Abstract
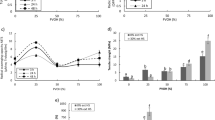
Transglutaminase (TGase) and succinylation could modify the physicochemical characteristics and the functional properties of proteins. The aim of this work was to cross-link egg white protein (EWP) and succinylated casein with TGase and to assess the feasibility of making a novel composite protein film. The effects of succinylated casein content, reaction time, and TGase concentration on the mechanical properties, physical characteristics (thermal property and degree of crystallinity), and structure properties (secondary structure and surface micrograph structure) of the film were investigated in this study. The results revealed that the susceptibility of EWP to TGase-mediated cross-linking modification was enhanced by succinylated casein. Meanwhile, the films with TGase were more homogeneous and smoother and possessed better water resistance and thermal stability. The content of α-helix, β-turn structures were increased whereas β-sheet structure was decreased. The spatial conformation and degree of crystallinity of composite protein film were also affected by TGase. The increase of the degree of crystallinity of the composite film further proved the improvement of film mechanical properties induced by TGase and succinylated casein. Based on the above results, this study provides relevant data and insights for the TGase/chemical modification of protein-based edible films.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arfat, Y., Benjakul, S., Prodpran, T., Sumpavapol, P., & Songtipya, P. (2016). Physico-mechanical characterization and antimicrobial properties of fish protein isolate/fish skin gelatin-zinc oxide (ZnO) nanocomposite films. Food & Bioprocess Technology, 9(1), 101–112.
Bae, H. J., Park, H. J., Hong, S. I., Byun, Y. J., Darby, D. O., Kimmel, R. M., & Whiteside, W. S. (2009). Effect of clay content, homogenization RPM, pH, and ultrasonication on mechanical and barrier properties of fish gelatin/montmorillonite nanocomposite films. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 42(6), 1179–1186.
Bigi, A., Borghi, M., Cojazzi, G., Fichera, A. M., Panzavolta, S., & Roveri, N. (2000). Structural and mechanical properties of crosslinked drawn gelatin films. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 61(2), 451–459.
Chen, T., Embree, H. D., Brown, E. M., Taylor, M. M., & Payne, G. F. (2003). Enzyme-catalyzed gel formation of gelatin and chitosan: potential for in situ applications. Biomaterials, 24(17), 2831–2841.
Espitia, P. J. P., Du, W.-X., Avena-Bustillos, R. J., Soares, N. F. F., & McHugh, T. H. (2014). Edible films from pectin: physical-mechanical and antimicrobial properties—a review. Food Hydrocolloids, 35, 287–296.
Gennadios, A., Weller, C. L., Hanna, M. A., & Froning, G. W. (1996). Mechanical and barrier properties of egg albumen films. Journal of Food Science, 61(3), 585–589.
Gounga, M. E., Xu, S.-Y., & Wang, Z. (2007). Whey protein isolate-based edible films as affected by protein concentration, glycerol ratio and pullulan addition in film formation. Journal of Food Engineering, 83(4), 521–530.
Gu, L., Wang, M., & Zhou, J. (2013). Effects of protein interactions on properties and microstructure of zein–gliadin composite films. Journal of Food Engineering, 119(2), 288–298.
Han, X. Q., & Damodaran, S. (1996). Thermodynamic compatibility of substrate proteins affects their cross-linking by transglutaminase. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 44(5), 1211–1217.
Haq, M. A., Hasnain, A., & Azam, M. (2014). Characterization of edible gum cordia film: Effects of plasticizers. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 55(1), 163–169.
Kieliszek, M., & Misiewicz, A. (2014). Microbial transglutaminase and its application in the food industry. A review. Folia Microbiologia (Praha), 59(3), 241–250.
Kowalczyk, D., & Baraniak, B. (2011). Effects of plasticizers, pH and heating of film-forming solution on the properties of pea protein isolate films. Journal of Food Engineering, 105(2), 295–305.
Larré, C., Desserme, C., Barbot, J., & Gueguen, J. (2000). Properties of deamidated gluten films enzymatically cross-linked. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48(11), 5444–5449.
Li, C., Luo, J., Qin, Z., Chen, H., Gao, Q., & Li, J. (2015). Mechanical and thermal properties of microcrystalline cellulose-reinforced soy protein isolate-gelatin eco-friendly films. RSC Advances, 5(70), 56518–56525.
Lim, L.-T., Mine, Y., & Tung, M. A. (1998). Transglutaminase cross-linked egg white protein films: tensile properties and oxygen permeability. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 46(10), 4022–4029.
Liu, F., Majeed, H., Antoniou, J., Li, Y., Ma, Y., Yokoyama, W., Ma, J., & Zhong, F. (2016). Tailoring physical properties of transglutaminase-modified gelatin films by varying drying temperature. Food Hydrocolloids, 58, 20–28.
Mahmoud, R., & Savello, P. A. (1993). Solubility and hydrolyzability of films produced by transglutaminase catalytic crosslinking of whey protein1. Journal of Dairy Science, 76(1), 29–35.
McCluskie, M., & Kennedy, J. F. (2003). Protein-based films and coatings: Aristippos Gennadios (Ed.). Carbohydrate Polymers, 53(4), 508.
Mizuno, A., Mitsuiki, M., & Motoki, M. (2000). Effect of transglutaminase treatment on the glass transition of soy protein. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48(8), 3286–3291.
Motoki, M., & Seguro, K. (1998). Transglutaminase and its use for food processing. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 9(5), 204–210.
Motoki, M., Aso, H., Seguro, K., & Nio, N. (1987). αs1-casein film prepared using transglutaminase. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 51(4), 993–996.
Niu, F., Dong, Y., Shen, F., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Su, Y., Xu, R., Wang, J., & Yang, Y. (2015). Phase separation behavior and structural analysis of ovalbumin–gum Arabic complex coacervation. Food Hydrocolloids, 43, 1–7.
Nuanmano, S., Prodpran, T., & Benjakul, S. (2015). Potential use of gelatin hydrolysate as plasticizer in fish myofibrillar protein film. Food Hydrocolloids, 47, 61–68.
Oster, G. (1954). Principles of polymer chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education, 31(12), 669.
Qiao, L., Jiazhen, P., Zhiying, H., Jianqiang, B., & Qiannan, X. (2014). Characterization of WPI-NaCas composite films modified by transglutaminase. Scientific Research and Essays, 9(9), 391–399.
Ramirezsuarez, J. (2003). Effect of transglutaminase-induced cross-linking on gelation of myofibrillar/soy protein mixtures*1. Meat Science, 65(2), 899–907.
Rhim, J.-W., Gennadios, A., Weller, C. L., Carole, C., & Hanna, M. A. (1998). Soy protein isolate–dialdehyde starch films1. Industrial Crops and Products, 8(3), 195–203.
Richards, R. B. (1951). Polyethylene-structure, crystallinity and properties. Journal of Applied Chemistry, 1(8), 370–376.
Rivero, S., García, M. A., & Pinotti, A. (2010). Correlations between structural, barrier, thermal and mechanical properties of plasticized gelatin films. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies., 11(2), 369–375.
Shilpashree, B. G., Arora, S., Sharma, V., & Singh, A. K. (2015) Preparation of succinylated sodium caseinate–iron complex by adopting ultrafiltration technology: a novel food fortificant. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 32, 165–171.
Song, C.-L., & Zhao, X.-H. (2014). The preparation of an oligochitosan-glycosylated and cross-linked caseinate obtained by a microbial transglutaminase and its functional properties. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 67(1), 110–116.
Subirade, M., Kelly, I., Guéguen, J., & Pézolet, M. (1998). Molecular basis of film formation from a soybean protein: comparison between the conformation of glycinin in aqueous solution and in films. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 23(4), 241–249.
Surewicz, W. K., Mantsch, H. H., & Chapman, D. (1993). Determination of protein secondary structure by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: a critical assessment. Biochemistry, 32(2), 389–394.
Tang, C. H., Wu, H., Yu, H. P., Li, L., Chen, Z., & Yang, X. Q. (2006a). Coagulation and gelation of soy protein isolates induced by microbial transglutaminas. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 30(1), 35–55.
Tang, C. H., Chen, Z., Li, L., & Yang, X.-Q. (2006b). Effects of transglutaminase treatment on the thermal properties of soy protein isolates. Food Research International, 39(6), 704–711.
Tian, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Quan, C., & Zhang, X. (2010). Improved flexibility and water resistance of soy protein thermoplastics containing waterborne polyurethane. Industrial Crops and Products, 32(1), 13–20.
William, H., & George, W. (2000). Official methods of analysis of AOAC international. USA, AOAC International Suite, 500, 481.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, N., Gu, L., Li, J. et al. Films Based on Egg White Protein and Succinylated Casein Cross-Linked with Transglutaminase. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 1422–1430 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1901-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1901-8