Abstract
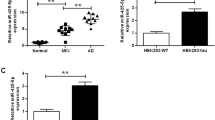
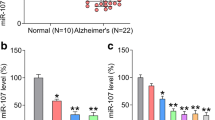
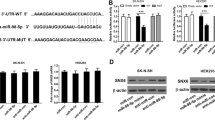
The production of amyloid β (Aβ) and tau hyperphosphorylation have been identified as key processes in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis. MiR-539-5p has been found to be abnormally expressed in brain tissue; however, the functional role of miR-539-5p in the pathogenesis of AD remains unclear. In our study, we found that the expression of miR-539-5p was significantly downregulated in humans and mice with AD and was negatively correlated with expression of APP, caveolin 1, and GSK-3β. Moreover, upregulation of miR-539-5p inhibited Aβ accumulation, tau phosphorylation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis and improved memory ability in AD mice. Furthermore, by using bioinformatics tool and dual-luciferase reporter assay, APP, Caveolin 1, and GSK-3β were confirmed as direct targets of miR-539-5p. In addition, the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway can be regulated by miR-539-5p. In conclusion, this study provided a novel insight into the pathologic mechanism of AD by identifying that miR-539-5p plays a neuroprotective role in AD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bekris LM, Leverenz JB (2015) The biomarker and therapeutic potential of miRNA in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis Manag 5:61–74. https://doi.org/10.2217/nmt.14.52
Birnbaum JH, Wanner D, Gietl AF, Saake A, Kundig TM et al (2018) Oxidative stress and altered mitochondrial protein expression in the absence of amyloid-beta and tau pathology in iPSC-derived neurons from sporadic Alzheimer’s disease patients. Stem Cell Res 27:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2018.01.019
Bondi MW, Edmonds EC, Salmon DP (2017) Alzheimer's disease: past, present, and future. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 23:818–831. https://doi.org/10.1017/s135561771700100x
Brion JP (1998) Neurofibrillary tangles and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Neurol 40:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1159/000007969
Brody DL, Jiang H, Wildburger N, Esparza TJ (2017) Non-canonical soluble amyloid-beta aggregates and plaque buffering: controversies and future directions for target discovery in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 9:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-017-0293-3
Cheignon C, Tomas M, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Faller P, Hureau C et al (2018) Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol 14:450–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.10.014
Chen Z, Zhong C (2014) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 30:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1423-y
Denk J, Boelmans K, Siegismund C, Lassner D, Arlt S et al (2015) MicroRNA profiling of CSF reveals potential biomarkers to detect Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 10:e0126423. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126423
Femminella GD, Ferrara N, Rengo G (2015) The emerging role of microRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Physiol 6:40. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00040
Feng MG, Liu CF, Chen L, Feng WB, Liu M et al (2018) MiR-21 attenuates apoptosis-triggered by amyloid-beta via modulating PDCD4/ PI3K/AKT/GSK-3beta pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Biomed Pharmacother 101:1003–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.043
Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L et al (2005) Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet 366:2112–2117. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67889-0
Fu H, Rodriguez GA, Herman M, Emrani S, Nahmani E et al (2017) Tau pathology induces excitatory neuron loss, grid cell dysfunction, and spatial memory deficits reminiscent of early Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 93:533–541.e535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.023
Garcia-Font N, Hayour H, Belfaitah A, Pedraz J, Moraleda I et al (2016) Potent anticholinesterasic and neuroprotective pyranotacrines as inhibitors of beta-amyloid aggregation, oxidative stress and tau-phosphorylation for Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur J Med Chem 118:178–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.04.023
Guo R, Fan G, Zhang J, Wu C, Du Y et al (2017) A 9-microRNA signature in serum serves as a noninvasive biomarker in early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 60:1365–1377. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-170343
Guo J, Cai H, Liu X, Zheng J, Liu Y et al (2018) Long Non-coding RNA LINC00339 stimulates glioma vasculogenic mimicry formation by regulating the miR-539-5p/TWIST1/MMPs axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 10:170–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.11.011
Hammond SM (2015) An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 87:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.001
Head BP, Peart JN, Panneerselvam M, Yokoyama T, Pearn ML et al (2010) Loss of caveolin-1 accelerates neurodegeneration and aging. PLoS One 5:e15697. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015697
Hebert LE, Weuve J, Scherr PA, Evans DA (2013) Alzheimer disease in the United States (2010-2050) estimated using the 2010 census. Neurology 80:1778–1783. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828726f5
Hu L, Liu Y, Wang B, Wu Z, Chen Y et al (2019) MiR-539-5p negatively regulates migration of rMSCs induced by Bushen Huoxue decoction through targeting Wnt5a. Int J Med Sci 16:998–1006. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.33437
Jazvinscak Jembrek M, Hof PR, Simic G (2015) Ceramides in Alzheimer’s disease: key mediators of neuronal apoptosis induced by oxidative stress and abeta accumulation. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:346783–346717. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/346783
Jhang KA, Park JS, Kim HS, Chong YH (2017) Resveratrol ameliorates tau hyperphosphorylation at Ser396 site and oxidative damage in rat hippocampal slices exposed to vanadate: implication of ERK1/2 and GSK-3beta signaling cascades. J Agric Food Chem 65:9626–9634. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03252
Jian C, Lu M, Zhang Z, Liu L, Li X et al (2017) miR-34a knockout attenuates cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice through inhibition of the amyloidogenic processing of APP. Life Sci 182:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.05.023
Kang Q, Xiang Y, Li D, Liang J, Zhang X et al (2017) MiR-124-3p attenuates hyperphosphorylation of tau protein-induced apoptosis via caveolin-1-PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta pathway in N2a/APP695swe cells. Oncotarget 8:24314–24326. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15149
Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM (2018) Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur J Neurol 25:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13439
Lukiw WJ (2007) Micro-RNA speciation in fetal, adult and Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. Neuroreport 18:297–300. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e3280148e8b
Ma RH, Zhang Y, Hong XY, Zhang JF, Wang JZ et al (2017) Role of microtubule-associated protein tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 37:307–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-017-1732-x
Masters CL, Multhaup G, Simms G, Pottgiesser J, Martins RN et al (1985) Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J 4:2757–2763
Muche A, Arendt T, Schliebs R (2017) Oxidative stress affects processing of amyloid precursor protein in vascular endothelial cells. PLoS One 12:e0178127. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178127
O’Brien RJ, Wong PC (2011) Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 34:185–204. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113613
Prema A, Justin Thenmozhi A, Manivasagam T, Mohamed Essa M, Guillemin GJ (2017) Fenugreek seed powder attenuated aluminum chloride-induced tau pathology, oxidative stress, and inflammation in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 60:S209–s220. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-161103
Qiu C, Kivipelto M, von Strauss E (2009) Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease: occurrence, determinants, and strategies toward intervention. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 11:111–128
Rajasekhar K, Chakrabarti M, Govindaraju T (2015) Function and toxicity of amyloid beta and recent therapeutic interventions targeting amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Commun (Camb) 51:13434–13450. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc05264e
Rajmohan R, Reddy PH (2017) Amyloid-beta and phosphorylated tau accumulations cause abnormalities at synapses of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurons J Alzheimers Dis 57:975–999. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-160612
Reitz C, Brayne C, Mayeux R (2011) Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 7:137–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.2
Riancho J, Vazquez-Higuera JL, Pozueta A, Lage C, Kazimierczak M et al (2017) MicroRNA profile in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: analysis of miR-9-5p and miR-598 in raw and exosome enriched cerebrospinal fluid samples. J Alzheimers Dis 57:483–491. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-161179
Sharma S, Verma S, Kapoor M, Saini A, Nehru B (2016) Alzheimer’s disease like pathology induced six weeks after aggregated amyloid-beta injection in rats: increased oxidative stress and impaired long-term memory with anxiety-like behavior. Neurol Res 38:838–850. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2016.1209337
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y, Yu Q (2015) MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Oncotarget 6:8474–8490. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3523
Sun J, Zhang X, Wang C, Teng Z, Li Y (2017) Curcumin decreases hyperphosphorylation of tau by down-regulating caveolin-1/GSK-3beta in N2a/APP695swe cells and APP/PS1 double transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mice. Am J Chin Med 45:1667–1682. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0192415x17500902
Tamaoka A (2011) Alzheimer’s disease: definition and National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke and the Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association (NINCDS-ADRDA). Nihon Rinsho 69(Suppl 10 Pt 2):240–245
Trushina E, Du Charme J, Parisi J, McMurray CT (2006) Neurological abnormalities in caveolin-1 knock out mice. Behav Brain Res 172:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2006.04.024
Vishnoi A, Rani S (2017) MiRNA biogenesis and regulation of diseases: an overview. Methods Mol Biol 1509:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6524-3_1
Wang JZ, Wu Q, Smith A, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1998) Tau is phosphorylated by GSK-3 at several sites found in Alzheimer disease and its biological activity markedly inhibited only after it is prephosphorylated by A-kinase. FEBS Lett 436:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01090-4
Wang J, Kong X, Cong L, Xu Z, Du J et al (2018a) Associations between CD33 rs3865444 and ABCA7 rs3764650 polymorphisms and susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease. J Integr Neurosci 17:313–321
Wang X, Liu D, Huang HZ, Wang ZH, Hou TY et al (2018b) A novel MicroRNA-124/PTPN1 signal pathway mediates synaptic and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Psychiatry 83:395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.07.023
Xu Y, Chen P, Wang X, Yao J, Zhuang S (2018) miR-34a deficiency in APP/PS1 mice promotes cognitive function by increasing synaptic plasticity via AMPA and NMDA receptors. Neurosci Lett 670:94–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.01.045
Yaribeygi H, Panahi Y, Javadi B, Sahebkar A (2018) The underlying role of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: a mechanistic review. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 17:207–215. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527317666180425122557
Zhao YL, Song JN, Ma XD, Zhang BF, Li DD et al (2016) Rosiglitazone ameliorates diffuse axonal injury by reducing loss of tau and up-regulating caveolin-1 expression. Neural Regen Res 11:944–950. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.184493
Funding
This work was supported by the Shenzhen Science & Technology Commission Grants (Grant No. JCYJ20180507184656626).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ conceived and designed the experiments; YSJ analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments; LS performed the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
For animal studies, all experimental protocols employed in this study were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital. All protocols of human studies were reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital (Approval no. 20181106007). Before the actual data collection, verbal and written informed consent was obtained from the study participants.
Consent to Participate
All participants in the human study have written informed consent before enrollment.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Zhang, Y. & Su, L. MiR-539-5p Decreases amyloid β-protein production, hyperphosphorylation of Tau and Memory Impairment by Regulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Pathways in APP/PS1 Double Transgenic Mice. Neurotox Res 38, 524–535 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00217-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00217-w