Characterization, Processing and Specific Applications, Croatia: InTech, 2011.
Mallesh, S., Prabu, D., and Srinivas, V., Thermal stability and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4@ZnO nanoparticles, AIP Adv., 2017, vol. 7, p. 56103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4975355
Chavarriaga, E.A., Lopera, A.A., Franco, V., Bergmann, C.P., and Alarcón, J., Gel combustion synthesis and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4, ZnFe2O4, and MgFe2O4 using 6-aminohexanoic acid as a new fuel, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2020, vol. 497, p. 166054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166054
Khot, V.M., Salunkhe, A.B., Thorat, N.D., Phadatare, M.R., and Pawar, S.H., Induction heating studies of combustion synthesized MgFe2O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2013, vol. 332, pp. 48–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.12.010
Kang, D., Yu, X., Ge, M., and Song, W., One-step fabrication and characterization of hierarchical MgFe2O4 microspheres and their application for lead removal, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2015, vol. 207, pp. 170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.01.023
Shakir, I., Sarfraz, M., Ali, Z., Aboud, M.F.A., and Agboola, P.O., Magnetically separable and recyclable graphene–MgFe2O4 nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic applications, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 660, pp. 450–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.11.055
Narsimulu, D., Rao, B.N., Venkateswarlu, M., Srinadhu, E.S., and Satyanarayana, N., Electrical and electrochemical studies of nanocrystalline mesoporous MgFe2O4 as anode material for lithium battery applications, Ceram. Int., 2016, vol. 42, pp. 16789–16797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.07.168
Reza Barati, M., Selomulya, C., and Suzuki, K., Particle size dependence of heating power in MgFe2O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia therapy application, J. Appl. Phys., 2014, vol. 115, p. 17B522. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4867751
Ensafi, A.A., Allafchian, A.R., and Mohammadzadeh, R., Characterization of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles as a novel electrochemical sensor: application for the voltammetric determination of ciprofloxacin, Anal. Sci., 2012, vol. 28, pp. 705–710. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.28.705
Chen, Q., Rondinone, A.J., Chakoumakos, B.C., and Zhang, Z.J., Synthesis of superparamagnetic MgFe2O4 nanoparticles by coprecipitation, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1999, vol. 194, pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00585-X
Das, H., Debnath, N., Toda, A., Kawaguchi, T., Sakamoto, N., Aono, H., Shinozaki, K., Suzuki, H., and Wakiya, N., Impact of precursor solution concentration to form superparamagnetic MgFe2O4 nanospheres by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique for magnetic thermotherapy, Adv. Powder Technol., 2017, vol. 28, pp. 1696–1703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.04.007
Kurian, J. and Mathew, M.J., Structural, optical and magnetic studies of CuFe2O4, MgFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal/solvothermal method, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2018, vol. 451, pp. 121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.10.124
Ali, N.A., Yahya, M.S., Mustafa, N.S., Sazelee, N.A., Idris, N.H., and Ismail, M., Modifying the hydrogen storage performances of NaBH4 by catalyzing with MgFe2O4 synthesized via hydrothermal method, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2019, vol. 44, pp. 6720–6727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.149
Akbari, S., Masoudpanah, S.M., Mirkazemi, S.M., and Aliyan, N., PVA assisted coprecipitation synthesis and characterization of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles, Ceram. Int., 2017, vol. 43, pp. 6263–6267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.030
Ajeesha, T., Ashwini, A., George, M., Manikandan, A., Mary, J.A., Slimani, Y., Almessiere, M.A., and Baykal, A., Nickel substituted MgFe2O4 nanoparticles via co-precipitation method for photocatalytic applications, Phys. B Condens. Matter., 2021, vol. 606, p. 412660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.412660
Heidari, P. and Masoudpanah, S.M., Structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 powders synthesized by solution combustion method: the effect of fuel type, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, vol. 9, pp. 4469–4475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.02.07
Rúbia, Y.S.Z., Claudir Jr, G.K., Annelise, K.A., and Carlos, P.B., Influence of the fuel composition and the fuel/oxidizer ratio on the combustion solution synthesis of MgFe2O4 catalyst nanoparticles, FME Trans., 2018, vol. 46, pp. 157–164. https://doi.org/10.5937/fmet1802157Z
Fan, H.-T., Liu, X.-G., Xing, X.-J., Li, B., Wang, K., Chen, S.-T., Wu, Z., and Qiu, D.-F., Ordered mesoporous silica cubic particles decorated with silver nanoparticles: a highly active and recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol, Dalton Trans., 2019, vol. 48, pp. 2692–2700. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8DT04663H
Thoda, O., Xanthopoulou, G., Vekinis, G., and Chroneos, A., Review of recent studies on solution combustion synthesis of nanostructured catalysts, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2018, vol. 20, p. 1800047. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201800047
Deganello, F. and Tyagi, A.K., Solution combustion synthesis, energy and environment: Best parameters for better materials, Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater., 2018, vol. 64, pp. 23–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2018.03.001
Hossain, M.K., Kecsenovity, E., Varga, A., Molnár, M., Janáky, C., and Rajeshwar, K., Solution combustion synthesis of complex oxide semiconductors, Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 2018, vol. 27, pp. 129–140. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386218030032
Rai, A.K., Thi, T.V., Gim, J., and Kim, J., Combustion synthesis of MgFe2O4/graphene nanocomposite as a high-performance negative electrode for lithium ion batteries, Mater. Charact., 2014, vol. 95, pp. 259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2014.06.024.
Nguyen, L.T.T., Nguyen, L.T.H., Manh, N.C., Quoc, D.N., Quang, H.N., Nguyen, H.T.T., Nguyen, D.C., and Bach, L.G., A facile synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles via the solution combustion method, J. Chem., 2019, vol. 2019, p. 3428681. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3428681
He, A., Lu, R., Wang, Y., Xiang, J., Li, Y., and He, D., Adsorption characteristic of congo red onto magnetic MgFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared via the solution combustion and gel calcination process, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2017, vol. 17, pp. 3967–3974. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.13091
Patil, K.C., Hegde, M.S., Rattan, T., and Aruna, S.T., Chemistry of Nanocrystalline Oxide Materials: Combustion Synthesis, Properties and Applications. World Scientific, 2008, 364 p. https://doi.org/10.1142/6754
Chen, W., Li, F., Yu, J., and Liu, L., A facile and novel route to high surface area ceria-based nanopowders by salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2006, vol. 133, pp. 151–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2006.06.020
Chen, W., Hong, J., and Li, Y., Facile fabrication of perovskite single-crystalline LaMnO3 nanocubes via a salt-assisted solution combustion process, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, vol. 484, pp. 846–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.05.059
Yang, J., Li, X., Deng, X., Huang, Z., and Zhang, Y., Salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles and photocatalytic activity with TiO2 (P25) as nanocomposite, J. Ceram. Soc. Japan., 2012, vol. 120, pp. 579–583. https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.120.579
Chen, Y., Yang, J., Wang, X., Feng, F., Zhang, Y., and Tang, Y., Synthesis YFeO3 by salt-assisted solution combustion method and its photocatalytic activity, J. Ceram. Soc. Japan, 2014, vol. 122, pp. 146–150. https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.122.146
Zhong, X., Yang, J., Chen, Y., Qiu, X., and Zhang, Y., Synthesis of magnetically separable MnFe2O4 nanocrystals via salt-assisted solution combustion method and their utilization as dye adsorbent, J. Ceram. Soc. Japan, 2015, vol. 123, pp. 394–398. https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.123.394
Lopera, A.A., Chavarriaga, E.A., Zuluaga, B., Marin, S., Giraldo, G.O., Estupiñan, H.A., Zapata, V., and Garcia, C.P., Effect of salt concentration on the electrical and morphological properties of calcium phosphates obtained via microwave-induced combustion synthesis, Adv. Powder Technol., 2017, vol. 28, pp. 2787–2795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.08.007
Lee, M.K. and Kang, S., A study of salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis of magnesium aluminate and sintering behaviour, Ceram. Int., 2019, vol. 45, pp. 6665–6672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.155
Biglari, Z., Alamolhoda, S., and Masoudpanah, S.M., Salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis of Ni and Ni/NiO powders, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn., 2019, vol. 32, pp. 3321–3327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-5100-x
Abbasian, A.R. and Rahmani, M., Salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis of nanostructured ZnFe2O4–ZnS powders, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2020, vol. 111, p. 107629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2019.107629
Aali, H., Baygi, N.J., Mollazadeh, S., and Khaki, J.V., Improving the physicochemical properties of NaCl-assisted solution combustion synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles by controlling the thermodynamics of the process, Ceram. Int., 2021, vol. 47, pp. 19315–19327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.233
Abbasian, A.R., Mahvary, A., and Alirezaei, S., Salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis of NiFe2O4: Effect of salt type, Ceram. Int., 2021, vol. 47, pp. 23794–23802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.086
Chavarriaga, E.A., Lopera, A.A., Wermuth, T.B., Arcaro, S., García, C., Alarcón, J., and Bergmann, C.P., Superparamagnetic MnFe2O4 ferrite by gel combustion synthesis using TRIS as a fuel: Influence of oxidizer to fuel ratio, Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 2021, vol. 30, pp. 73–80. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386221020059
Manukyan, K.V, Cross, A., Roslyakov, S., Rouvimov, S., Rogachev, A.S., Wolf, E.E., and Mukasyan, A.S., Solution combustion synthesis of nano-crystalline metallic materials: Mechanistic studies, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, vol. 117, pp. 24417–24427. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp408260m
Huang, Y., Tang, Y., Wang, J., and Chen, Q., Synthesis of MgFe2O4 nanocrystallites under mild conditions, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2006, vol. 97, pp. 394–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2005.08.035
Levy, D., Diella, V., Dapiaggi, M., Sani, A., Gemmi, M., and Pavese, A., Equation of state, structural behaviour and phase diagram of synthetic MgFe2O4 as a function of pressure and temperature, Phys. Chem. Miner., 2004, vol. 31, pp. 122–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00269-004-0380-4/METRICS
Jain, I.P., Hydrogen the fuel for 21st century, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, vol. 34, pp. 7368–7378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.05.093
Inoue, M. and Hirasawa, I., The relationship between crystal morphology and XRD peak intensity on CaSO4·2H2O, J. Cryst. Growth., 2013, vol. 380, pp. 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2013.06.017
Padhan, A.M., Rajaitha, P.M., Nayak, S., Hajra, S., Sahu, M., Jagličić, Z., Koželj, P., and Kim, H.J., Synthesis and application of mixed-spinel magnesioferrite: structural, vibrational, magnetic, and electrochemical sensing properties, Mater. Chem. Front., 2022, vol. 7, pp. 72–84. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2QM00628F
Chandradass, J., Jadhav, A.H., Kim, K.H., and Kim, H., Influence of processing methodology on the structural and magnetic behavior of MgFe2O4 nanopowders, J. Alloys Compd., 2012, vol. 517, pp. 164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.12.071
Tripathi, V.K. and Nagarajan, R., Magnetically separable, bifunctional catalyst MgFe2O4 obtained by epoxide mediated synthesis, Adv. Powder Technol., 2016, vol. 27, pp. 1251–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.04.013
Zhang, X., Jiang, W., Song, D., Sun, H., Sun, Z., and Li, F., Salt-assisted combustion synthesis of highly dispersed superparamagnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, vol. 475, pp. L34–L37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.131
Naaz, F., Dubey, H.K., Kumari, C., and Lahiri, P., Structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 nanopowder synthesized via co-precipitation route, SN Appl. Sci., 2020, vol. 2, p. 808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2611-9
Funding
The authors acknowledge the funding of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the program promotion of scientific and technological cooperation with Colombia (project 01DN21002).
J.G.R. and R.M. Acknowledge suport from Facultad de Ciencias y Vicerrectoría de Investigaciones Universidad de los Andes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Orozco, Y., Betancur, A., Chavarriaga, E. et al. Influence of NaCl on Magnetic Properties of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gel Combustion. Int. J Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth. 32, 139–149 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3103/S106138622302005X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S106138622302005X