Abstract
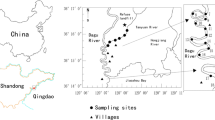
Synthetic musk fragrances (SMFs) in aquatic environments have been of increasing concern because of their potential characteristic of persistent, bioaccumulated, and ecological harm. However, little is known about the distribution of SMFs in river-lake systems. In this study, the occurrence and risks of six SMFs measured in sediments from Lake Chaohu (eastern China) and the rivers flowing into it were investigated. The total sedimentary SMF concentrations ranged from 2.43 to 15.5 ng/g in Lake Chaohu (median = 5.17 ng/g), and 2.34–104 ng/g in the rivers (median = 10.6 ng/g). Overall, moderate levels of SMFs were found in comparison with previous results from other areas. Galaxolide and tonalide dominated in the rivers whereas cashmeran was dominant in Lake Chaohu. A source assessment indicated that the discharge from industries contributed importantly to the pollution of SMFs in the studied waters, in addition to the inputs from domestic sewage. Our estimates suggested that the current sedimentary SMF concentrations were likely to pose extremely low ecological risk to aquatic organisms. However, more studies are needed to focus on the spatial and temporal trends in distribution as well as the ecotoxicological implications of SMFs in the Lake Chaohu area because there is a general lack of relevant information.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Azaroff A, Miossec C, Lanceleur L, Guyoneaud R, Monperrus M (2020) Priority and emerging micropollutants distribution from coastal to continental slope sediments: a case study of Capbreton Submarine Canyon (North Atlantic Ocean). Sci Total Environ 703:135057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135057
Barletta M, Lima AR, Costa MF (2019) Distribution, sources and consequences of nutrients, persistent organic pollutants, metals and microplastics in South American estuaries. Sci Total Environ 651:1199–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.276
Baugh P, Hutchinson S, Min L (2018) Organic Pollution in surface and core sediments from the Yangtze River estuarine region—historic research study and a review of recent investigations. Anal Bioanal Chem 2(1):64–73. https://doi.org/10.36959/525/441
Bitsch N, Dudas C, Körner W, Failing K, Biselli S, Rimkus G, Brunn H (2002) Estrogenic activity of musk fragrances detected by the E-screen assay using human mcf-7 cells. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 43(3):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-1192-5
Cavalheiro J, Zuloaga O, Prieto A, Preudhomme H, Amouroux D, Monperrus M (2017) Occurrence and fate of organic and organometallic pollutants in municipal wastewater treatment plants and their impact on receiving waters (Adour Estuary, France). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 73(4):619–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0422-9
Che JS, Yu RP, Song QJ, Wang LP, Wu SF (2011) Determination of synthetic musks in the sediment of the Taihu Lake by using accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) and GC/MS. Int J Environ Anal Chem 91(4):387–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067311003782633
Chen C, Zhou Q, Cai Z, Wang Y (2010a) Effects of soil polycyclic musk and cadmium on pollutant uptake and biochemical responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59(4):64–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9522-5
Chen D, Hale RC, Watts BD, La Guardia MJ, Harvey E, Mojica EK (2010b) Species-specific accumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardants in birds of prey from the Chesapeake Bay region, USA. Environ Pollut 158(5):1883–1889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.042
Chen H, Li Y, Sun W, Song L, Zuo R, Teng Y (2020) Characterization and source identification of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of an interconnected river-lake system. Environ Int 137:105538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105538
Dsikowitzky L, Nguyen TMI, Konzer L, Zhao H, Wang DR, Yang F, Schwarzbauer J (2020) Occurrence and origin of triazine herbicides in a tropical coastal area in China: a potential ecosystem threat. Estuar Coast Shelf S 235:106612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106612
ECB (European Chemicals Bureau) (2003) Technical guidance document on risk assessment; in support of commission directive 93/67/EEC on risk assessment for new notified substances, Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substances, Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the placing of biocidal products on the market. Part II
Fan M, Liu Z, Dyer S, Xia P, Zhang X (2017) Environmental risk assessment of polycyclic musks HHCB and AHTN in consumer product chemicals in China. Sci Total Environ 599:771–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.036
Fang T, Lu W, Li J, Zhao X, Yang K (2017a) Levels and risk assessment of metals in sediment and fish from Chaohu Lake, Anhui Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(18):15390–15400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9053-y
Fang H, Li G, Yao S, Liang X, An T (2017b) Kinetic and mechanism studies of musk tonalide reacted with hydroxyl radical and the risk assessment of degradation products. Catal Today 281:642–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.021
Felker I, Pupo G, Kraft P, List B (2015) Design and enantioselective synthesis of cashmeran odorants by using “Enol Catalysis”. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 54(6):1679. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201409591
Gao JH, Jia J, Kettner AJ, Xing F, Wang YP, Xu XN, Yang Y, Zou XQ, Gao S, Qi S (2014) Changes in water and sediment exchange between the Changjiang River and Poyang Lake under natural and anthropogenic conditions, China. Sci Total Environ 481:542–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.087
Gao Y, Li G, Qin Y, Ji Y, Mai B, An T (2019) New theoretical insight into indirect photochemical transformation of fragrance nitro-musks: mechanisms, eco-toxicity and health effects. Environ Int 129:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.020
Gu Y, Li X, Liang G, Xu Q, Yu Y, Zhang X (2017) Synthetic musk in surface water, sediment, and fish collected from Dianshan Lake and the human exposure assessment. Acta Sci Circumst 37(1):388–394. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2016.0133 (in Chinese)
Guo GH, Wu FC, He HP, Zhang RQ, Li HX (2013) Screening level ecological risk assessment for synthetic musks in surface water of Lake Taihu, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 27(1):111–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0581-1
He YJ, Chen W, Zheng XY, Wang XN, Huang X (2013) Fate and removal of typical pharmaceuticals and personal care products by three different treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 447:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.009
Heberer T (2002) Occurrence, fate, and assessment of polycyclic musk residues in the aquatic environment of urban areas: a review. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 30(5–6):227–243. https://doi.org/10.1002/aheh.200390005
Homem V, Alves A, Alves A, Santos L (2016) Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of synthetic musk fragrances in aqueous matrices by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta 148:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.10.049
Homem V, Magalhaes I, Alves A, Santos L (2017) Assessing seasonal variation of synthetic musks in beach sands from Oporto coastal area: a case study. Environ Pollut 226:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.022
Hu Z, Shi Y, Cai Y (2011) Reprint of: Concentrations, distribution, and bioaccumulation of synthetic musks in the Haihe River of China. Chemosphere 85(2):262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.09.002
Huang W, Xie Z, Yan W, Mi W, Xu W (2016) Occurrence and distribution of synthetic musks and organic UV filters from riverine and coastal sediments in the Pearl River estuary of China. Mar Pollut Bull 111(1–2):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.07.018
Klečka G, Persoon C, Currie R (2010) Chemicals of emerging concern in the Great Lakes Basin: an analysis of environmental exposures. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 207:1–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6406-9_1
Lange C, Kuch B, Metzger JW (2015) Occurrence and fate of synthetic musk fragrances in a small German river. J Hazard Mater 282:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.027
Lee IS, Kim UJ, Oh JE, Choi M, Hwang DW (2014) Comprehensive monitoring of synthetic musk compounds from freshwater to coastal environments in Korea: with consideration of ecological concerns and bioaccumulation. Sci Total Environ 470:1502–1508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.070
Llompart M, Celeiro M, Lamas JP, Sanchez-Prado L, Lores M, Garcia-Jares C (2013) Analysis of plasticizers and synthetic musks in cosmetic and personal care products by matrix solid-phase dispersion gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1293:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.03.067
Lou YH, Wang J, Wang L, Shi L, Yu Y, Zhang MY (2016) Determination of synthetic musks in sediments of Yellow River Delta Wetland, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97(1):78–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1814-7
Lu B, Feng Y, Gao P, Zhang Z, Lin N (2015) Distribution and fate of synthetic musks in the Songhua River, Northeastern China: influence of environmental variables. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(12):9090–9099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3973-6
Luigi V, Giuseppe M, Claudio R (2015) Emerging and priority contaminants with endocrine active potentials in sediments and fish from the River Po (Italy). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(18):14050–14066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4388-8
Martin C, Moeder M, Daniel X, Krauss G, Schlosser D (2007) Biotransformation of the polycyclic musks HHCB and AHTN and metabolite formation by fungi occurring in freshwater environments. Environ Sci Technol 41(15):5395–5402. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0711462
Martinez A, Schnoebelen DJ, Hornbuckle KC (2016) Polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in sediment cores from the Upper Mississippi River. Chemosphere 144:1943–1949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.090
Martínez-Girón AB, Crego AL, González MJ, Marina ML (2010) Enantiomeric separation of chiral polycyclic musks by capillary electrophoresis: application to the analysis of cosmetic samples. J Chromatogr A 1217(7):1157–1165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.12.021
Moldovan Z (2006) Occurrences of pharmaceutical and personal care products as micropollutants in rivers from Romania. Chemosphere 64(11):1808–1817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.00
Nakata H (2005) Occurrence of synthetic musk fragrances in marine mammals and sharks from Japanese coastal waters. Environ Sci Technol 39(10):3430–3434. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050199l
Parolini M, Magni S, Traversi I, Villa S, Finizio A, Binelli A (2015) Environmentally relevant concentrations of galaxolide (HHCB) and tonalide (AHTN) induced oxidative and genetic damage in Dreissena polymorpha. J Hazard Mater 285:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.11.037
Peck AM, Hornbuckle K (2006a) Synthetic musk fragrances in urban and rural air of Iowa and the Great Lakes. Atmos Environ 40(32):6101–6111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.058
Peck AM, Hornbuckle K (2006b) Aquatic processes and systems in perspective: environmental sources, occurrence, and effects of synthetic musk fragrances. J Environ Monit 8(9):874–879 http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=b608170n
Peck AM, Linebaugh EK, Hornbuckle KC (2006) Synthetic musk fragrances in Lake Erie and Lake Ontario sediment cores. Environ Sci Technol 40(18):5629–5635. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060134y
Pinkas A, Gonçalves CL, Aschner M (2017) Neurotoxicity of fragrance compounds: a review. Environ Res 158:342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.06.035
Pintado-Herrera MG, Combi T, Corada-Fernández C, González-Mazo E, Lara-Martín PA (2017) Occurrence and spatial distribution of legacy and emerging organic pollutants in marine sediments from the Atlantic coast (Andalusia, SW Spain). Sci Total Environ 605:980–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.055
Qin N, He W, Kong XZ, Liu WX, He QS, Yang B, Wang QM, Yang C, Jiang YJ, Jorgensen SE (2014) Distribution, partitioning and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water-SPM-sediment system of Lake Chaohu, China. Sci Total Environ 496:414–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.045
QY Research Inc (2019) Musk market growing at 0.8% CAGR will hit 170 million USD by the end of 2025. QY Research, Inc. Medgadget. https://www.medgadget.com/2019/03/musk-market-growing-at-0-8-cagr-will-hit-170-million-usd-by-the-end-of-2025-qy-research-inc.html. Accessed 15 June 2020
Randelli E, Rossini V, Corsi I, Focardi S, Fausto AM, Buonocore F, Scapigliati G (2011) Effects of the polycyclic ketone tonalide (AHTN) on some cell viability parameters and transcription of P450 and immunoregulatory genes in rainbow trout RTG-2 cells. Toxicol in Vitro 25(8):1596–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2011.06.003
Reiner JL, Kannan K (2011) Polycyclic musks in water, sediment, and fishes from the upper Hudson River, New York, USA. Water Air Soil Pollut 214(1–4):335–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0427-8
Reiner J, Berset J, Kannan K (2007) Mass flow of polycyclic musks in two wastewater treatment plants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52(4):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-006-0203-3
Reiner JL, Wong CM, Arcaro KF, Kannan K (2011) Synthetic musk fragrances in human milk from the United States. Environ Sci Technol 41(11):3815–3820. https://doi.org/10.1021/es063088a
Relić D, Popović A, Đorđević D, Čáslavský J (2017) Occurrence of synthetic musk compounds in surface, underground, waste and processed water samples in Belgrade, Serbia. Environ Earth Sci 76(3):122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6441-z
Sá SVD, Fernandes JO, Cunha SC (2019) In situ acetylation dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of musks, triclosan and methyl-triclosan in wastewaters. Int J Environ Anal Chem 99(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1566955
Sanchez-Prado L, Llompart M, Lamas JP, Garcia-Jares C, Lores M (2011) Multicomponent analytical methodology to control phthalates, synthetic musks, fragrance allergens and preservatives in perfumes. Talanta 85(1):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.03.079
Sang W, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Ma L, Sun X (2012) Occurrence and distribution of synthetic musks in surface sediments of Liangtan River, West China. Environ Eng Sci 29(1):19–25. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2010.0241
Sapozhnikova Y, Liebert D, Wirth E, Fulton M (2010) Polycyclic musk fragrances in sediments and shrimp tissues. Polycycl Aromat Compd 30(5):298–308
Schnell S, Martin-Skilton R, Fernandes D, Porte C (2009) The interference of nitro-and polycyclic musks with endogenous and xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in carp: an in vitro study. Environ Sci Technol 43(24):9458–9464. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902128x
Sommer C (2004) The role of musk and musk compounds in the fragrance industry, Series Anthropogenic Compounds. Springer. pp:1–16
Tang J, Shi T, Wu X, Cao H, Li X, Hua R, Tang F, Yue Y (2015) The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in Lake Chaohu, China: seasonal variation, potential source and risk assessment. Chemosphere 122:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.032
Tang Z, Han X, Li G, Tian S, Yang Y, Zhong F, Han Y, Yang J (2018) Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk of ultraviolet absorbents in water and sediment from Lake Chaohu and its inflowing rivers, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.045
Tseng WJ, Tsai SW (2019) Assessment of dermal exposures for synthetic musks from personal care products in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 669:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.046
Upadhyay N, Sun Q, Allen JO, Westerhoff P, Herckes P (2011) Synthetic musk emissions from wastewater aeration basins. Water Res 45(3):1071–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.10.024
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2018) ChemView. https://chemview.epa.gov/chemview. Accessed 25 June 2020
Wang B, Yu G, Huang J, Yu Y, Hu H, Wang L (2009) Tiered aquatic ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides and their mixture in Jiangsu reach of Huaihe River, China. Environ Monit Assess 157(1–4):29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0512-2
Wang FL, Zhou Y, Guo YW, Zou LY, Zhang XL, Zeng XY (2010) Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of synthetic musk in Suzhou Creek. J Shanghai Univ (Engl Ed) 14(4):306–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11741-010-0301-0649-3
Wang S, Jiang X, Jin X (2011) Classification and pollution characteristic analysis for inflow rivers of Chaohu Lake. Environ Sci 32(10):2834–2839 (in Chinese)
Wang X, Xi B, Huo S, Deng L, Pan H, Xia X, Zhang J, Ren Y, Liu H (2013) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers occurrence in major inflowing rivers of Lake Chaohu (China): characteristics, potential sources and inputs to lake. Chemosphere 93(8):1624–1631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.024
Wang XT, Hu BP, Cheng HX, Jia HH, Zhou Y (2018) Spatial variations, source apportionment and potential ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and synthetic musks in river sediments in Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 193:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.145
Witorsch RJ, Thomas JA (2010) Personal care products and endocrine disruption: a critical review of the literature. Crit Rev Toxicol 40(sup3):1–30. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2010.515563
Wollenberger L, Breitholtz M, Kusk KO, Bengtsson BE (2003) Inhibition of larval development of the marine copepod Acartia tonsa by four synthetic musk substances. Sci Total Environ 305(1–3):53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00471-0
Wong F, Robson M, Melymuk L, Shunthirasingham C, Alexandrou N, Shoeib M, Luk E, Helm P, Diamond ML, Hung H (2019) Urban sources of synthetic musk compounds to the environment. Environ Sci-Proc Imp 21(1):74–88. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8em00341f
Wu SF, Liu LL, Ding WH (2012) One-step microwave-assisted headspace solid-phase microextraction for the rapid determination of synthetic polycyclic musks in oyster by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem 133(2):513–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.017
Xie Z, Ebinghaus R, Temme C, Heemken O, Ruck W (2007) Air-sea exchange fluxes of synthetic polycyclic musks in the North Sea and the Arctic. Environ Sci Technol 41(16):5654–5659. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0704434
Yang JJ, Metcalfe CD (2006) Fate of synthetic musks in a domestic wastewater treatment plant and in an agricultural field amended with biosolids. Sci Total Environ 363(1–3):149–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.06.022
Zan F, Huo S, Xi B, Zhu C, Liao H, Zhang J, Yeager KM (2012) A 100-year sedimentary record of natural and anthropogenic impacts on a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. J Environ Monit 14(3):804–816. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1em10760g
Zeng X, Hu Q, He L, Liu Z, Gao S, Yu Z (2018a) Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks of organophosphate esters and synthetic musks in sediments from the Hun River. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 160:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.034
Zeng X, Xu L, Liu J, Wu Y, Yu Z (2018b) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants/plasticizers and synthetic musks in sediments from source water in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Toxicol Chem 37(4):975–982. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4040
Zhang X, Yao Y, Zeng X, Qian G, Guo Y, Wu M, Sheng G, Fu J (2008) Synthetic musks in the aquatic environment and personal care products in Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 72(10):1553–1558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.039
Zhang Y, Huang L, Zhao Y, Hu T (2017) Musk xylene induces malignant transformation of human liver cell line L02 via repressing the TGF-β signaling pathway. Chemosphere 168:1506–1514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.001
Zheng M, Hu S, Liu X, Wang W, Yin X, Zheng L, Wang L, Lou Y (2019) Levels and distribution of synthetic musks in farmland soils from the three northeast provinces of China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:303–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.100
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 41877467 and 41571445) and the National Key R&D Program of China (grant no. 2018YFC1900104). The authors thank Kara Bogus, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 41877467 and 41571445) and the National Key R&D Program of China (grant no. 2018YFC1900104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang Lyu: analyses, data curation; visualization, writing—original draft. Shan Ren: investigation, validation, writing—original draft. Fuyong Zhong: investigation. Xue Han: investigation. Ying He: data curation, visualization. Zhenwu Tang: conceptualization, methodology, resources, project administration, Funding acquisition, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
All of the co-authors agreed that the article will be published in Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Further, the potential publish has been approved by the institutions where the study was conducted.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Esther Heath
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 128 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, Y., Ren, S., Zhong, F. et al. Synthetic musk fragrances in sediments from a subtropical river-lake system in eastern China: occurrences, profiles, and ecological risks. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 14597–14606 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11486-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11486-5