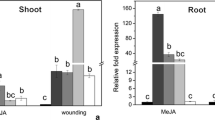
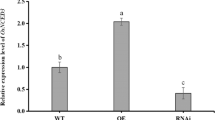
Abstract
Xylanase inhibitors have been reported to play an important role in plant defense against fungal pathogens. However, little to nothing is known about their role in defense against herbivores. Here, we cloned a rice xylanase-inhibiting protein (XIP)-type gene OsHI-XIP whose encoding protein is located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Transcriptional analysis revealed a low constitutive mRNA level of OsHI-XIP, while herbivore infestation, mechanical wounding, and treatment with jasmonic acid (JA), a signal that can be induced after infestation by the rice striped stem borer (SSB) Chilo suppressalis, result in an obvious increase in transcript levels. Overexpression of OsHI-XIP, which increased mRNA levels of the gene by 14.7- to 17.7-fold and 7.5- to 9.6-fold at 0 and 12 h, respectively, after SSB infestation, enhanced constitutive and SSB-induced xylanase inhibitor activity and reduced the larval performance of SSB. Moreover, overexpression of OsHI-XIP decreased the feeding and oviposion preferences of the rice brown planthopper (BPH) Nilaparvata lugens, but did not influence the growth and development of rice plants. The results suggest that the rice XIP-type xylanase inhibitor OsHI-XIP is involved in the resistance in rice to herbivores.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPH:
-
Brown planthopper
- GH:
-
Glycoside hydrolase
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- PGIPs:
-
Polygalacturonase inhibitors
- PR proteins:
-
Pathogenesis-related proteins
- QRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SSB:
-
Striped stem borer
- TAXI:
-
Triticum aestivum xylanase inhibitor
- TLXI:
-
Thaumatin-like xylanase inhibitor
- TrypPIs:
-
Trypsin protease inhibitors
- UTR:
-
Untranslated regions
- XI:
-
Xylanase inhibitor
- XIP:
-
Xylanase-inhibiting protein
- WT:
-
Wild-type
References
Beaugrand J, Gebruers K, Ververken C, Fierens E, Croes E, Goddeeris B, Courtin CM, Delcour JA (2006) Antibodies against wheat xylanase inhibitors as tools for the selective identification of their homologues in other cereals. J Cereal Sci 44:59–67
Bostock RM (2005) Signal crosstalk and induced resistance: straddling the line between cost and benefit. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:545–580
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. J Biochem 72:248–254
Brennan YL, Callen WN, Christoffersen L, Dupree P, Goubet F, Healey S, Hernández M, Keller M, Li K, Palackal N, Sittenfeld A, Tamayo G, Wells S, Hazlewood GP, Mathur EJ, Short JM, Robertson DE, Steer BA (2004) Unusual microbial xylanases from insect guts. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3609–3617
Brito N, Espino JJ, Gonzalez C (2006) The endo-beta-1,4-xylanase xyn11A is required for virulence in Botrytis cinerea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:25–32
Chivasa S, Simon WJ, Yu XL, Yalpani N, Slabas AR (2005) Pathogen elicitor-induced changes in the maize extracellular matrix proteome. Proteomics 5:4894–4904
Di CX, Zhang MX, Xu SJ, Cheng T, An LZ (2006) Role of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein in plant defense. Crit Rev Microbiol 32:91–100
Dornez E, Croes E, Gebruers K, De Coninck B, Cammue BPA, Delcour JA, Courtin CM (2010) Accumulated evidence substantiates a role for three classes of wheat xylanase inhibitors in plant defense. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29:244–264
Durand A, Hughes R, Roussel A, Flatman R, Henrissat B, Juge N (2005) Emergence of a subfamily of xylanase inhibitors within glycoside hydrolase family 18. FEBS J 272:745–1755
Elliott GO, McLauchlan WR, Williamson G, Kroon PA (2003) A wheat xylanase inhibitor protein (XIP-I) accumulates in the grain and has homologues in other cereals. J Cereal Sci 37:187–194
Erb M, Meldau S, Howe GA (2012) Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends Plant Sci 17:250–259
Ferrari S, Vairo D, Ausubel FM, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G (2003) Arabidopsis polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIP) are regulated by different signal transduction pathways during fungal infection. Plant Cell 15:93–106
Fierens E (2007) TLXI, a thaumatin-like xylanase inhibitor: isolation, characterisation and comparison with other wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) xylanase inhibiting proteins. Dissertation, KU Leuven
Fierens E, Rombouts S, Gebruers K, Goesaert H, Brijs K, Beaugrand J, Volckaert G, Van Campenhout S, Proost P, Courtin CM, Delcour JA (2007) TLXI, a novel type of xylanase inhibitor from wheat (Triticum aestivum) belonging to the thaumatin family. Biochem J 403:583–591
Franco OL, Rigden DJ, Melo FR, Grossi-de-Sa MF (2002) Plant alpha-amylase inhibitors and their interaction with insect alpha-amylases -Structure, function and potential for crop protection. Eur J Biochem 269:397–412
Goesaert H, Elliott G, Kroon PA, Gebruers K, Courtin CM, Robben J, Delcour JA, Juge N (2004) Occurrence of proteinaceous endoxylanase inhibitors in cereals. BBA Proteins Proteom 1696:193–202
Goesaert H, Gebruers K, Courtin CM, Delcour JA (2005) Purification and characterization of a XIP-type endoxylanase inhibitor from rice (Oryza sativa). J Enzym Inhib Med Chem 20:95–101
Grenier J, Potvin C, Trudel J, Asselin A (1999) Some thaumatin-like proteins hydrolyse polymeric beta-1,3-glucans. Plant J 19:473–480
Hogenhout SA, Bos JIB (2011) Effector proteins that modulate plant-insect interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:422–428
Igawa T, Ochiai-Fukuda T, Takahashi-Ando N, Ohsato S, Shibata T, Yamaguchi I, Kimura M (2004) New TAXI-type xylanase inhibitor genes are inducible by pathogens and wounding in hexaploid wheat. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1347–1360
Igawa T, Tokai T, Kudo T, Yamaguchi I, Kimura M (2005) A wheat xylanase inhibitor gene, Xip-I, but not Taxi-I, significantly induced by biotic and abiotic signals that trigger plant defense. Biosci Biotech Biochem 69:1058–1063
Jeong MJ, Lee SK, Kim BG et al (2006) A rice (Oryza sativa L.) MAP kinase gene, OsMAPK44, is involved in response to abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Tissue Organ 85:151–160
Juge N, Delcour JA (2006) Proteinaceous xylanase inhibitors: structure, functions and evolution. Curr Enzym Inhib 2:29–35
Juge N, Svensson B (2006) Proteinaceous inhibitors of carbohydrate-active enzymes in cereals: implication in agriculture, cereal processing and nutrition. J Sci Food Agric 86:1573–1586
Juge N, Payanc F, Williamsona G (2004) XIP-I, a xylanase inhibitor protein from wheat: a novel protein function. BBA Proteins Proteom 1696:203–211
Koiwa H, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1997) Regulation of protease inhibitors and plants defense. Trends Plant Sci 2:379–384
Konishi H, Noda H, Tamura Y, Hattori M (2009) Proteomic analysis of the salivary glands of the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Appl Entomol Zool 44:525–534
Levorson J, Chlan CA (1997) Plant chitinase consensus sequences. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15:122–133
Lou Y, Baldwin IT (2003) Manduca sexta recognition and resistance among allopolyploid Nicotiana host plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14581–14586
Lu J, Ju H, Zhou G, Zhu C, Erb M, Wang X, Wang P, Lou Y (2011) An EAR-motif-containing ERF transcription factor affects herbivore-induced signaling, defense and resistance in rice. Plant J 68:583–596
Mithofer A, Boland W (2012) Plant defense against herbivores: chemical aspects. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:431–450
Nelson BK, Cai X, Nebenführ A (2007) A multicolored set of in vivo organelle markers for co-localization studies in Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant J 51:1126–1136
Padilla-Hurtado B, Flórez-Ramos C, Aguilera-Gálvez C, Medina-Olaya J, Ramírez-Sanjuan A, Rubio-Gómez J, Acuña-Zornosa R (2012) Cloning and expression of an endo-1,4-β-xylanase from the coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus hampei. BMC Res Notes 5:23
Powell AL, van Kan J, ten Have A, Visser J, Greve LC, Bennett AB, Labavitch JM (2000) Transgenic expression of pear PGIP in tomato limits fungal colonization. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 139:942–950
Sá-Pereira P, Paveia H, Costa-Ferreira M, Aires-Barros M (2003) A new look at xylanases: an overview of purification strategies. Mol Biotechnol 24:257–281
Sels J, Mathys J, Coninck BMA, Cammue BPA, De Bolle MFC (2008) Plant pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins: a focus on PR peptides. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:941–950
Sorensen JF, Kragh KM, Sibbesen O, Delcour JA, Goesaert H, Svensson B, Tahir TA, Brufau J, Perez-Vendrell AM, Bellincampi D, D’Ovidio R, Camardella L, Giovane A, Bonnin E, Juge N (2004) Potential role of glycosidase inhibitors in industrial biotechnological applications. BBA Proteins Proteom 1696:275–287
Takahashi-Ando N, Inaba M, Ohsato S, Igawa T, Usami R, Kimura M (2007) Identification of multiple highly similar XIP-type xylanase inhibitor genes in hexaploid wheat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:880–884
Tokunaga T, Esaka M (2007) Induction of a novel XIP-type xylanase inhibitor by external ascorbic acid treatment and differential expression of XIP-family genes in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 48:700–714
Tokunaga T, Miyata Y, Fujikawa Y, Esaka M (2008) RNAi-Mediated knockdown of the XIP-type endoxylanase inhibitor gene, OsXIP, has no effect on grain development and germination in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1122–1127
Van Dam NM, Horn M, Mares M, Baldwin IT (2001) Ontogeny constrains systemic protease inhibitor response in Nicotiana attenuata. J Chem Ecol 27:547–568
Vasconcelos EA, Santana CG, Godoy CV, Seixas CD, Silva MS, Moreira LR, Oliveira-Neto OB, Price D, Fitches E, Filho EX, Mehta A, Gatehouse JA, Grossi-De-Sa MF (2011) A new chitinase-like xylanase inhibitor protein (XIP) from coffee (Coffea arabica) affects soybean Asian rust (Phakopsora pachyrhizi) spore germination. BMC Biotechnol 11:14
von Dahl CC, Winz RA, Halitschke R, Kühnemann F, Gase K, Baldwin IT (2007) Tuning the herbivore-induced ethylene burst: the role of transcript accumulation and ethylene perception in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant J 51:293–307
Wang X, Zhou G, Xiang C, Du M, Cheng J, Liu S, Lou Y (2008) Beta-glucosidase treatment and infestation by the rice brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens elicit similar signaling pathways in rice plants. Chin Sci Bull 53(1):53–57
Wroblewski T, Tomczak A, Michelmore R (2005) Optimization of Agrobacterium-mediated transient assays of gene expression in lettuce, tomato and Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol J 3:259–273
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. Manila, Philippines
Young TE, Meeley RB, Gallie DR (2004) ACC synthase expression regulates leaf performance and drought tolerance in maize. Plant J 40:813–825
Zhou G, Qi J, Ren N, Cheng J, Erb M, Mao B, Lou YG (2009) Silencing OsHI-LOX makes rice more susceptible to chewing herbivores, but enhances resistance to a phloem feeder. Plant J 60:638–648
Zhou G, Wang X, Yan F, Wang X, Li R, Cheng J, Lou Y (2011) Genome-wide transcriptional changes and defence-related chemical profiling of rice in response to infestation by the rice striped stem borer Chilo suppressalis. Physiol Plant 143:21–40
Acknowledgments
We thank Emily Wheeler for editorial assistance. The study was jointly sponsored by the National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB126200), the Innovation Research Team Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31021003), the National Program of Transgenic Variety Development of China (2011ZX08001-001), and the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-01-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Specific probes and primers for QRT-PCR of OsHI-XIP and OsACT. (DOC 31 kb)
Figure S1
Schematic of the expression vector of pCAMBIA-XIP::EGFP (a), pCAMBIA-WAK2::EGFP (b) and pCAMBIA-XIP (c) used for transformation in this study. (DOC 407 kb)
Figure S2
Growth phenotype and DNA gel-blot analysis of three oe-xip lines. (a,b) Growth phenotype of oe-xip lines and WT line at 30-d-old (a) and maturity stage (b). (c) DNA gel-blot analysis of three oe-xip lines (oe-22, oe-23, and oe-24). (DOC 2120 kb)
Figure S3
cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of a rice XIP gene OsHI-XIP. The start and stop codes are shown in red boxes. (DOC 234 kb)
Figure S4
Mean transcript levels (+ SE, n=5) of OsHI-XIP in rice stems that were treated with 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid (ACC, a) or H2O2 (b). Transcript levels were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. (DOC 91 kb)
Figure S5
JA levels and TrypPI activity in oe-xip lines and WT plants at different times after SSB larvae feeding. (a) Mean levels (+SE, n = 5) of JA in stems of oe-xip lines and WT plants when they were individually infested by a third-instar SSB larva for 0, 1.5, and 3 h. (b) Mean levels (+ SE, n=5) of trypsin proteinase inhibitors (TrypPIs) in stems of oe-xip lines and WT line when they were individually infested by a third-instar SSB larva for 3 days (SSB) or kept untreated (Con). (DOC 164 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Z., Wang, Q., Yu, Z. et al. Overexpression of a Xylanase Inhibitor Gene, OsHI-XIP, Enhances Resistance in Rice to Herbivores. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32, 465–475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0661-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0661-5