Abstract
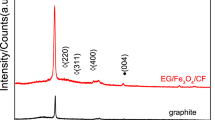
The different graphite morphologies, like graphite intercalation compound (GIC), expanded graphite (EG), and exfoliated graphite (ExfG), were investigated as microwave absorbing materials (MAMs). The modification of the GIC was carried out in two independent parts, consisting of heat treatment and subsequent ultrasound agitation, forming the EG and ExfG, respectively. The surface morphology and structural characterization were investigated using the scanning electron microscope and Raman spectroscopy. Electromagnetic characterization was performed with a vector network analyzer and rectangular waveguide in the frequency range from 8.2 to 12.4 GHz (X-band) and from 12.4 to 18 GHz (Ku-band). The effects of different graphite morphologies and thickness of the composite were analyzed on the electromagnetic properties. The results of the reflection loss show that the samples affect the performance of the MAMs. The EG sample presents an excellent attenuation of around − 22.5 dB (≈ 99 microwave attenuation) for 2 mm thickness samples within the X-band frequency range. This behavior can be attributed to the expanded and interconnected structure of the EG, which has a large surface area and connectivity between the structures within the composite. Thus, it was found that EG is the best graphite structure for application in microwave absorber of broadband. The GIC and ExfG exhibited poor performance of microwave absorption (above − 10 dB).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Zhang, T. Chen, S. Zhong, J. Wang, W. Zhang, X. Zuo, R.G. Maunder, L. Hanzo, Aeronautical ad hoc networking for the internet-above-the-clouds. Proc. IEEE. 107, 868–911 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2019.2909694
M.A. Do Amaral Junior, J.S. Marcuzzo, B.D.S. Pinheiro, B.H.K. Lopes, A.P.S. De Oliveira, J.T. Matsushima, M.R. Baldan, Study of reflection process for nickel coated activated carbon fiber felt applied with electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 4040–4047 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.07.014
R.C. Portes, B.H.K. Lopes, M.A. Amaral Junior, D.E. Florez-Vergara, S.F. Quirino, M.R. Baldan, Effect of granulometric distribution on electromagnetic shielding effectiveness for polymeric composite based on natural graphite. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 26, 531–539 (2019)
R. Pandey, S. Tekumalla, M. Gupta, Enhanced (X-band) microwave shielding properties of pure magnesium by addition of diamagnetic titanium micro-particulates. J. Alloys Compd. 770, 473–482 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.147
A.M. Anjaneyalu, A.S. Zeraati, U. Sundararaj, Enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of hybrid fillers by segregated structure. AIP Conf. Proc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5088329
M.A. do Amaral Junior, N.A.S. dos Gomes, S.S. de Pinto, M.C. Rezende, J.S. Marcuzzo, S.F. Quirino, M.R. Baldan, Influence of the permittivity on carbon fiber particulates applied in radiation absorbing materials. Glob. J. Res. Eng. F Electr. Electron. Eng. 17, 1–7 (2017)
R. Anwar, L. Mao, H. Ning, Frequency selective surfaces: a review. Appl. Sci. 8, 1689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091689
A. Syahmi, H. Abdullah, R. Akhbar, N.R. Ahmad, N.S. Sazalee, A.R. Razali, M.N. Taib, Radiation cross section characteristics for isosceles slotted triangle on hollow pyramidal absorber, Proc. – 2018 IEEE Int. Conf. Autom. Control Intell. Syst. I2CACIS 2018. (2019) 35–38. https://doi.org/10.1109/I2CACIS.2018.8603697
C. Xu, S. Qu, Y. Pang, J. Wang, M. Yan, J. Zhang, Z. Wang, W. Wang, Metamaterial absorber for frequency selective thermal radiation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 88, 133–138 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2017.08.017
K.-H. Wu, K.-F. Cheng, J.-C. Wang, Y.-C. Chang, Preparation of magnetic expanded graphite with microwave absorption and infrared stealth characteristics. Mater. Express. 7, 500–508 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2017.1400
D.P. Gurgel, I.S. Queiroz, M.Q. da Silva, H.D. de Andrade, U.U. Gomes, M.M. Karimi, Development of a microwave absorbing material based on molybdenum-doped niobium pentoxide. Cerâmica 65, 7–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1590/0366-6913201965s12559
Y. Qing, Y. Li, F. Luo, Electromagnetic interference shielding properties of nitrogen-doped graphene/epoxy composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03938-y
S.K. Nayak, S. Mohanty, S.K. Nayak, Silver (Ag) nanoparticle-decorated expanded graphite (EG) epoxy composite: evaluating thermal and electrical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 20574–20587 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02423-5
S. Konwer, J.P. Gogoi, A. Kalita, S.K. Dolui, Synthesis of expanded graphite filled polyaniline composites and evaluation of their electrical and electrochemical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 22, 1154–1161 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-010-0276-7
K. Sever, I.H. Tavman, Y. Seki, A. Turgut, M. Omastova, I. Ozdemir, Electrical and mechanical properties of expanded graphite/high density polyethylene nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 53, 226–233 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.04.069
D. Borah, N.S. Bhattacharyya, Design and development of expanded graphite-based non-metallic and flexible metamaterial absorber for X-band applications. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 226–232 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4918-2
K. Jia, W. Liu, K. Li, D. Wang, C. Ma, A novel synthesize approach and electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of expanded graphite/Fe3O4/carbon nanorod composite microstructure. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 17011–17019 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02034-0
A. Nazir, H. Yu, L. Wang, S. Fahad, K.R. Naveed, A. Khan, B.U. Amin, T. Lin, M. Usman, T. Elshaarani, F. Haq, Electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of polymer/carbon composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 16636–16650 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02043-z
Y. Qing, W. Zhou, F. Luo, D. Zhu, Epoxy-silicone filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and carbonyl iron particles as a microwave absorber. Carbon N. Y. 48, 4074–4080 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.07.014
M.A. do Amaral Junior, J.T. Matsushima, M.C. Rezende, E.S. Gonçalves, J.S. Marcuzzo, M.R. Baldan, Production and characterization of activated carbon fiber from textile PAN Fiber. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manage 9, 423–430 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5028/jatm.v9i4.831
L.G. Cançado, M.A. Pimenta, B.R.A. Neves, M.S.S. Dantas, A. Jorio, Influence of the atomic structure on the Raman spectra of graphite edges. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 5–8 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.247401
A. Sadezky, H. Muckenhuber, H. Grothe, R. Niessner, U. Pöschl, Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon N. Y. 43, 1731–1742 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2005.02.018
A.M. Nicolson, G.F. Ross, Measurement of the intrinsic properties of materials by time-domain techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 19, 377–382 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.1970.4313932
L.C. de Folgueras, M.A. Alves, M.C. Rezende, Dielectric properties of microwave absorbing sheets produced with silicone and polyaniline. Mater. Res. 13, 197–201 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-14392010000200013
J.P. Gogoi, N.S. Bhattacharyya et al., Synthesis and microwave characterization of expanded graphite/novolac phenolic resin composite for microwave absorber applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 42, 1291–1297 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.01.026
D.D.L. Chung, A review of exfoliated graphite. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 554–568 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9284-6
D.D.L. Chung, Graphite intercalation compounds. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-803581-8.02311-0
P. Singh, V.K. Babbar, A. Razdan, R.K. Puri, T.C. Goel, Complex permittivity, permeability, and X-band microwave absorption of CaCoTi ferrite composites. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 4362–4366 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.373079
X. Zhang, G. Zhang, C. Zhao, X. Cheng, Wave-absorbing properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced cement-based composites, Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Durab. Concr. Struct. ICDCS 2014. (2014) 212–218
P. Lespade, R. Al-Jishi, M.S. Dresselhaus, Model for Raman scattering from incompletely graphitized carbons. Carbon N. Y. 20, 427–431 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(82)90043-4
J.P. Gogoi, N.S. Bhattacharyya, Expanded graphite/Novolac phenolic resin composite as single layer electromagnetic wave absorber for x-band applications, Int. Conf. Commun. Electron. Syst. Des., SPIE, 2013: 876005. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2009485
X. Chen, F. Meng, Z. Zhou, X. Tian, L. Shan, S. Zhu, X. Xu, M. Jiang, L. Wang, D. Hui, Y. Wang, J. Lu, J. Gou, One-step synthesis of graphene/polyaniline hybrids by in situ intercalation polymerization and their electromagnetic properties. Nanoscale 6, 8140–8148 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr01738b
U.J. Mahanta, M. Borah, N.S. Bhattacharyya, J.P. Gogoi, High-performance broadband microwave absorbers using multilayer dual-phase dielectric composites. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 2438–2448 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07038-4
Acknowledgements
The authors thank INPE facilities and CAPES for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batista, A.F., de Oliveira, A.P.S., Rodrigues, A.C. et al. Investigation of different graphite morphologies for microwave absorption at X and Ku-band frequency range. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 19064–19073 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04443-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04443-y