Abstract
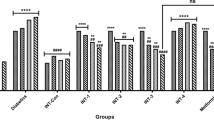
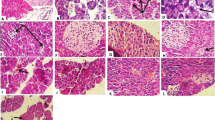
Nowadays, medicinal plants have been widely used everywhere to provide essential care for many disorders including diabetes. Recent reports assumed that the antidiabetic activities of pomegranate aril juice (PAJ) may be ascribed to its punicalagin (PCG). Therefore, the present study evaluated and compared the antidiabetic activities of PAJ and its PCG, and monitored some mechanisms of their actions in streptozotocin-nicotinamide (STZ-NA) type 2 diabetic rats. STZ-NA diabetic rats were given, orally/daily, PAJ (100 or 300 mg/kg body weight, containing 2.6 and 7.8 mg of PCG/kg body weight, respectively), pure PCG (2.6 or 7.8 mg/kg body weight), or distilled water (vehicle) for 6 weeks. PAJ (especially at the high dose) alleviated significantly (P < 0.05–0.001) most signs of type 2 diabetes including body-weight loss, insulin resistance (IR) and hyperglycemia through decreasing serum tumor necrosis factor-α concentration and the expression of hepatic c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and increasing the skeletal muscle weight and the expression of hepatic insulin receptor substrate-1 in STZ-NA diabetic rats. Also, it decreased significantly (P < 0.001) the oxidative liver injury in STZ-NA diabetic rats through decreasing the hepatic lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide production, and improving the hepatic antioxidant defense system. Although the low dose of PCG induced some modulation in STZ-NA diabetic rats, the high dose of PCG did not show any valuable antidiabetic activity, but induced many side effects. In conclusion, PAJ was safer and more effective than pure PCG in alleviating IR and oxidative liver injury in STZ-NA diabetic rats.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE (2014) Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 103(2):137–149
Ndisang JF, Vannacci A, Rastogi S (2017) Insulin resistance, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and related complications 2017. J Diabetes Res 2017:1478294. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1478294
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414(6865):813–820
Li H, Yu X (2013) Emerging role of JNK in insulin resistance. Curr Diabetes Rev 9(5):422–428
Lee YH, Giraud J, Davis RJ, White MF (2003) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mediates feedback inhibition of the insulin signaling cascade. J Biol Chem 278(5):2896–2902
Rui L, Aguirre V, Kim JK, Shulman GI, Lee A, Corbould A, Dunaif A, White MF (2001) Insulin/IGF-1 and TNF-alpha stimulate phosphorylation of IRS-1 at inhibitory Ser307 via distinct pathways. J Clin Invest 107(2):181–189
Manukumar HM, Shiva Kumar J, Chandrasekhar B, Raghava S, Umesha S (2017) Evidences for diabetes and insulin mimetic activity of medicinal plants: present status and future prospects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57(12):2712–2729
World Health Organization (2013) WHO traditional medicine strategy: 2014-2023. http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/92455
Arun N, Singh DP (2012) Punica granatum: a review on pharmacological and therapeutic properties. IJPSR 3(5):1240–1245
Harzallah A, Hammami M, Kepczynska MA, Hislop DC, Arch JR, Cawthorne MA, Zaibi MS (2016) Comparison of potential preventive effects of pomegranate flower, peel and seed oil on insulin resistance and inflammation in high-fat and high-sucrose diet-induced obesity mice model. Arch Physiol Biochem 122(2):75–87
Jurenka JS (2008) Therapeutic applications of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.): a review. Altern Med Rev 13(2):128–144
Yuan T, Ding Y, Wan C, Li L, Xu J, Liu K, Slitt A, Ferreira D, Khan IA, Seeram NP (2012) Antidiabetic ellagitannins from pomegranate flowers: inhibition of alpha-glucosidase and lipogenic gene expression. Org Lett 14(20):5358–5361
Zhishen J, Mengcheng T, Jainming W (1999) The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem 64:555–559
Gil MI, Tomas-Barberan FA, Hess-Pierce B, Holcroft DM, Kader AA (2000) Antioxidant activity of pomegranate juice and its relationship with phenolic composition and processing. J Agric Food Chem 48(10):4581–4589
Madkor HR, Mansour SW, Ramadan G (2011) Modulatory effects of garlic, ginger, turmeric and their mixture on hyperglycaemia, dyslipidaemia and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-nicotinamide diabetic rats. Br J Nutr 105(8):1210–1217
Chatuphonprasert W, Lao-Ong T, Jarukamjorn K (2014) Improvement of superoxide dismutase and catalase in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced type 2-diabetes in mice by berberine and glibenclamide. Pharm Biol 52(2):419–427
Gumuslu E, Cine N, Ertan M, Mutlu O, Komsuoglu Celikyurt I, Ulak G (2018) Exenatide upregulates gene expression of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and nerve growth factor in streptozotocin/nicotinamide-induced diabetic mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 32(2):174–180
Hwang J, Shieh DE, Shyu YS, Hsu CK, Lin CW (2018) Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic, and antioxidant activities of mulberry lees fermented products in diabetic mice. J Food Sci 83(11):2866–2872
Najafian M, Jahromi MZ, Nowroznejhad MJ, Khajeaian P, Kargar MM, Sadeghi M, Arasteh A (2012) Phloridzin reduces blood glucose levels and improves lipids metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep 39(5):5299–5306
Oliveira GO, Braga CP, Fernandes AA (2013) Improvement of biochemical parameters in type 1 diabetic rats after the roots aqueous extract of yacon [Smallanthus sonchifolius (Poepp. & Endl.)] treatment. Food Chem Toxicol 59:256–260
Ramadan G, El-Beih NM, Abd El-Ghffar EA (2009) Modulatory effects of black v green tea aqueous extract on hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidaemia and liver dysfunction in diabetic and obese rat models. Br J Nutr 102(11):1611–1619
Ramadan G, El-Beih NM, Abd El-Kareem HF (2011) Anti-metabolic syndrome and immunostimulant activities of Egyptian fenugreek seeds in diabetic/obese and immunosuppressive rat models. Br J Nutr 105(7):995–1004
Thomson M, Al-Qattan KK, Js D, Ali M (2016) Anti-diabetic and anti-oxidant potential of aged garlic extract (AGE) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 16:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-0992-5
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR (2004) Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 27(6):1487–1495
Winer J, Jung CK, Shackel I, Williams PM (1999) Development and validation of real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for monitoring gene expression in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Anal Biochem 270(1):41–49
Turner JR, Thayer J (2001) Introduction to analysis of variance: design, analysis & interpretation. SAGE, Thousand Oaks
Szkudelski T (2001) The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol Res 50(6):537–546
Ghasemi A, Khalifi S, Jedi S (2014) Streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced rat model of type 2 diabetes (review). Acta Physiol Hung 101(4):408–420
Rezaei E, Hosseini SE, Mehrabani D (2013) Effects of pomegranate juice on insulin and glucose in diabetic and non-diabetic male rats. J Birjand Univ Med Sci 20(3):244–251
Punithavathi VR, Prince PS, Kumar R, Selvakumari J (2011) Antihyperglycaemic, antilipid peroxidative and antioxidant effects of gallic acid on streptozotocin induced diabetic Wistar rats. Eur J Pharmacol 650(1):465–471
El-Missiry MA, Amer MA, Hemieda FAE, Othman AI, Sakr DA, Abdulhadi HL (2015) Cardioameliorative effect of punicalagin against streptozotocin-induced apoptosis, redox imbalance, metabolic changes and inflammation. EJBAS 2:247–260
Kim Y, Keogh JB, Clifton PM (2016) Polyphenols and glycemic control. Nutrients 8(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8010017
Li Y, Wen S, Kota BP, Peng G, Li GQ, Yamahara J, Roufogalis BD (2005) Punica granatum flower extract, a potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, improves postprandial hyperglycemia in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Ethnopharmacol 99(2):239–244
Prashanth D, Padmaja R, Samiulla DS (2001) Effect of certain plant extracts on alpha-amylase activity. Fitoterapia 72(2):179–181
Lin CC, Hsu YF, Lin TC, Hsu HY (2001) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of punicalagin and punicalin on acetaminophen-induced liver damage in rats. Phytother Res 15(3):206–212
Kulkarni AP, Mahal HS, Kapoor S, Aradhya SM (2007) In vitro studies on the binding, antioxidant, and cytotoxic actions of punicalagin. J Agric Food Chem 55(4):1491–1500
Peper A (2009) Aspects of the relationship between drug dose and drug effect. Dose Response 7(2):172–192
Ramachandran B, Jayavelu S, Murhekar K, Rajkumar T (2016) Repeated dose studies with pure Epigallocatechin-3-gallate demonstrated dose and route dependant hepatotoxicity with associated dyslipidemia. Toxicol Rep 3:336–345
Ali RE, Rattan SI (2006) Curcumin’s biphasic hormetic response on proteasome activity and heat-shock protein synthesis in human keratinocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1067:394–399
Aboonabi A, Rahmat A, Othman F (2014) Antioxidant effect of pomegranate against streptozotocin-nicotinamide generated oxidative stress induced diabetic rats. Toxicol Rep 1:915–922
Swaroop JJ, Rajarajeswari D, Naidu JN (2012) Association of TNF-alpha with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Med Res 135:127–130
Nandi J, Saud B, Zinkievich JM, Yang ZJ, Levine RA (2010) TNF-alpha modulates iNOS expression in an experimental rat model of indomethacin-induced jejunoileitis. Mol Cell Biochem 336(1–2):17–24
Garcia-Ruiz C, Fernandez-Checa JC (2007) Redox regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(Supplement 1):S38–S42
Ramadan G, El-Beih NM, Ahmed RS (2017) Aged garlic extract ameliorates immunotoxicity, hematotoxicity and impaired burn-healing in malathion- and carbaryl-treated male albino rats. Environ Toxicol 32(3):789–798
Cawthorn WP, Sethi JK (2008) TNF-a and adipocyte biology. FEBS Lett 582(1):117–131
Shema-Didi L, Sela S, Ore L, Shapiro G, Geron R, Moshe G, Kristal B (2012) One year of pomegranate juice intake decreases oxidative stress, inflammation, and incidence of infections in hemodialysis patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Free Radic Biol Med 53(2):297–304
Sohrab G, Nasrollahzadeh J, Zand H, Amiri Z, Tohidi M, Kimiagar M (2014) Effects of pomegranate juice consumption on inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Res Med Sci 19(3):215–220
Yoon JH, Baek SJ (2005) Molecular targets of dietary polyphenols with anti-inflammatory properties. Yonsei Med J 46(5):585–596
Acknowledgements
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. NME-B, GR and EAE-H planned the study, designed all experiments, summarized, discussed and interpreted the results. AMH with assistance from EAE-H carried out all the experiments. AMH performed the statistical analysis with assistance from GR. GR and AMH drafted the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All animals were humanely treated in accordance with the principles of laboratory animal care of National Institutes of Health (NIH publication No. 86-23, revised 1985), and the study design including the animal experiments was approved by the Ain Shams University Research Ethics Committee (4/2013).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Beih, N.M., Ramadan, G., El-Husseiny, E.A. et al. Effects of pomegranate aril juice and its punicalagin on some key regulators of insulin resistance and oxidative liver injury in streptozotocin-nicotinamide type 2 diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep 46, 3701–3711 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04813-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04813-8