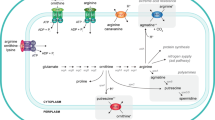
Abstract
In most bacteria the activity of glutamine synthetase (GS) is regulated by covalent protein modifications. Remarkably, cyanobacteria, which are of increasing interest in biotechnology, have evolved fundamentally different regulatory mechanisms for the same enzyme. This includes GS inhibition by the interaction with small proteins, the inactivating factors (IF). In addition, they evolved unique mechanisms to monitor GS activity and to respond with IF biosynthesis accordingly.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Merrick MJ, Edwards RA (1995) Nitrogen control in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 59:604–622
Woolfolk CA, Stadtman ER (1964) Cumulative feedback inhibition in the multiple end product regulation of glutamine synthetase activity in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 17:313–319
Stadtman ER (2001) The story of glutamine synthetase regulation. J Biol Chem 276:44357–44364
Fisher SH, Wray LV (2008) Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase regulates its own synthesis by acting as a chaperone to stabilize GlnR-DNA complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1014–1019
García-Domínguez M, Reyes JC, Florencio FJ (1999) Glutamine synthetase inactivation by protein-protein interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7161–7166
García-Domínguez M, Reyes JC, Florencio FJ (2000) NtcA represses transcription of gifA and gifB, genes that encode inhibitors of glutamine synthetase type I from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol Microbiol 35:1192–1201
Tanigawa R, Shirokane M, Maeda Si S et al. (2002) Transcriptional activation of NtcA-dependent promoters of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 by 2-oxoglutarate in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4251–4255
Bolay P, Muro-Pastor M, Florencio FJ et al. (2018) The distinctive regulation of cyanobacterial glutamine synthetase. Life 8:52
Klähn S, Schaal C, Georg J et al. (2015) The sRNA NsiR4 is involved in nitrogen assimilation control in cyanobacteria by targeting glutamine synthetase inactivating factor IF7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E6243–E6252
Forchhammer K (2007) Glutamine signalling in bacteria. Front Biosci 12:358–370
Klähn S, Bolay P, Wright PR et al. (2018) A glutamine riboswitch is a key element for the regulation of glutamine synthetase in cyanobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 46:10082–10094
Winkler WC, Breaker RR (2005) Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches. Annu Rev Microbiol 59:487–517
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Stephan Klähn 2001–2006 Biologiestudium an der Universität Rostock; dort 2010 Promotion. 2010–2018 Postdoc und wissenschaftlicher Mitarbeiter an der Universität Freiburg. Forschungsaufenthalte an der Yale University und Oklahoma State University, USA, und am Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, China. Seit 2018 Gruppenleiter am Helmholtz-Zentrum für Umweltforschung - UFZ, Leipzig. 2019 Habilitation. Seit 2019 Sprecher der VAAM-Fachgruppe Cyanobakterien.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klähn, S. Same same but different: Wie Cyanobakterien ein zentrales Enzym regulieren. Biospektrum 25, 610–613 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-019-0208-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-019-0208-x